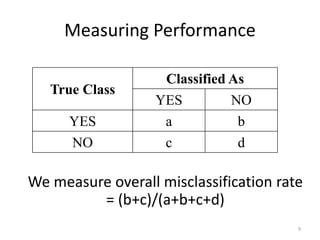
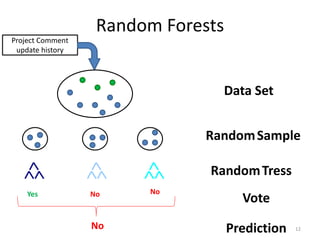
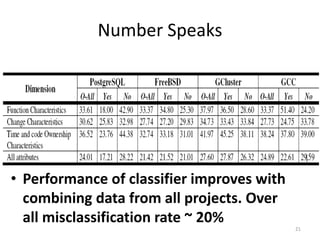
This document discusses a study that used machine learning to predict whether a comment associated with a code function would be updated based on characteristics of the function, change, and development process. The study analyzed comment update histories from four open source projects over 39 years. It found that comments were more likely to be updated for complex functions with many comments, changes that fixed bugs or had many dependent changes, and on certain weekdays. Combining data from all projects improved the predictive model's performance, with an overall misclassification rate of around 20%.