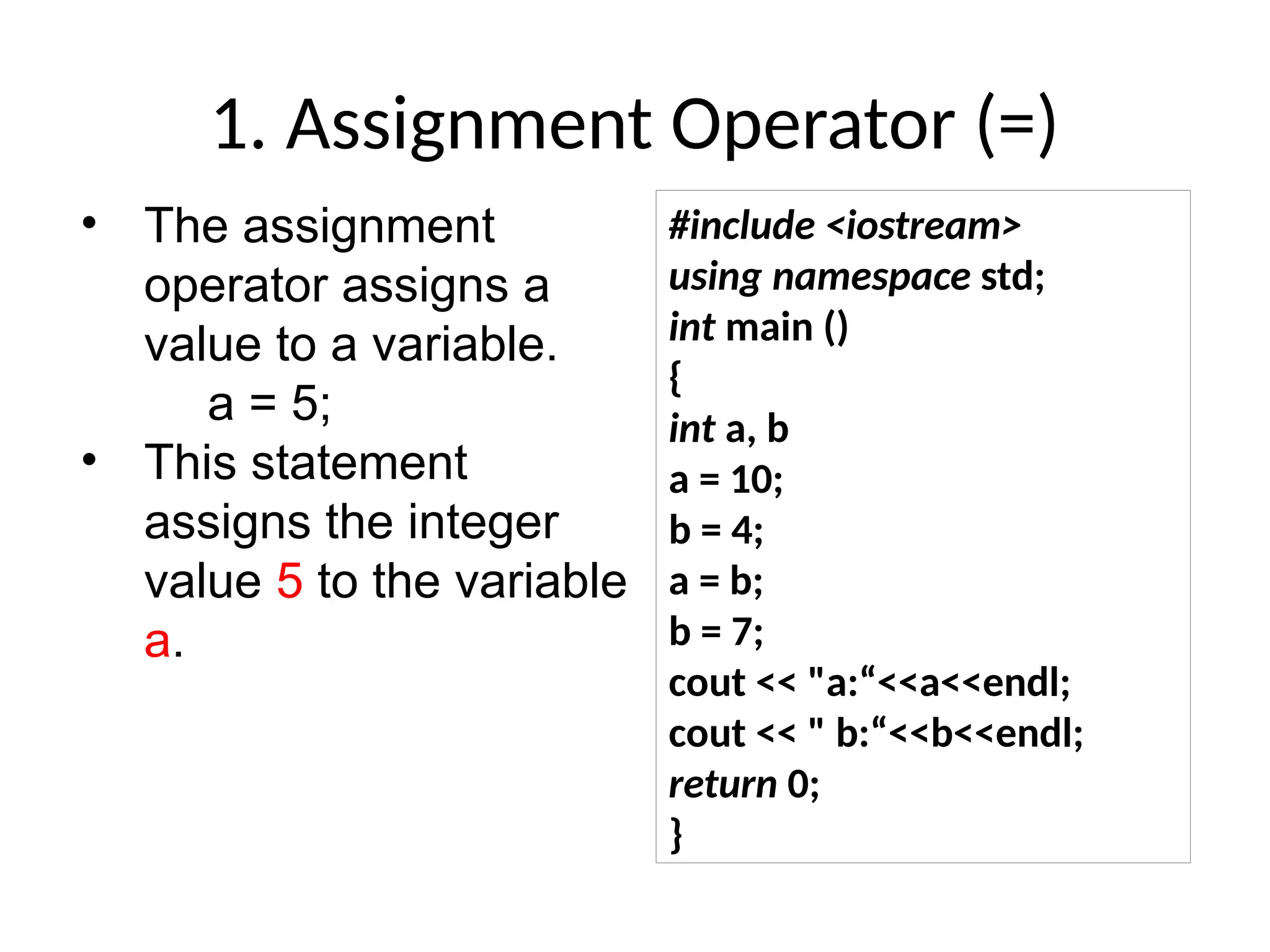
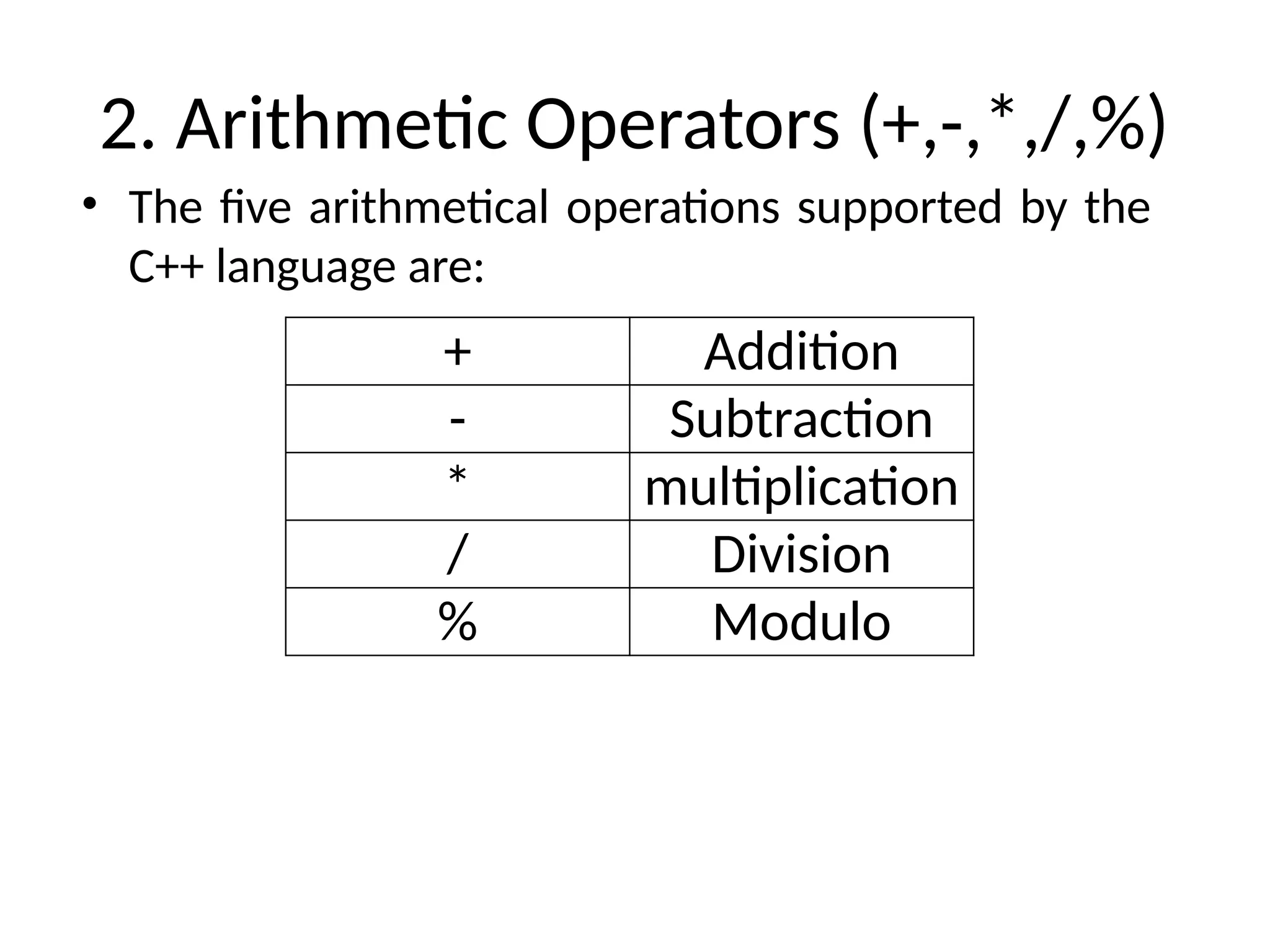
