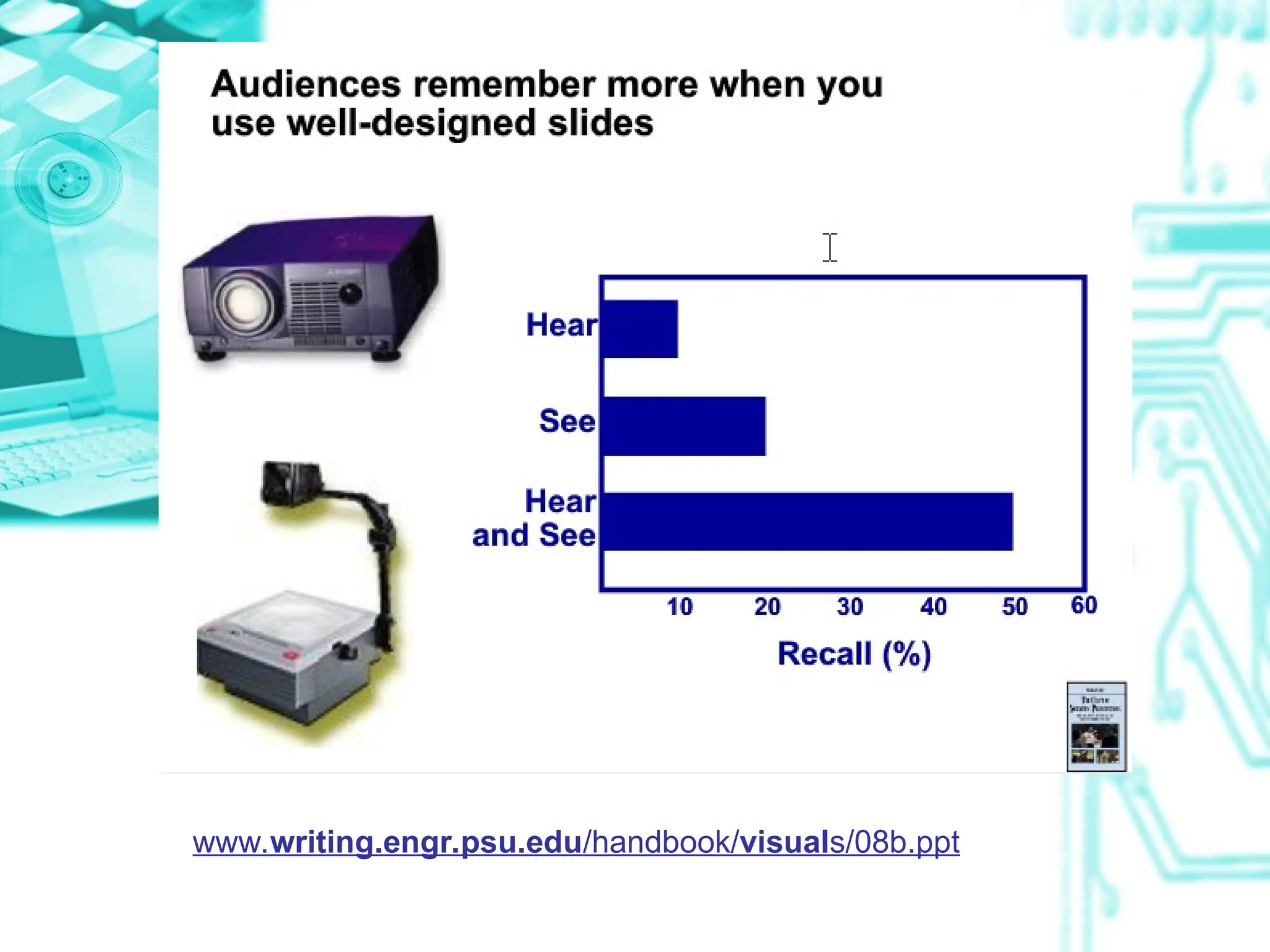
