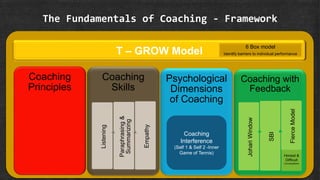
This document outlines the fundamentals of coaching, including key models and skills. It discusses coaching principles like listening, paraphrasing, empathy and the TGROW model. It explores psychological dimensions of coaching like the inner and outer dimensions of performance. Difficult conversations are examined using models like Johari Window, SBI, and the Fierce Model. The document provides references on coaching classics like The Inner Game of Tennis and Fierce Conversations. Overall it serves as a framework for applying a structured coaching approach to improve employee performance through development of core coaching skills.