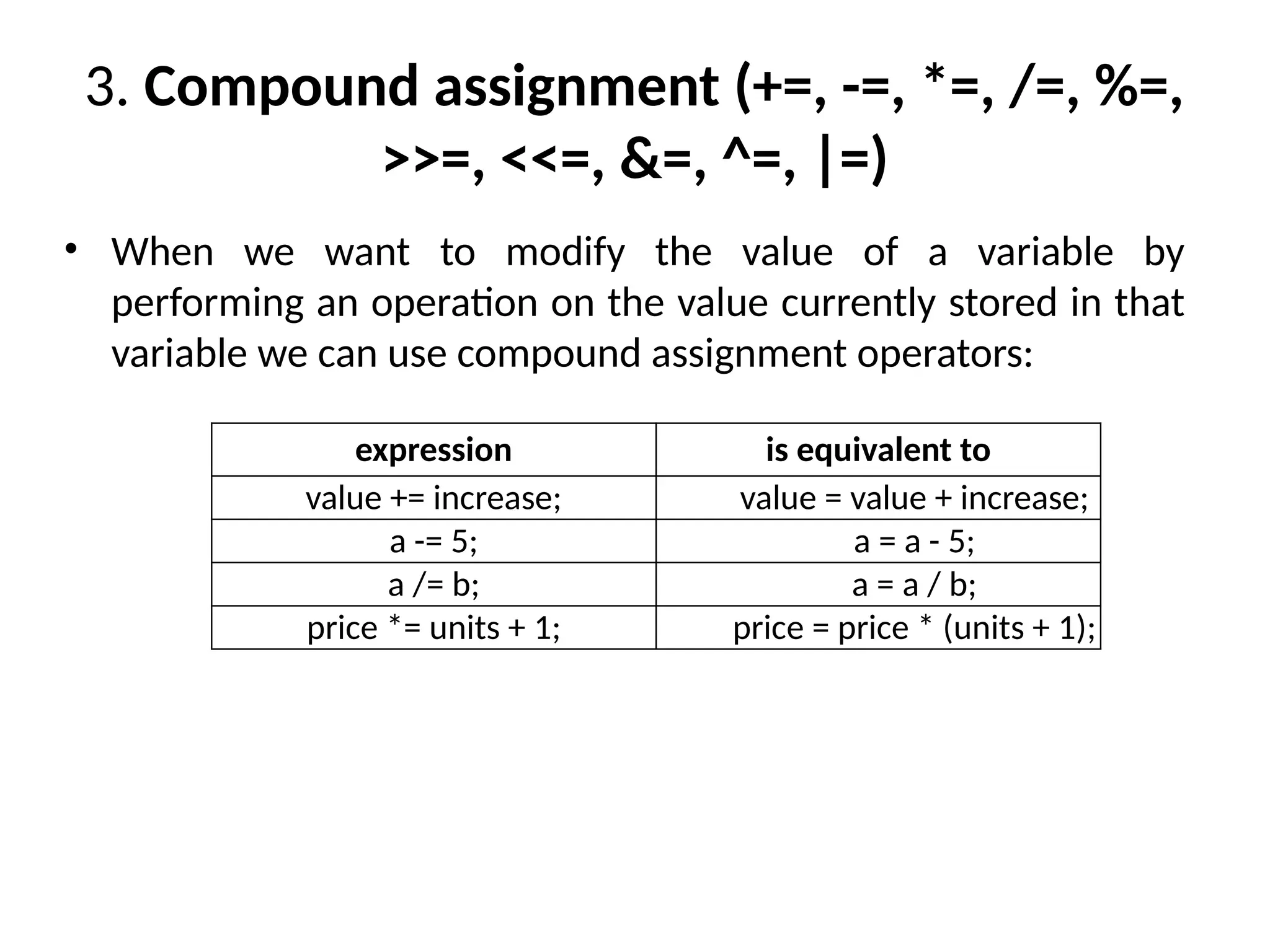
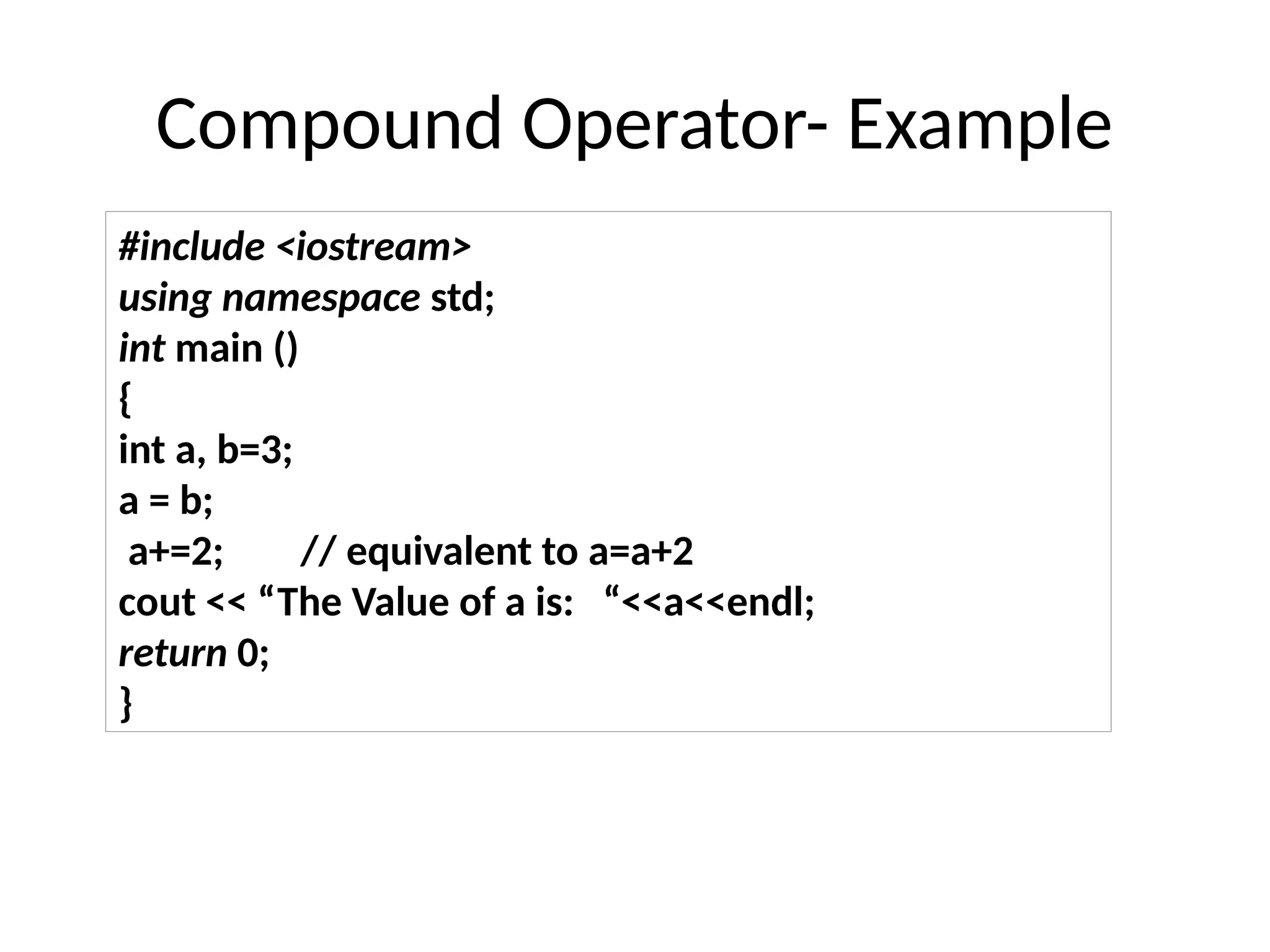
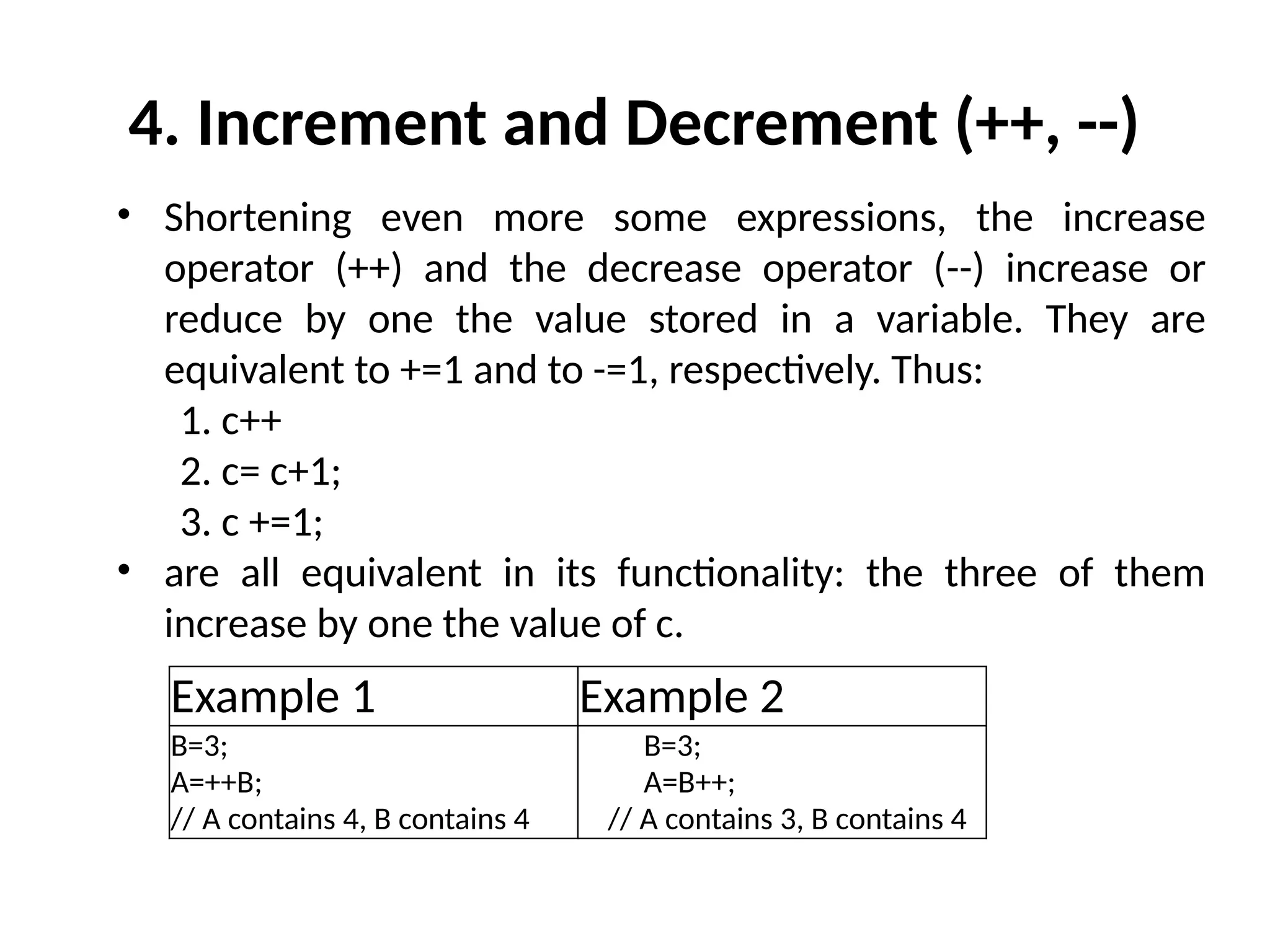
