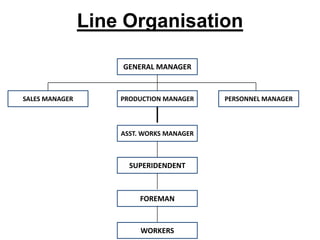
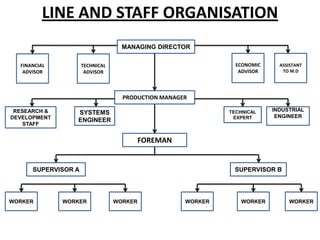
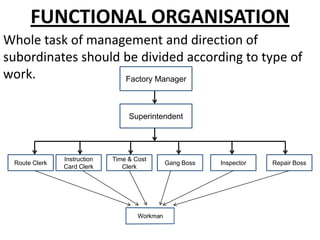
The document discusses different types of organizational structures including line, staff, functional and committee organizations. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each type of structure. Different forms of documentation for organizations are also examined such as manuals, which can help standardize procedures but also limit flexibility.