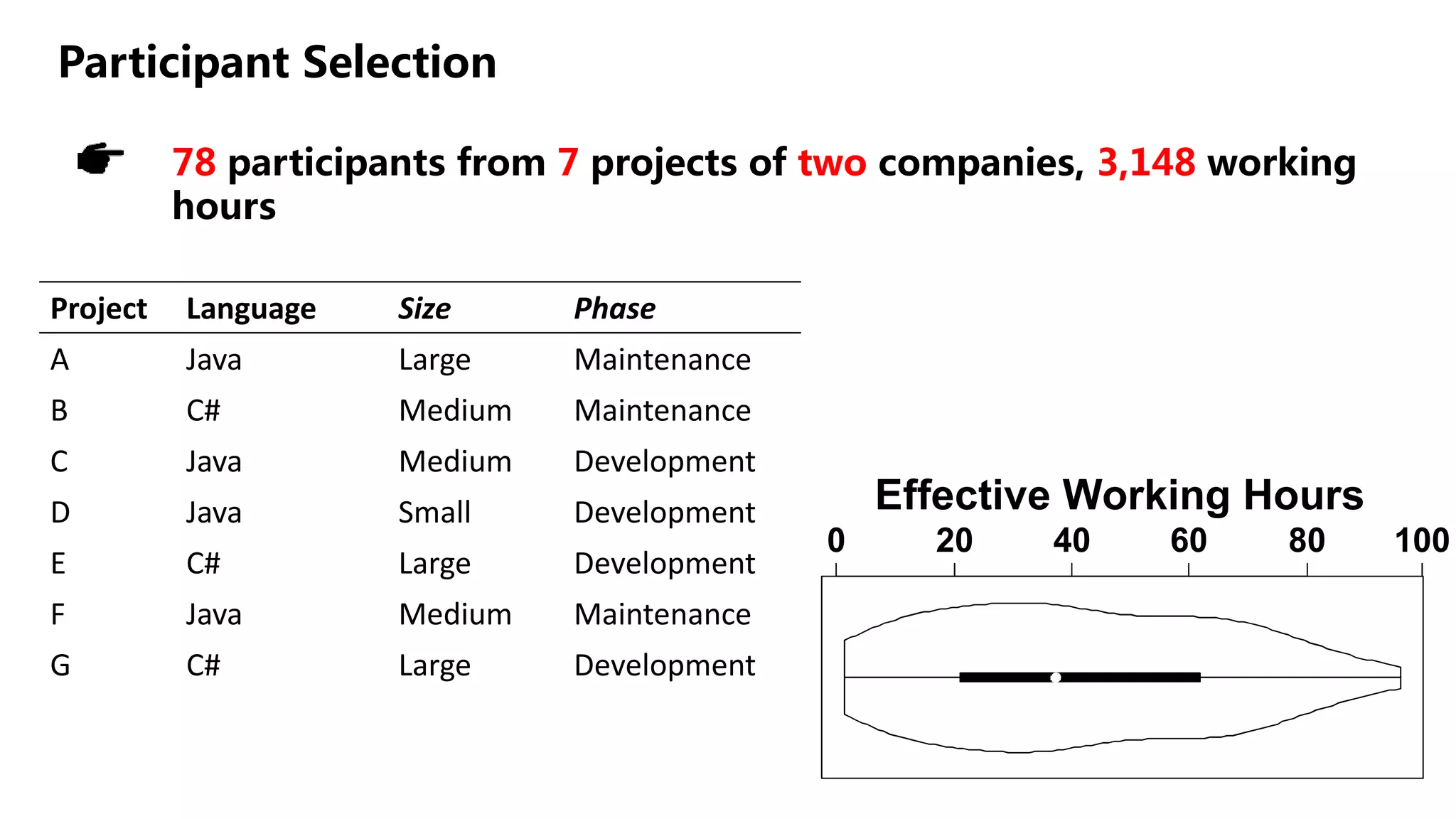
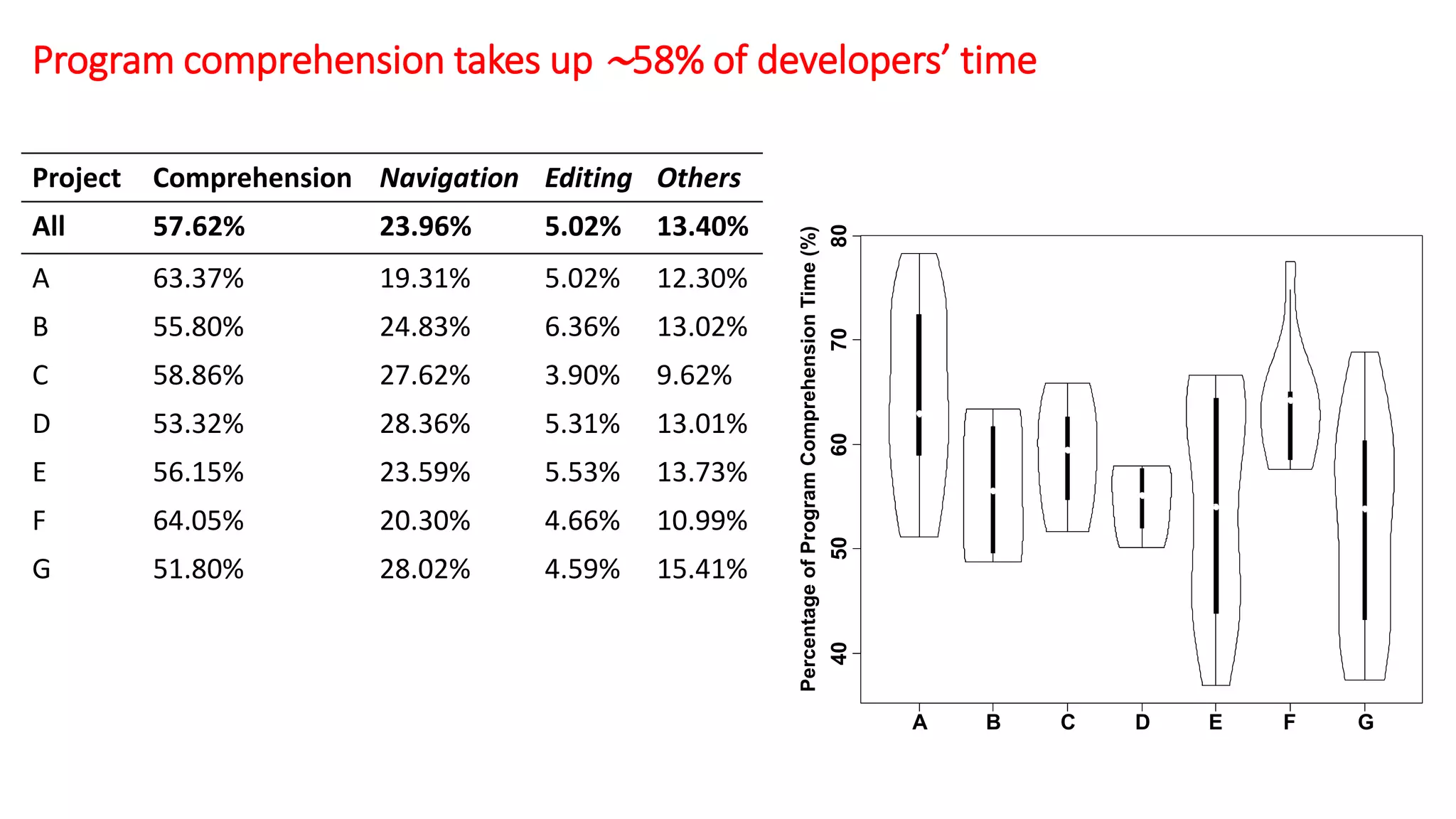
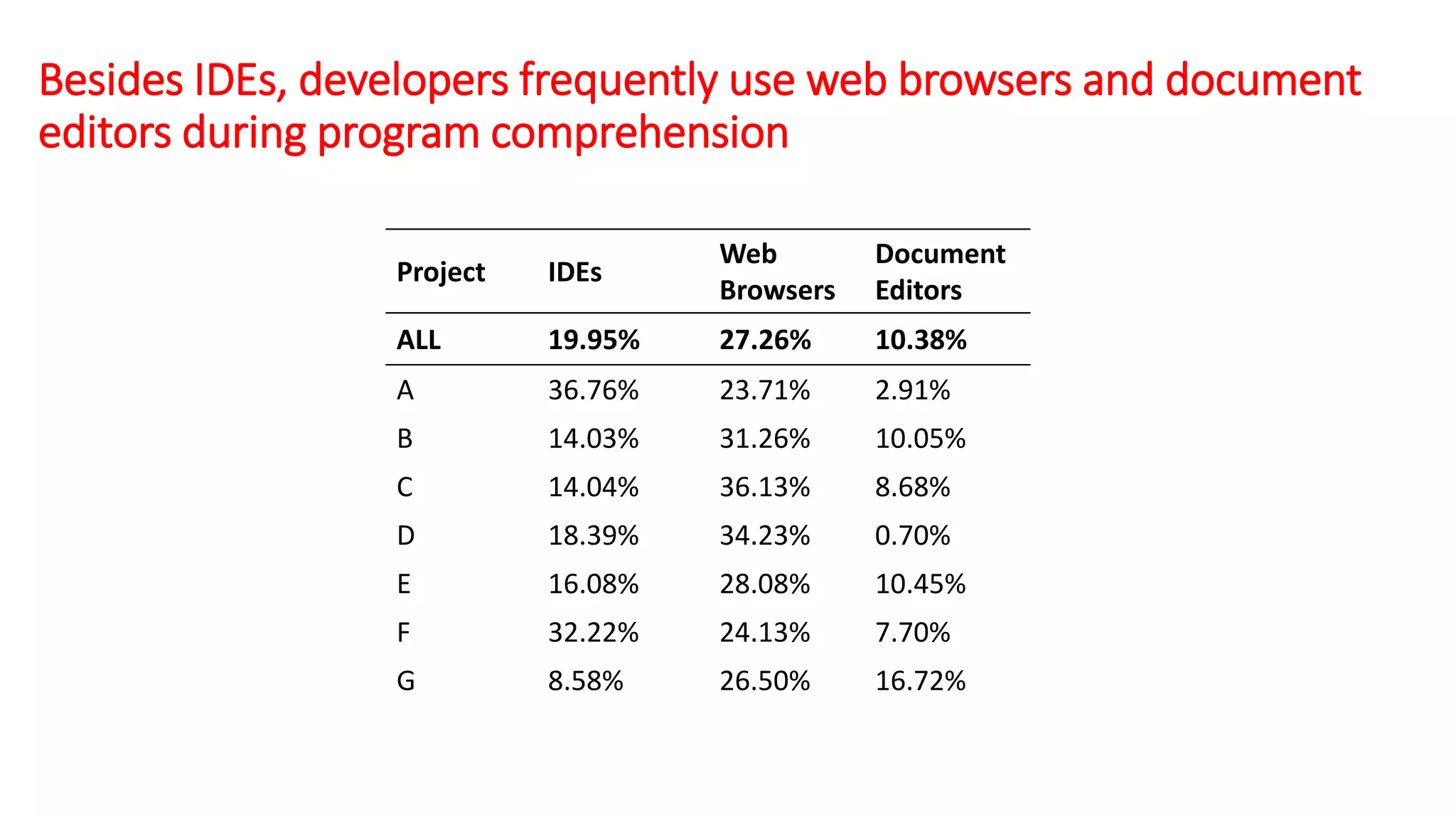
