The document discusses several key aspects of personality:
1. Personality can be defined as the psychological characteristics that determine how a person responds to their environment. It distinguishes individuals and influences choices.
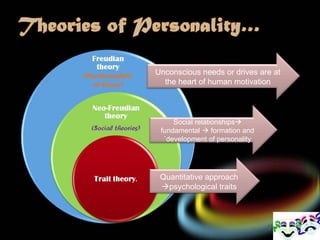
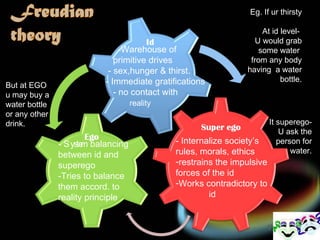
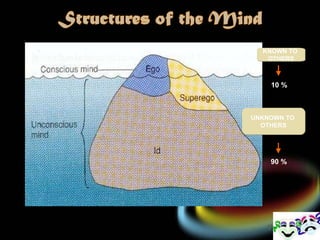
2. Sigmund Freud believed personality is made up of the id, ego, and superego. The id represents instincts, the superego aims for morality, and the ego balances the two.
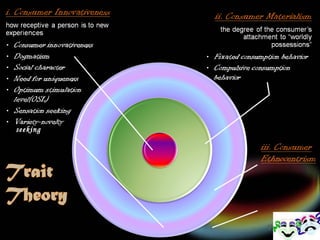
3. Traits are enduring ways people differ and are measured empirically to categorize personality characteristics. Traits like innovativeness and dogmatism influence consumer preferences.