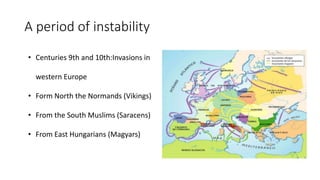
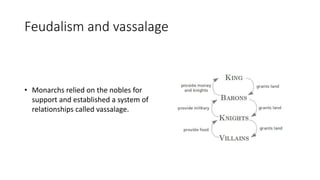
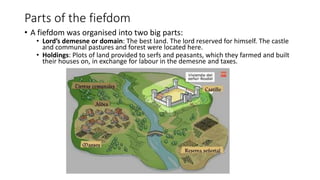
Feudalism emerged in Europe between the 9th and 10th centuries as a response to instability from invasions. Under this system, monarchs established relationships of vassalage where nobles pledged loyalty and military service in exchange for land holdings. Society was strictly stratified with nobility, clergy, and peasants. Peasants lived and worked on manorial estates, owing labor and taxes to lords in exchange for use of land. The Catholic Church was the dominant social and political institution, accumulating vast wealth and influencing all aspects of life.