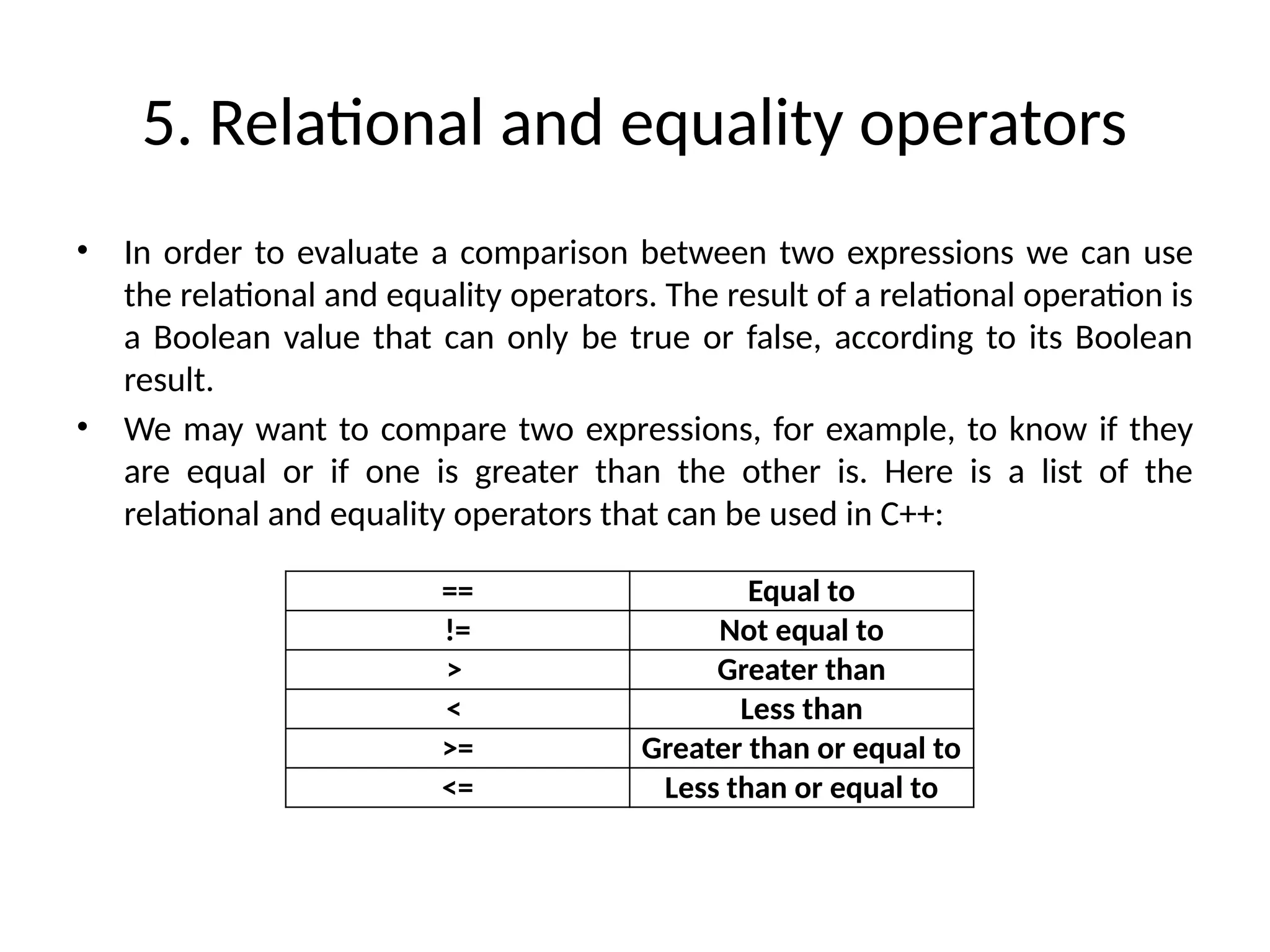
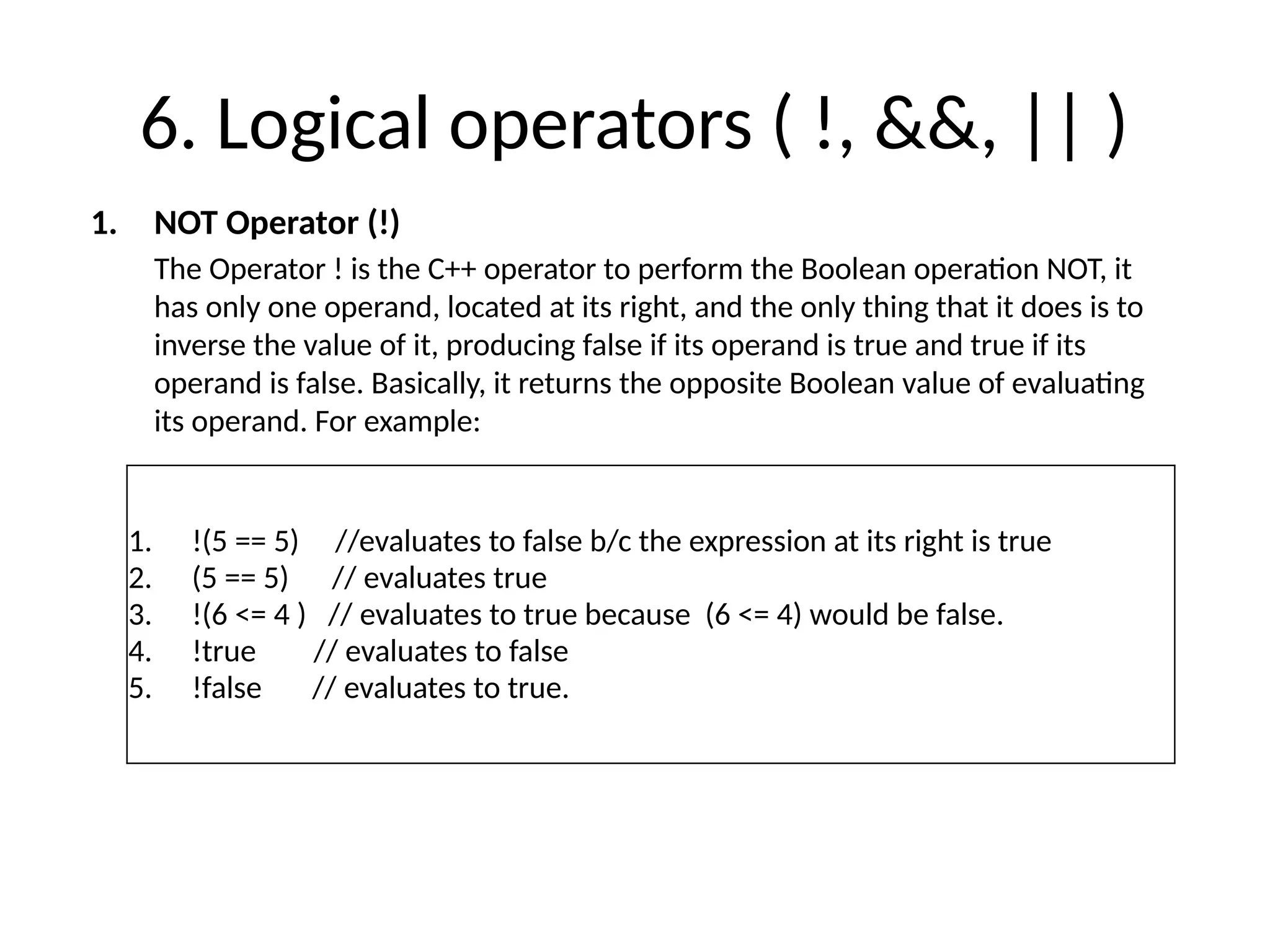
