This document contains information about adjectives and the passive voice in English grammar:
1) It defines adjectives and explains that they typically precede nouns and come in two types: opinion and fact adjectives.
2) Details are provided on the order of adjectives and examples are given of adjective usage.
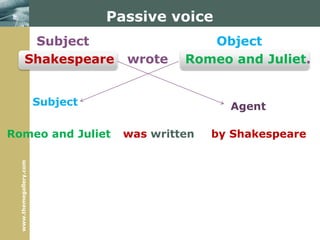
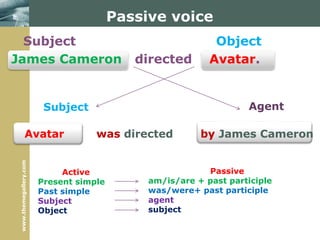
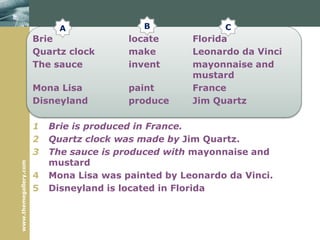
3) The passive voice is described including formation, typical uses, and transforming sentences from active to passive voice.
4) Question tags are outlined regarding their use, formation, and different structures depending on the main clause.