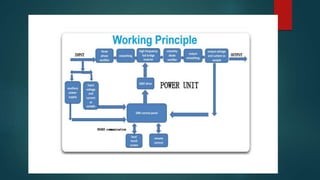
This presentation discusses uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). It begins by defining a UPS as a device that provides battery backup power to critical loads when utility power drops to unacceptable levels, with switchover times of 2-4 milliseconds to prevent disruptions. It then covers power problems UPS addresses like voltage distortions, basic UPS components like rectifiers, batteries, and inverters, power quality provided, topologies of line-interactive and double conversion UPS, and applications in data centers, telecommunications, healthcare, and industries. The conclusion emphasizes UPS's strategic aim of best service and lowest rates through information technology upgrades to meet customer needs.