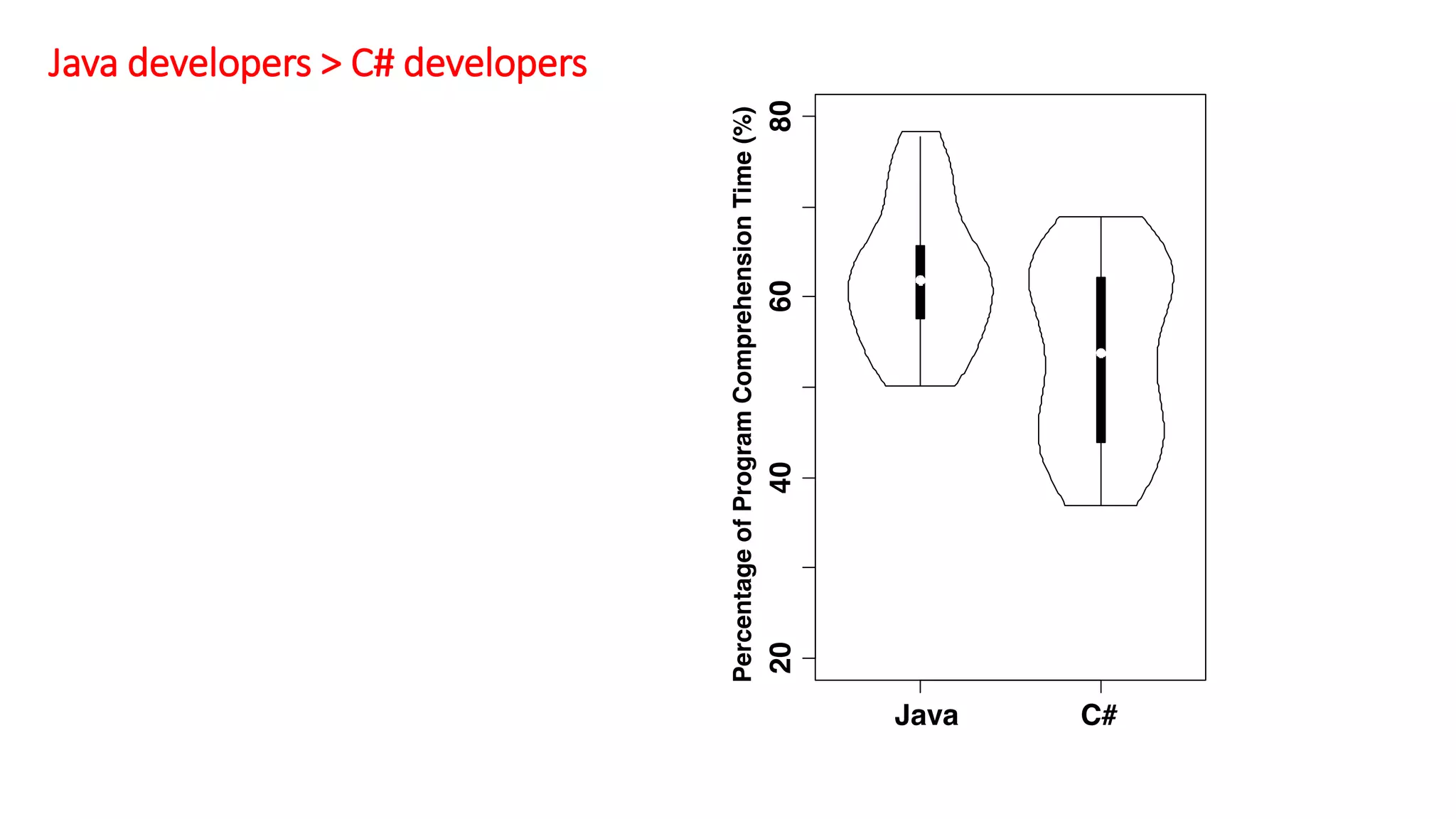
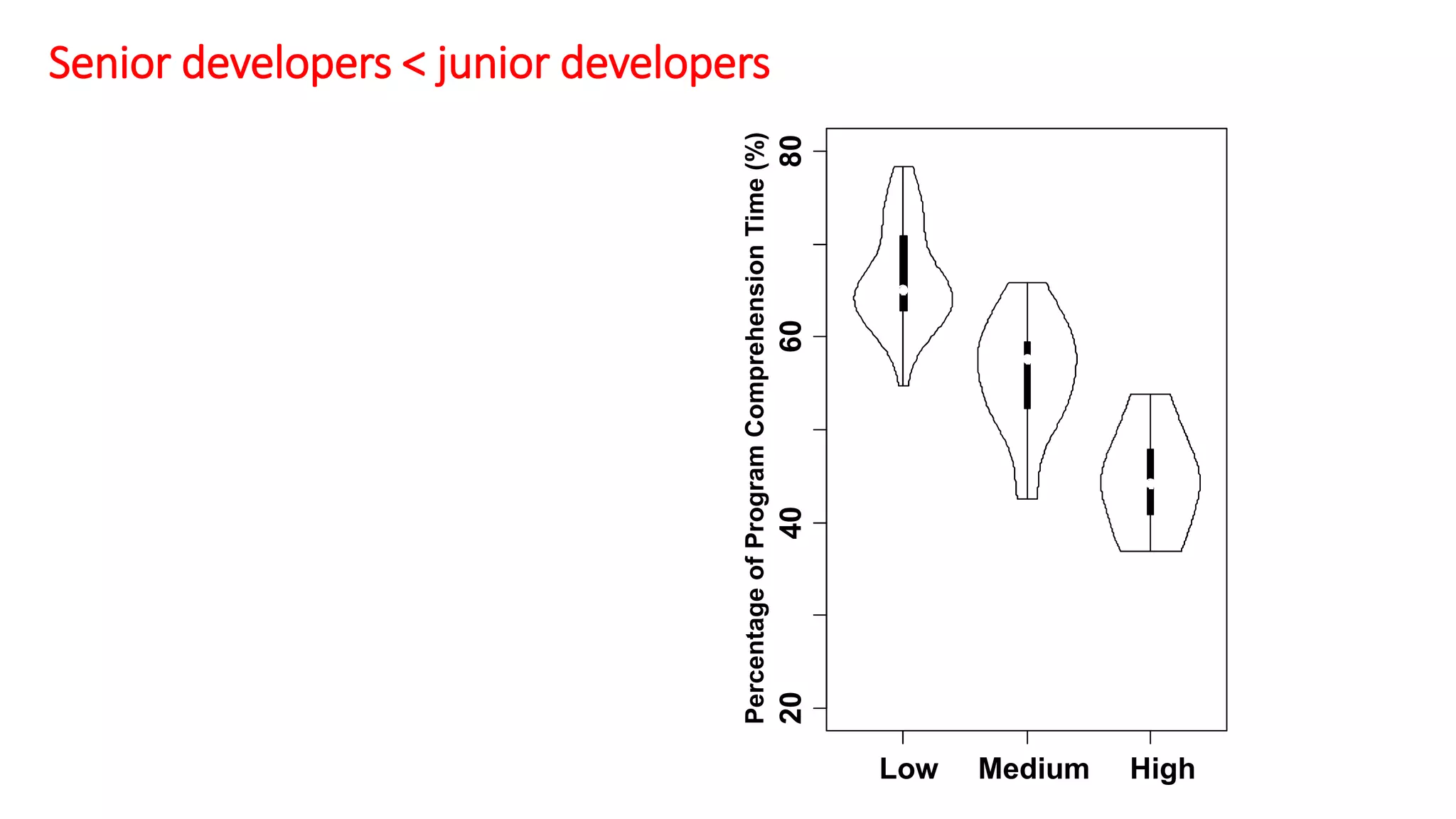
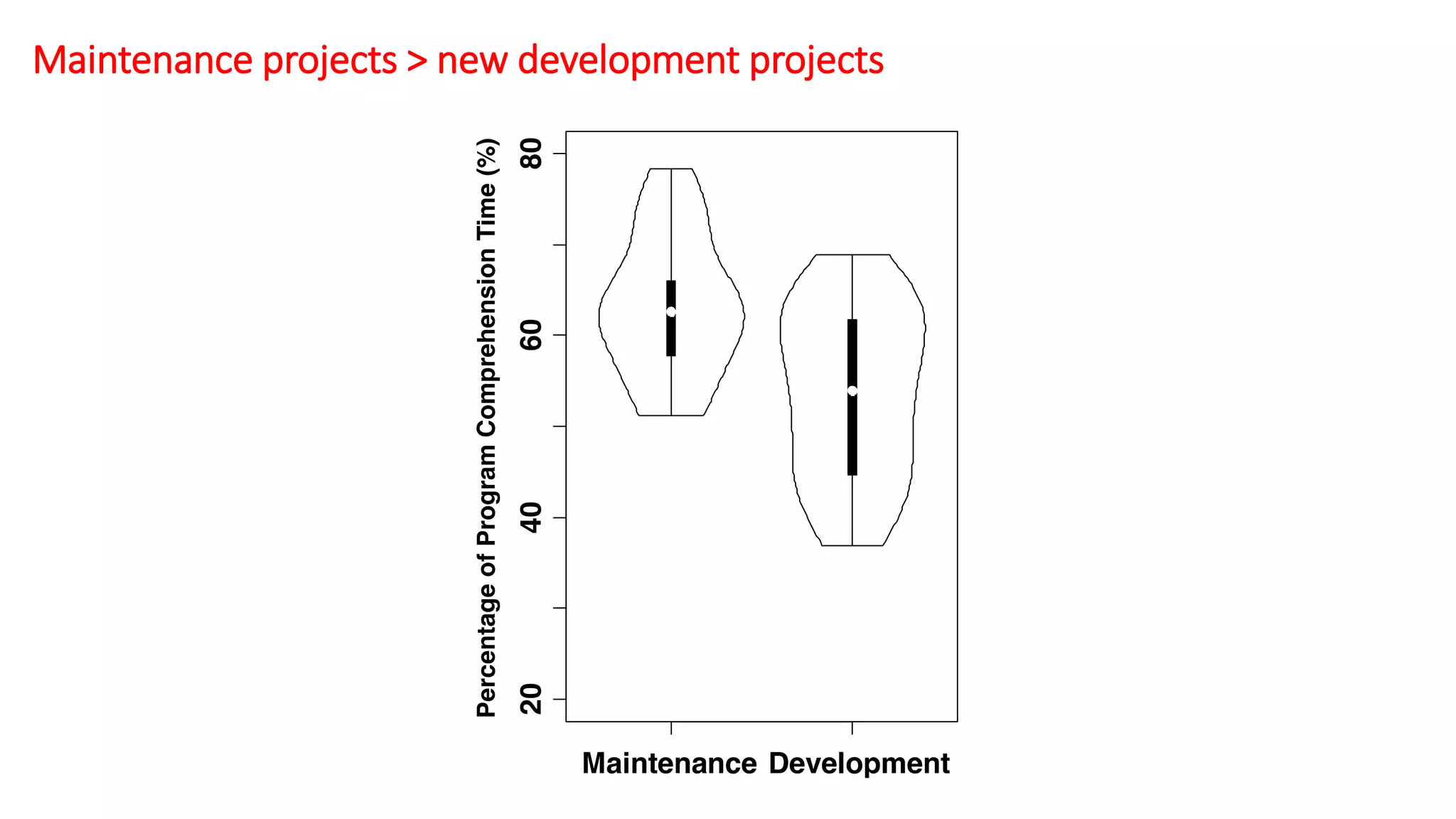
