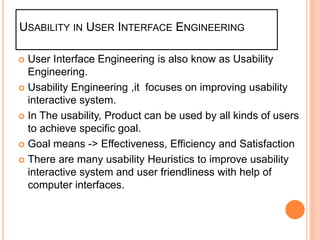
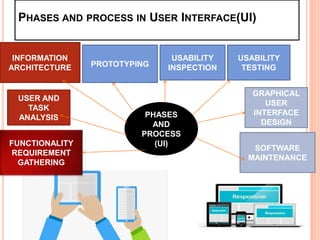
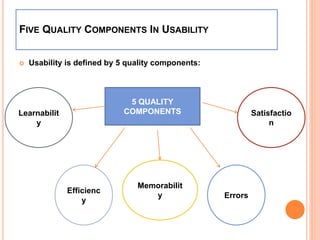
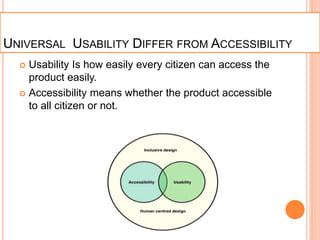
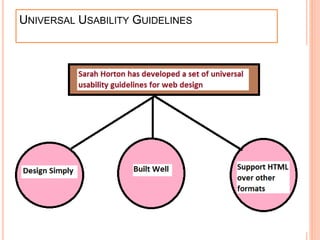
The document discusses universal usability, defined as enabling all users, including those with disabilities, to succeed in using information and communication technologies. It outlines the principles of usability in user interface engineering, including five essential quality components: learnability, efficiency, memorability, errors, and satisfaction. Additionally, it highlights challenges, current research, and the role of AI in enhancing user interaction, emphasizing that universal usability goes beyond mere accessibility to optimize user experience.