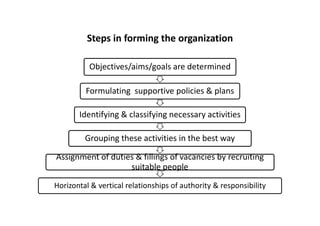
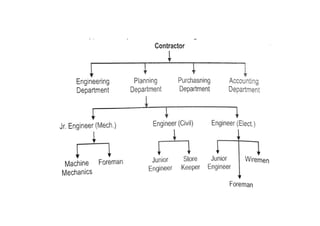
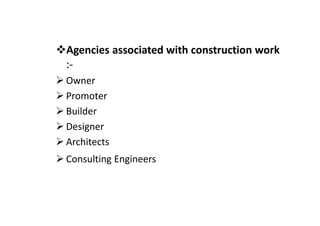
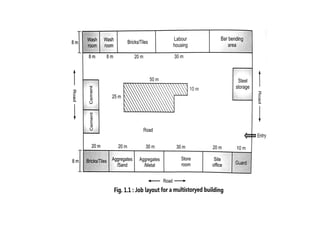
This document provides information about construction management and organization structures. It discusses the goals of an organization to complete work on time and profitably. It also describes the key roles in construction including site engineers, supervisors, mistries, operators and laborers. The document outlines different types of organization structures like line, functional, line and staff, and project-based organizations. It discusses the principles of organization, characteristics, steps to form an organization and their advantages and disadvantages.