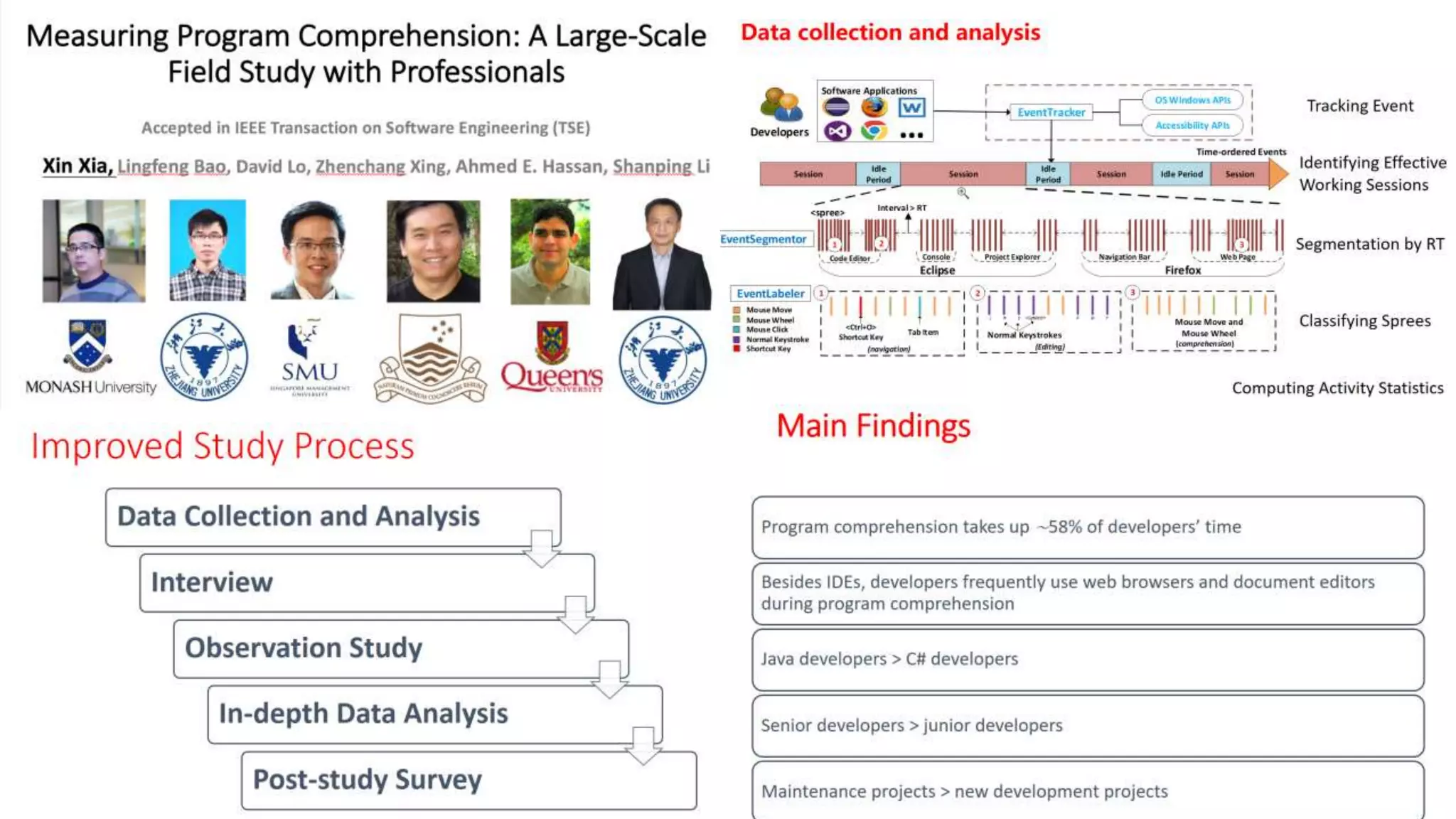
The document summarizes a large-scale field study that tracked the