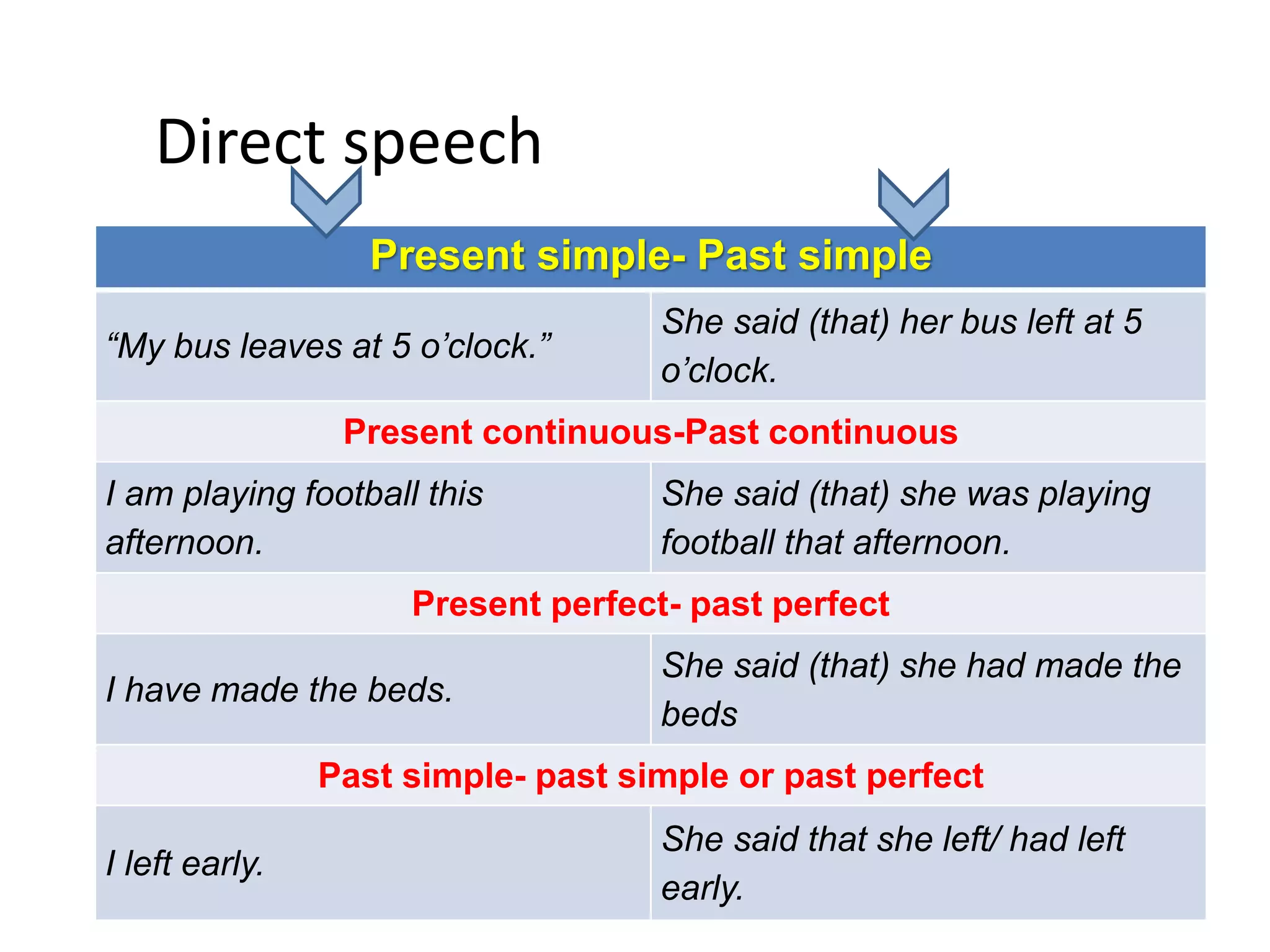
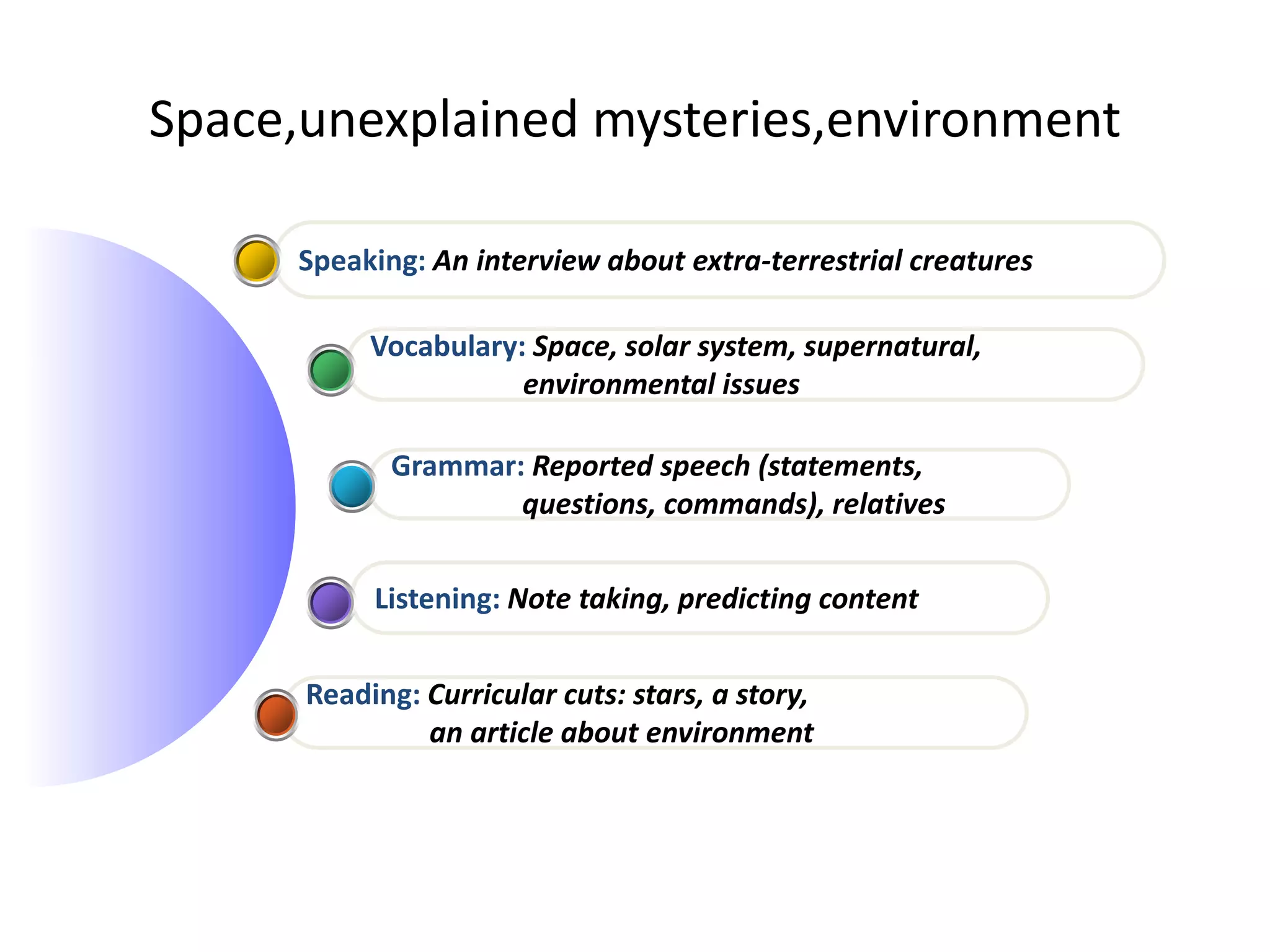
This unit covers space, unexplained mysteries, and the environment. It includes a reading on curricular cuts about stars, a story, and an article on the environment. There is also note taking and predicting content for a listening, and grammar on reported speech and relatives. The vocabulary focuses on space, the solar system, supernatural phenomena, and environmental issues. Speaking practice involves an interview about extra-terrestrial creatures.










![SAY v TELL
We can use say to name the listener, too, but
it’s not as common:
• She said to us she is over 30.
[okay]
• She told us she is over 30.
[More natural]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit10-140609094243-phpapp02/75/Unit-10-14-2048.jpg)






















![Changing Time Words
• Example:
• “There’s a big party tonight,” said Julie
[Saturday]
Julie said there was a big party last night.
[Sunday]
Julie said there was a big party that night.
[a few weeks later]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit10-140609094243-phpapp02/75/Unit-10-37-2048.jpg)





![• “I’ll buy balloons tomorrow,” said Wendy.
• Wendy said she would buy balloons
_____________ .
• [a week later]
the next day
Also: following day](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit10-140609094243-phpapp02/75/Unit-10-43-2048.jpg)

![• 3. “I didn’t see you at the party yesterday,”
Drake said.
• Drake said he hadn’t seen me at the party
________ .
[a week later]
the day before](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit10-140609094243-phpapp02/75/Unit-10-45-2048.jpg)