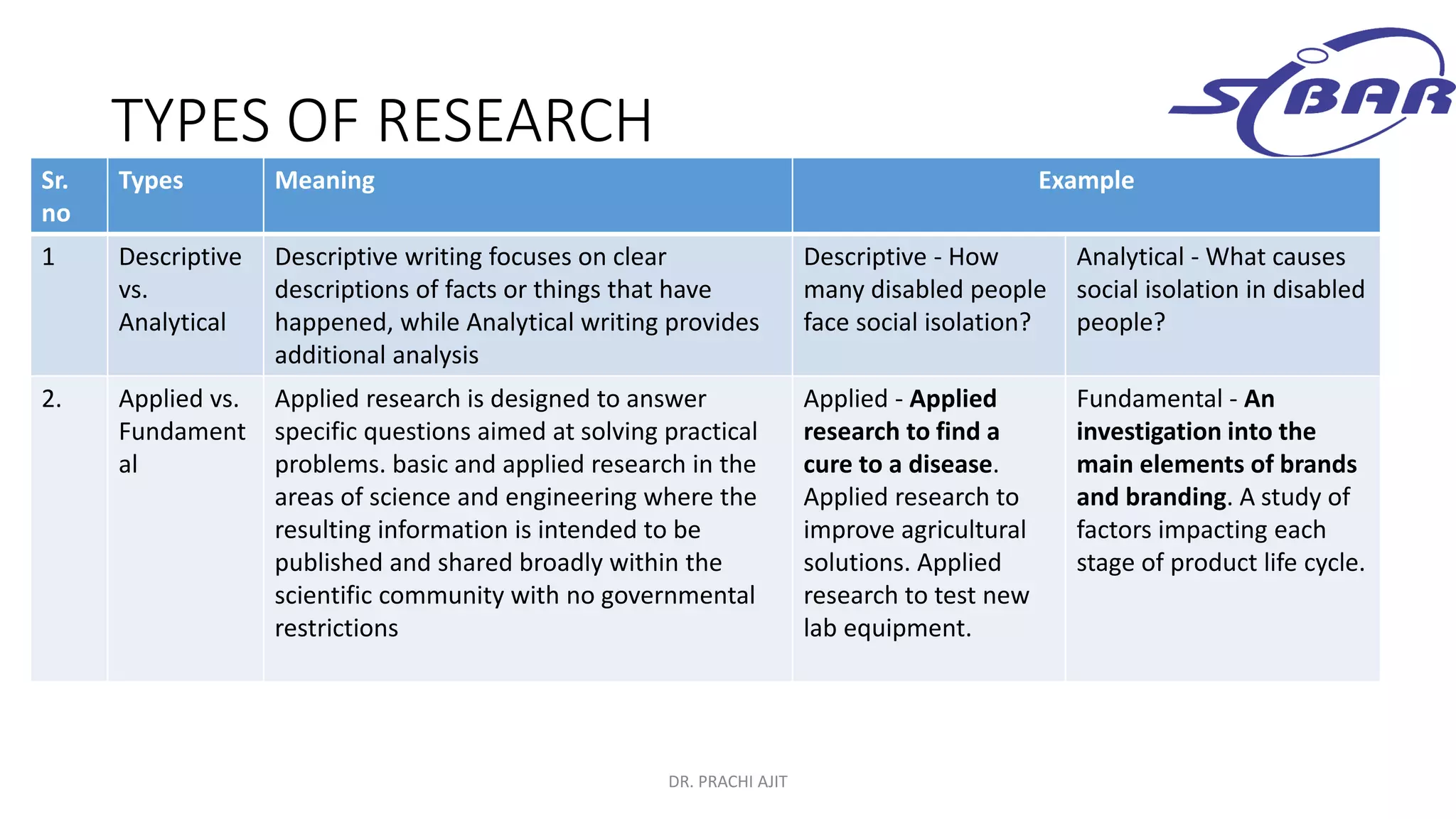
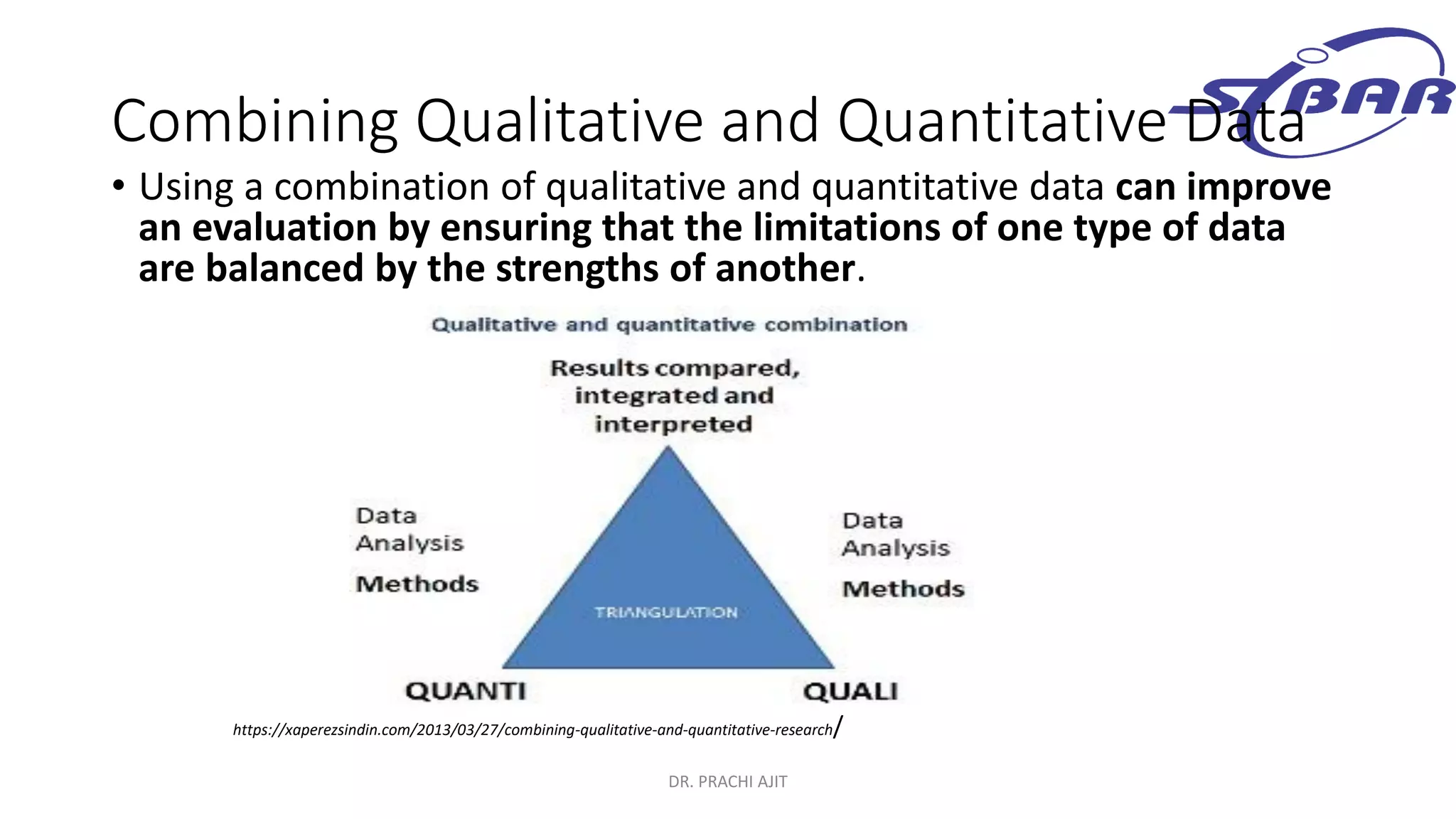
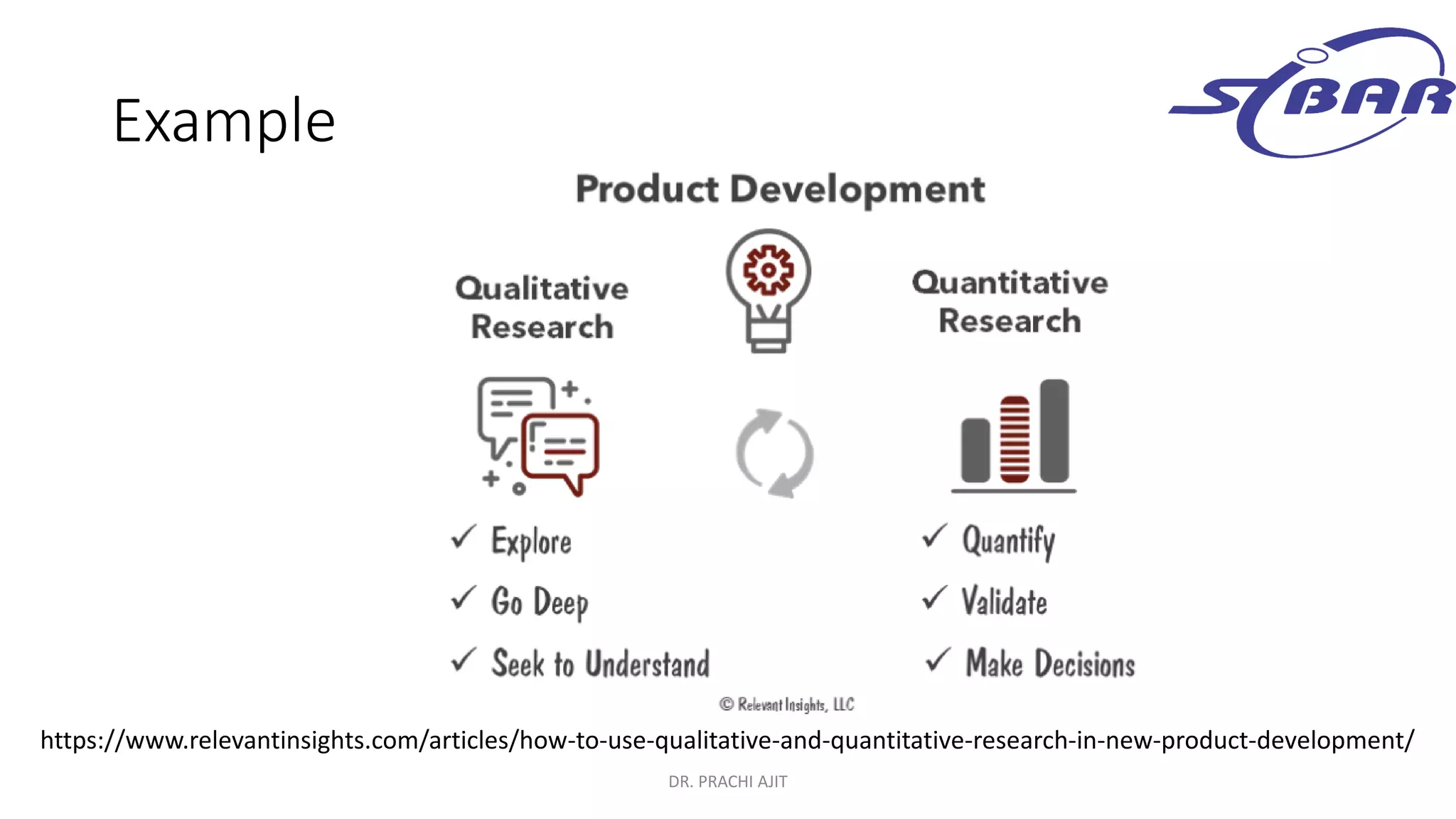
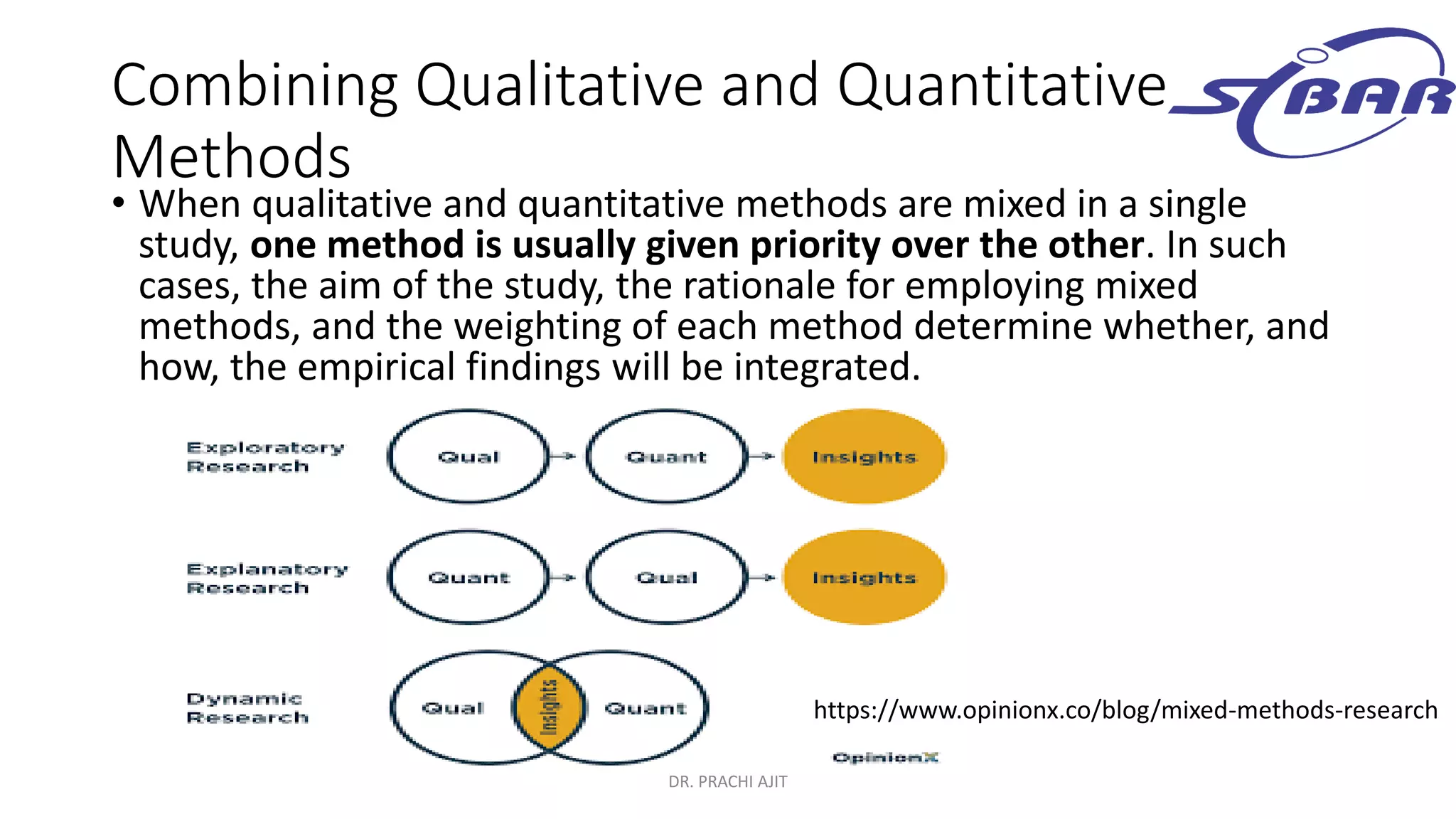