program comprehension activities of 78 professional developers over 3,148 hours. The study found that:
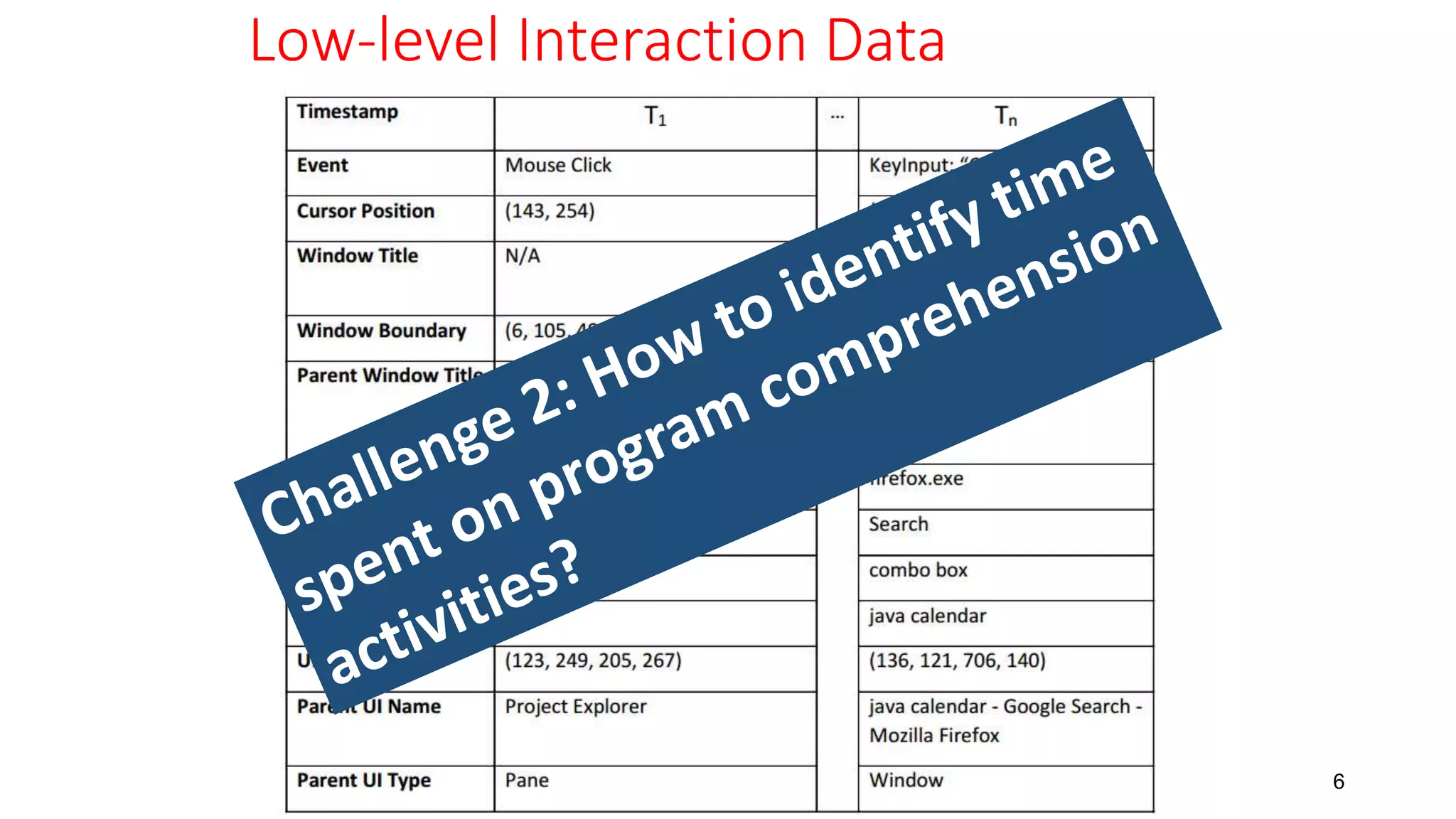
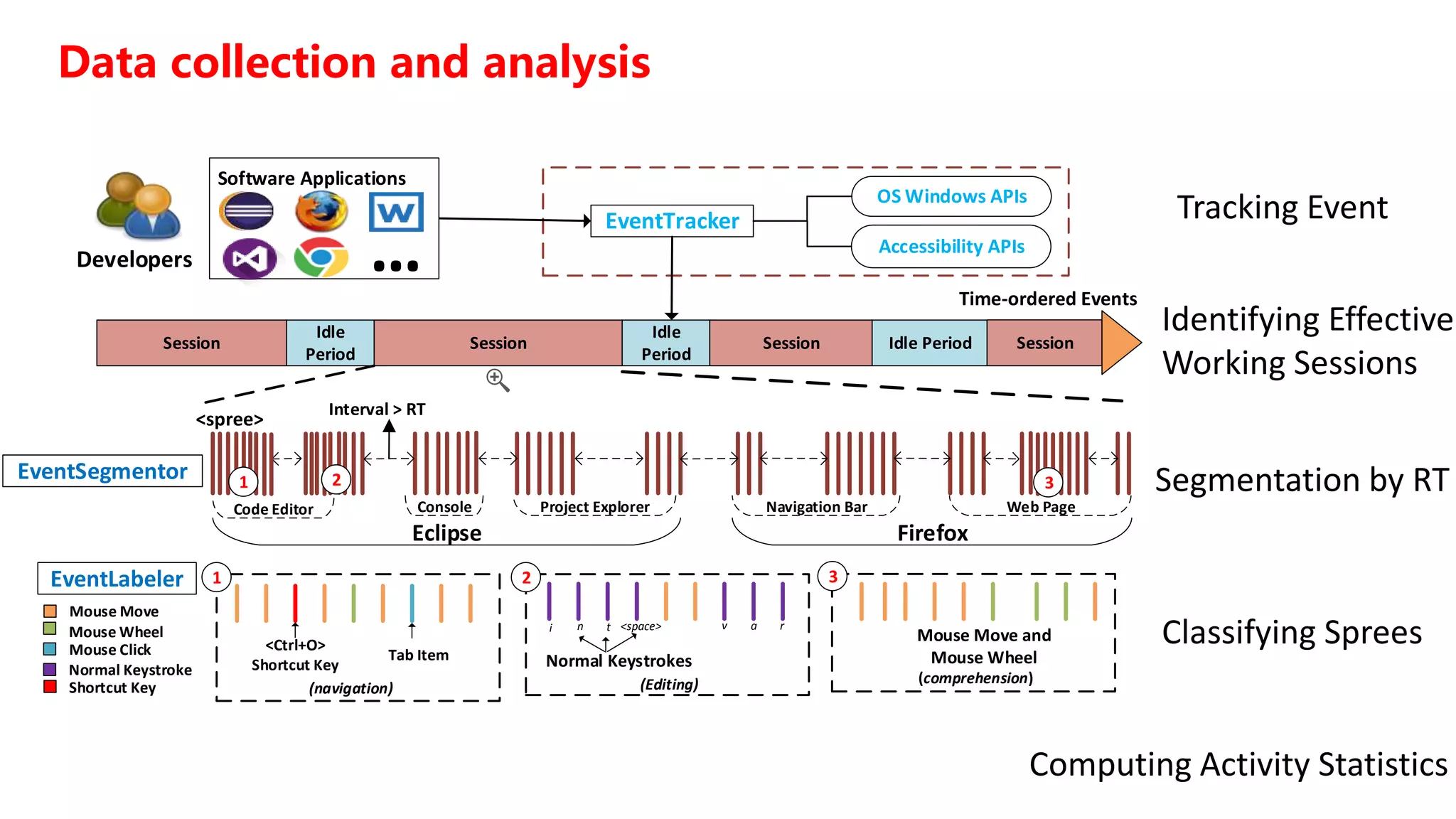
1) Program comprehension accounted for approximately 58% of