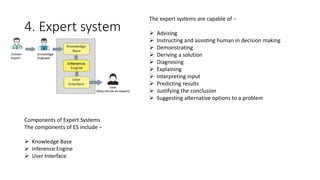
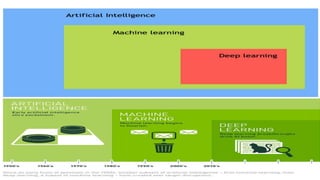
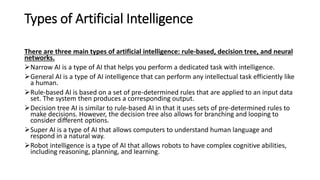
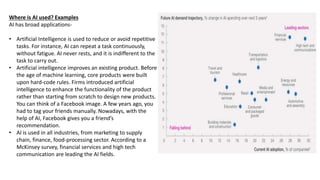
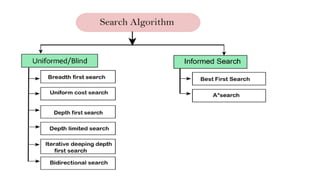
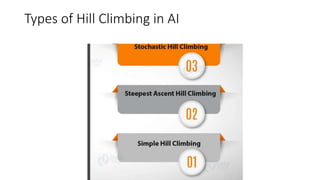
This document provides information about the course Code 22MCA262. It includes details like CIE Marks (50), Teaching Hours (2:0:2), SEE Marks (50), Total Hours of Pedagogy (40), Total Marks (100), Credits (03), and Exam Hours (03). The document then discusses 5 key modules that will be covered in the course: 1) Introduction to AI and Production Systems, 2) Introduction to Artificial Intelligence, 3) History of AI, 4) Application of AI, and 5) Intelligent Robots. It provides overviews and examples for each module topic.