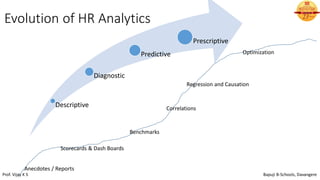
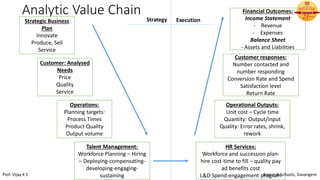
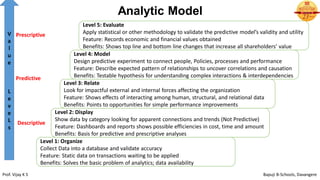
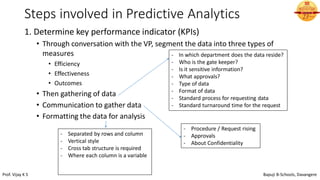
This document discusses the basics of HR analytics. It explains that analytics can be divided into three levels: descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive. Descriptive analytics reveal relationships in current and historical data using metrics, dashboards, and reports. Predictive analytics use statistical techniques to predict future probabilities and impacts. Prescriptive analytics provide decision options and show alternative business impacts. The document outlines the typical applications of analytics like assessing turnover patterns and reasons for employee disengagement. It also describes the steps involved in predictive analytics, which include determining key performance indicators, analyzing and reporting data, and interpreting results to enable predictions.