developers' time on average, with navigation and editing making up the remaining portions.
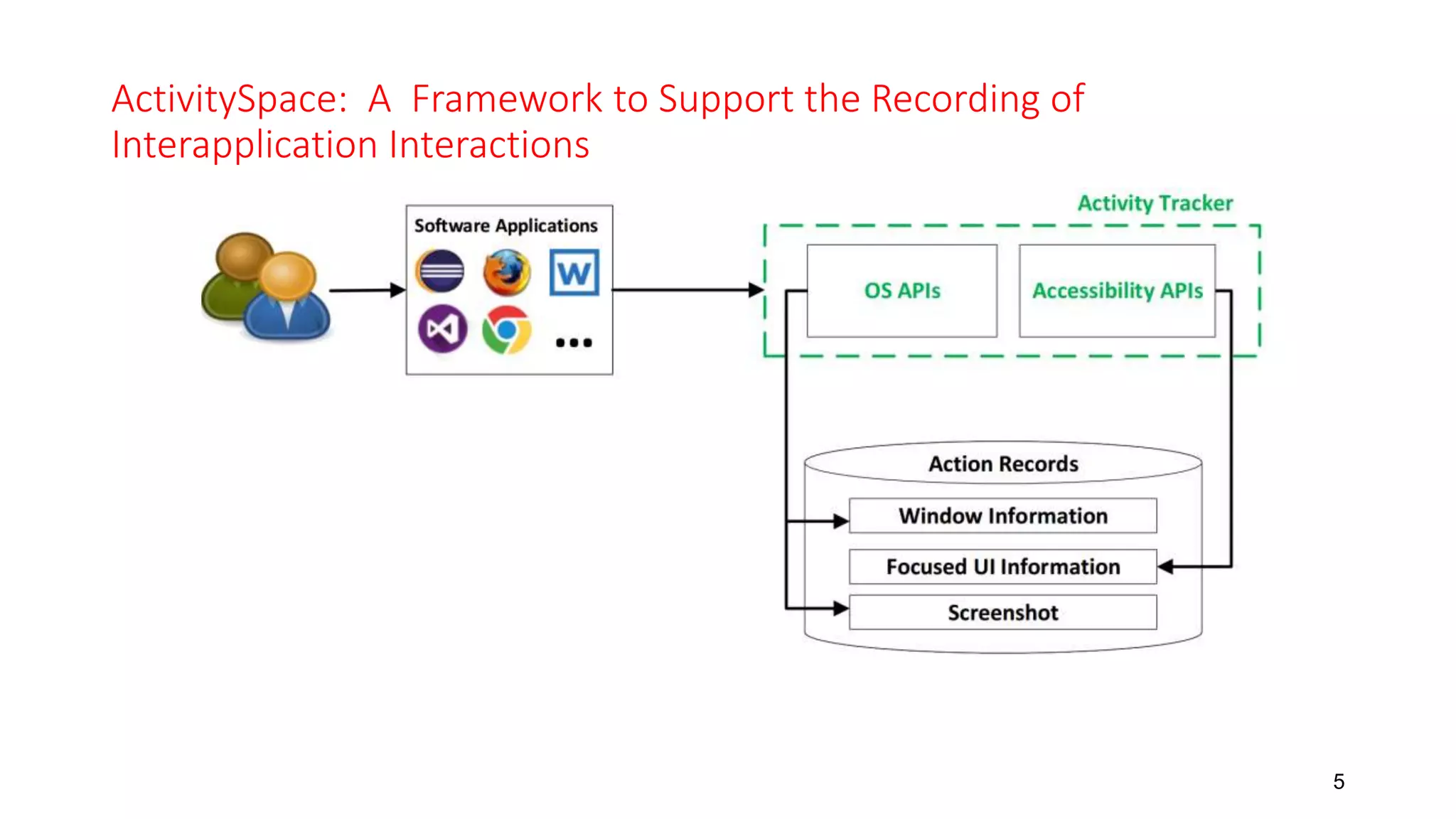
2) Developers frequently used web browsers and document editors to aid comprehension beyond just IDEs.
