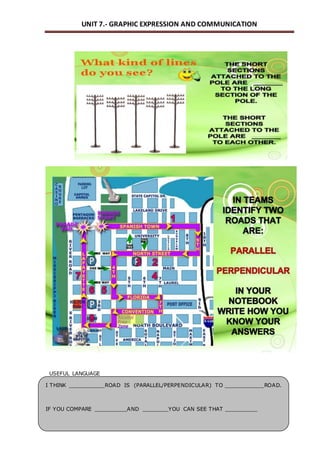
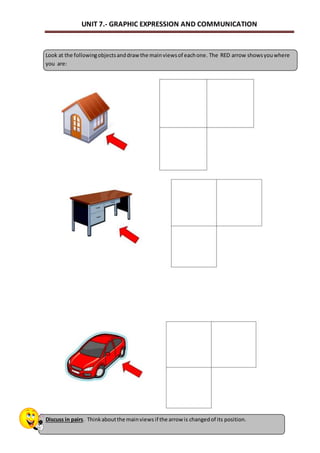
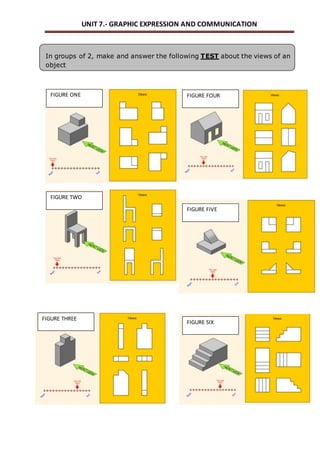
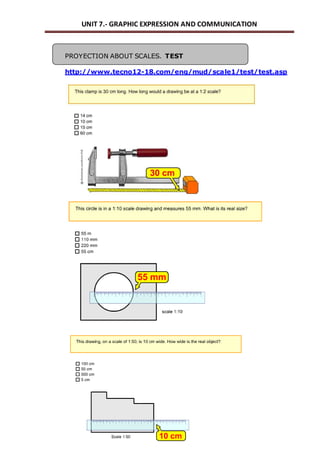
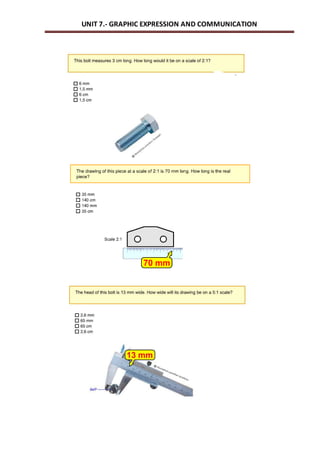
This document outlines a unit on graphic expression and communication techniques. The unit consists of 10 sessions and aims to teach students how to communicate technical ideas through drawing, use drawing tools and instruments to create accurate drawings, and distinguish different types of object views and perspectives. Key topics covered include drawing mediums and tools, sketches, diagrams and technical drawings, measurement, scales, and visualization of objects from different views. Students will practice these skills by drawing objects, learning technical drawing standards, and creating models with different views. The document provides detailed descriptions of learning outcomes, session structure and timing, vocabulary, exercises and assessments.