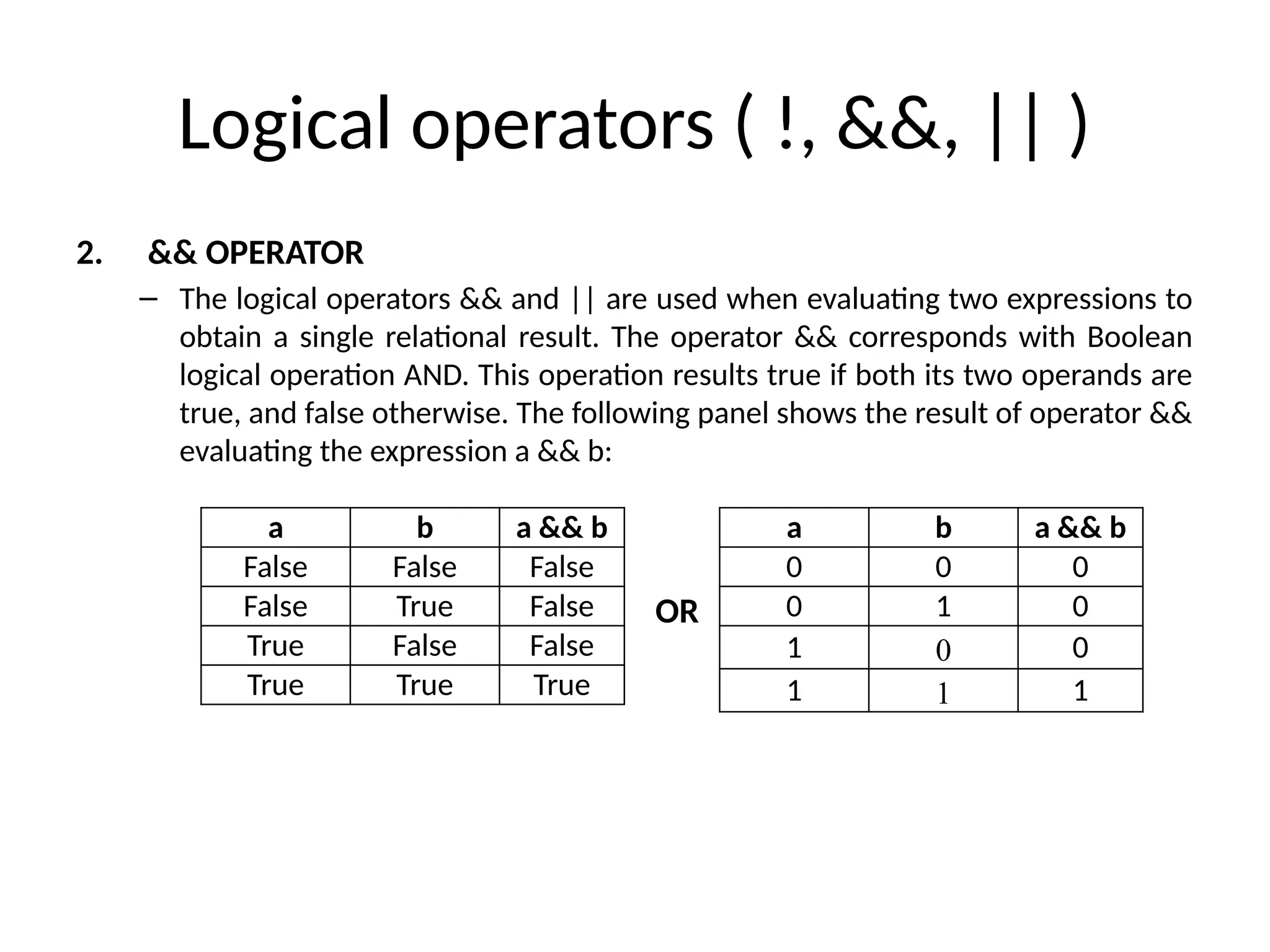
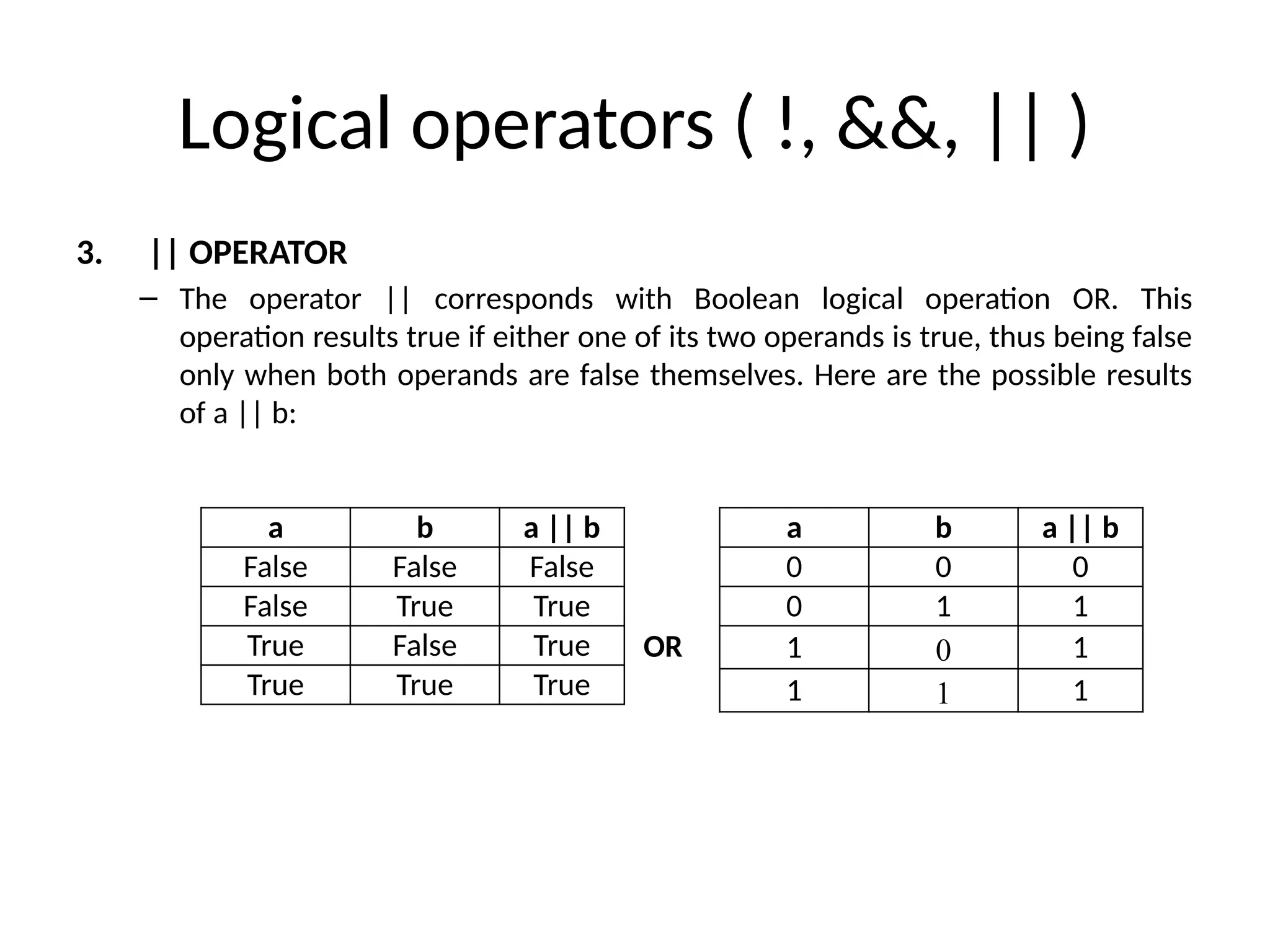
The document is a lecture on computing and programming, covering various types of operators in C++, including assignment, arithmetic, compound, increment and decrement, relational, equality, and logical operators. Each operator type is explained with examples demonstrating their functionality and syntax within C++. The lecture includes exercises for practical application of the concepts discussed.