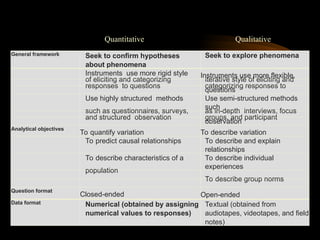
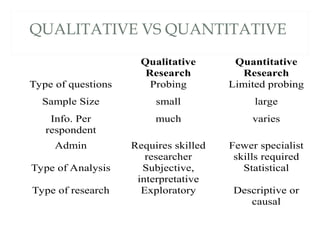
The document outlines the differences between quantitative and qualitative research, emphasizing their objectives, question types, data collection methods, and analysis styles. It also provides examples to differentiate between the two research types and offers insights into qualitative research's ability to obtain culturally specific information. Additionally, it discusses various research topics suitable for analysis while highlighting the significance of both research methodologies in understanding various phenomena.