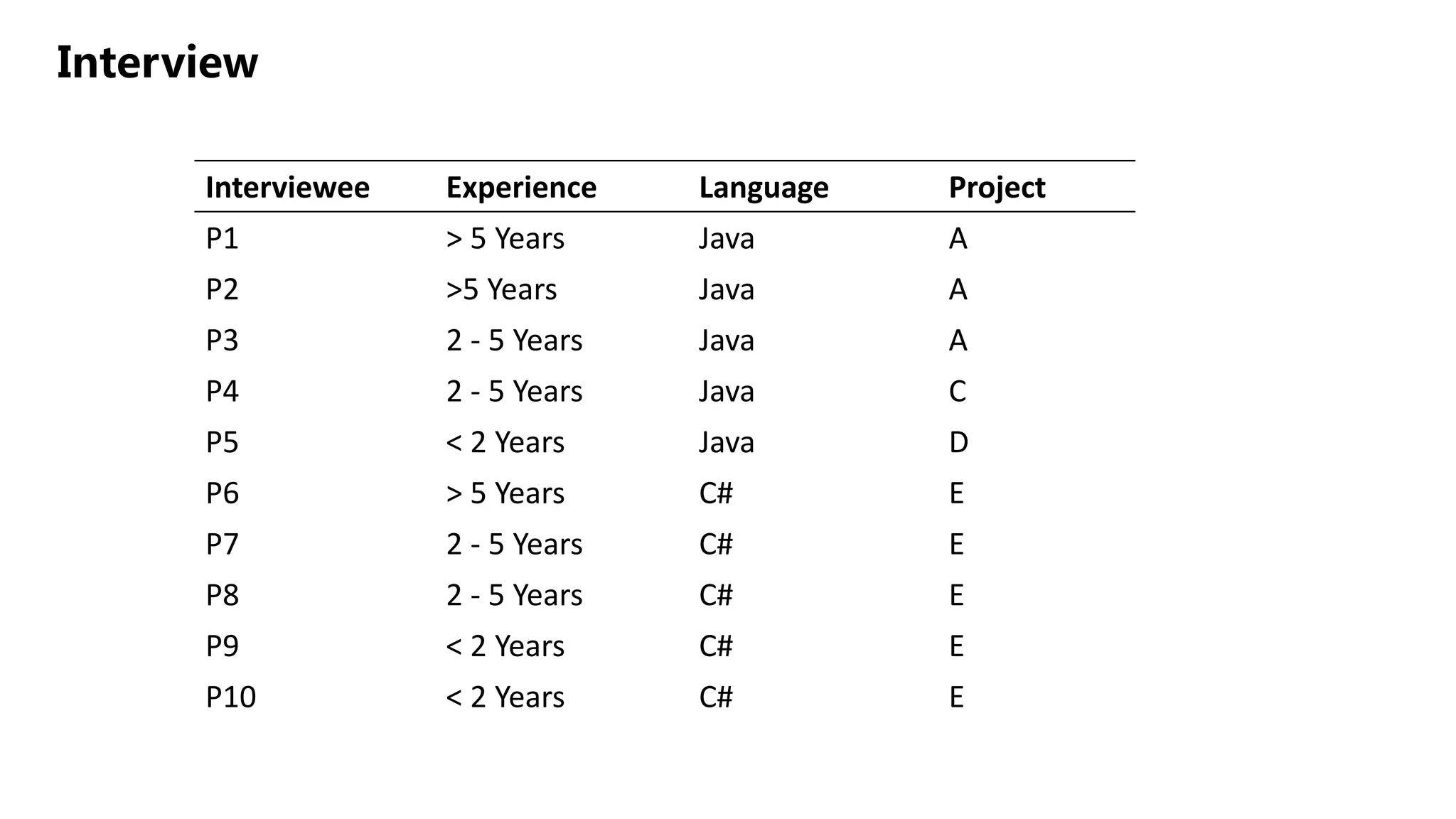
3) Interviews and observations revealed that insufficient documentation, unclear code, and complex inheritance hierarchies contributed to long comprehension sessions.