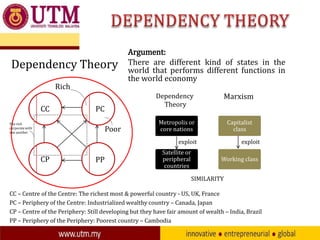
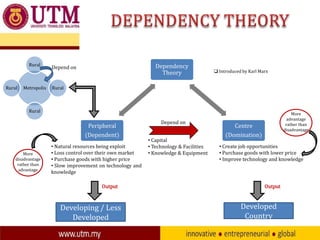
This document discusses factors that contribute to global and domestic inequalities. It introduces dependency theory, which argues that poorer countries are disadvantaged in the international system through exploitation by richer countries. Global factors like colonialism created economic gaps by exploiting resources from colonies. The structure of the world economy also favors richer nations. Domestically, overpopulation, unemployment, and the legacy of colonial social divisions contribute to inequality. Dependency theory asserts that underdeveloped countries must isolate from capitalist states to gain independence.