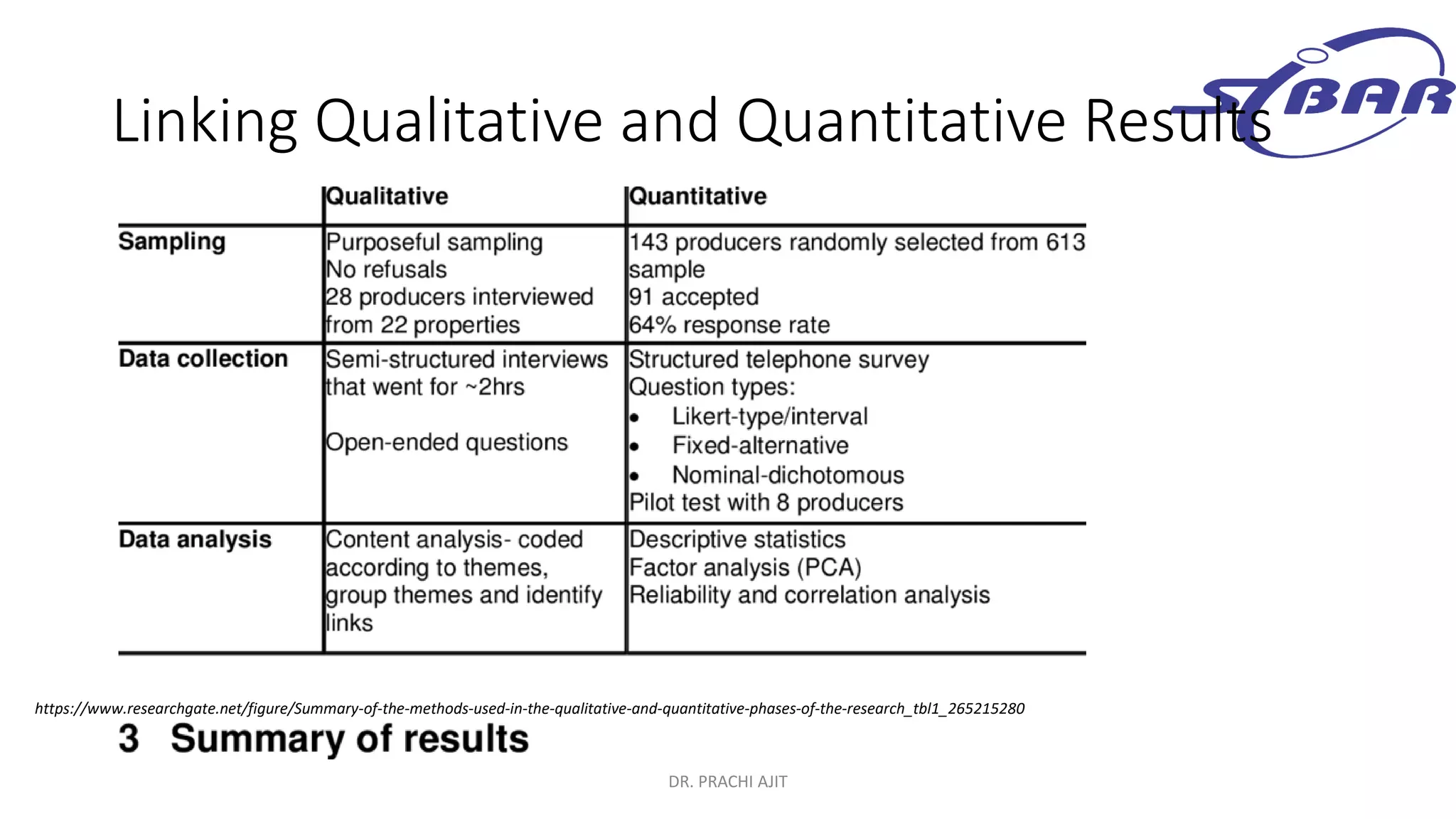
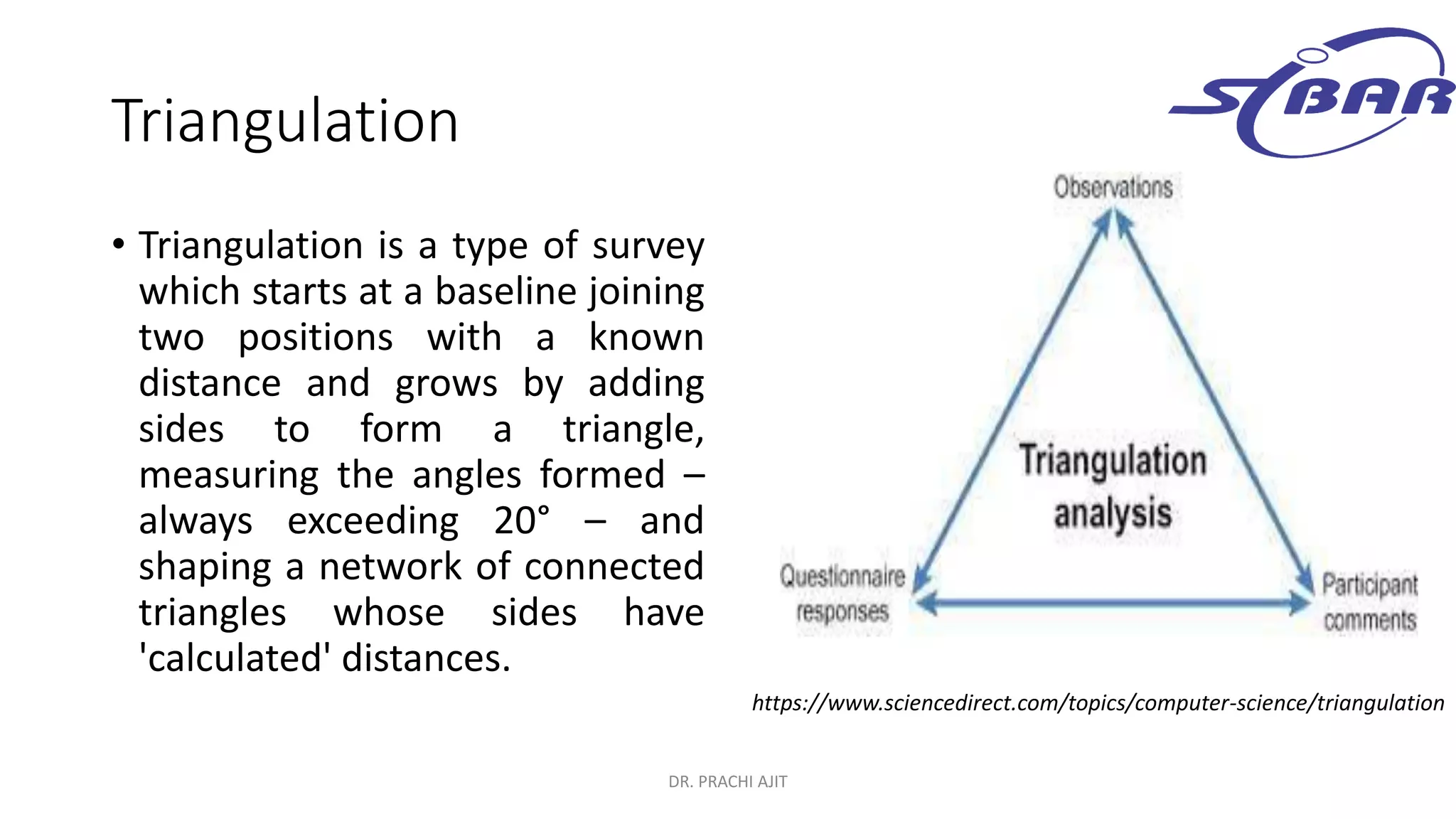
This document discusses qualitative research methods. It defines qualitative research as research that explores social problems through words and descriptions rather than numbers and statistics. It notes that qualitative research is relevant for understanding human experiences and answering "how" and "why" questions. The document outlines characteristics of qualitative research like being complex, holistic, and subjective. It also discusses limitations like being time-consuming and open to individual interpretations. Additionally, it explains how qualitative research can be combined with quantitative research through mixed methods designs and triangulation to provide a more comprehensive understanding.