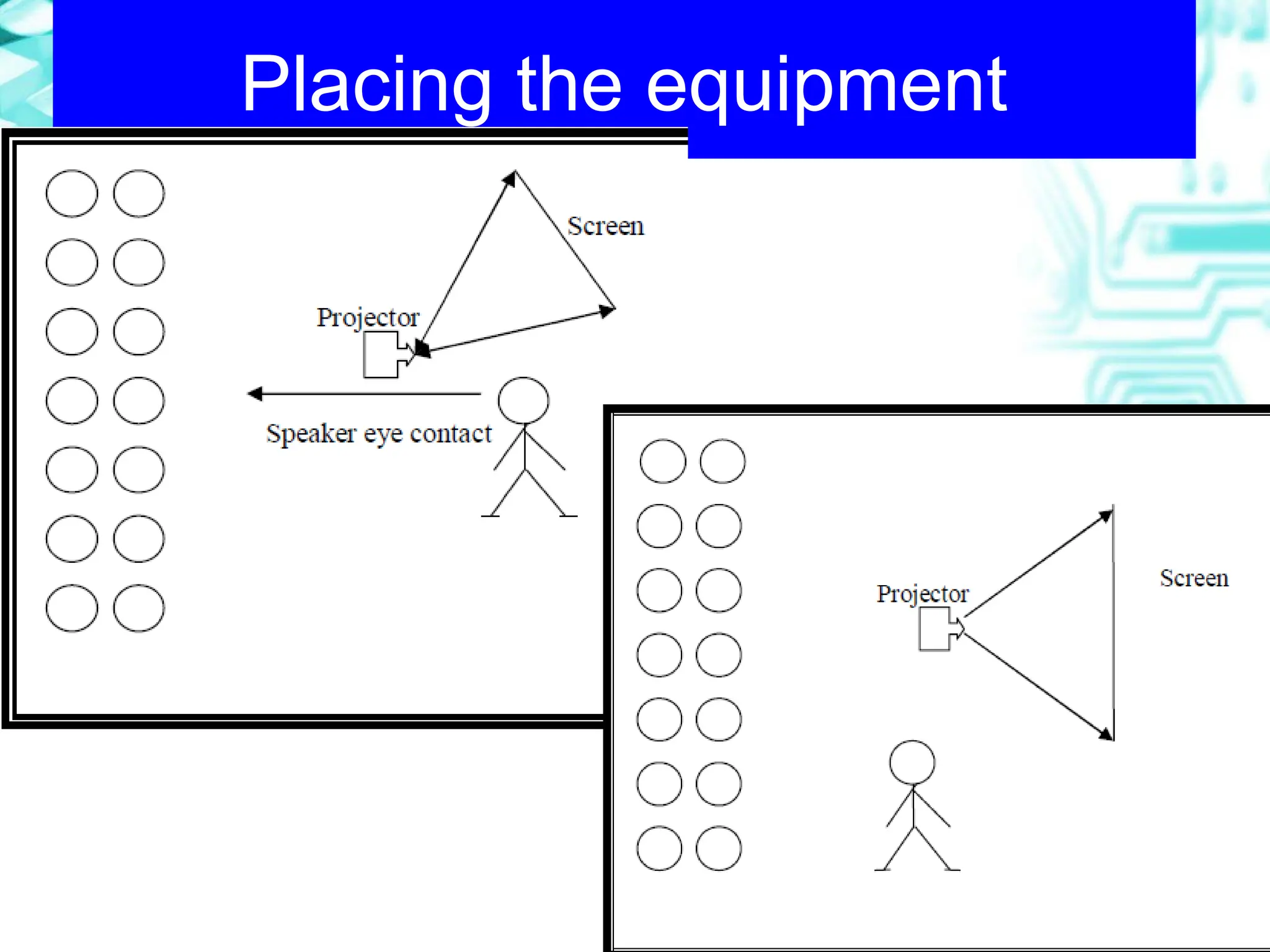
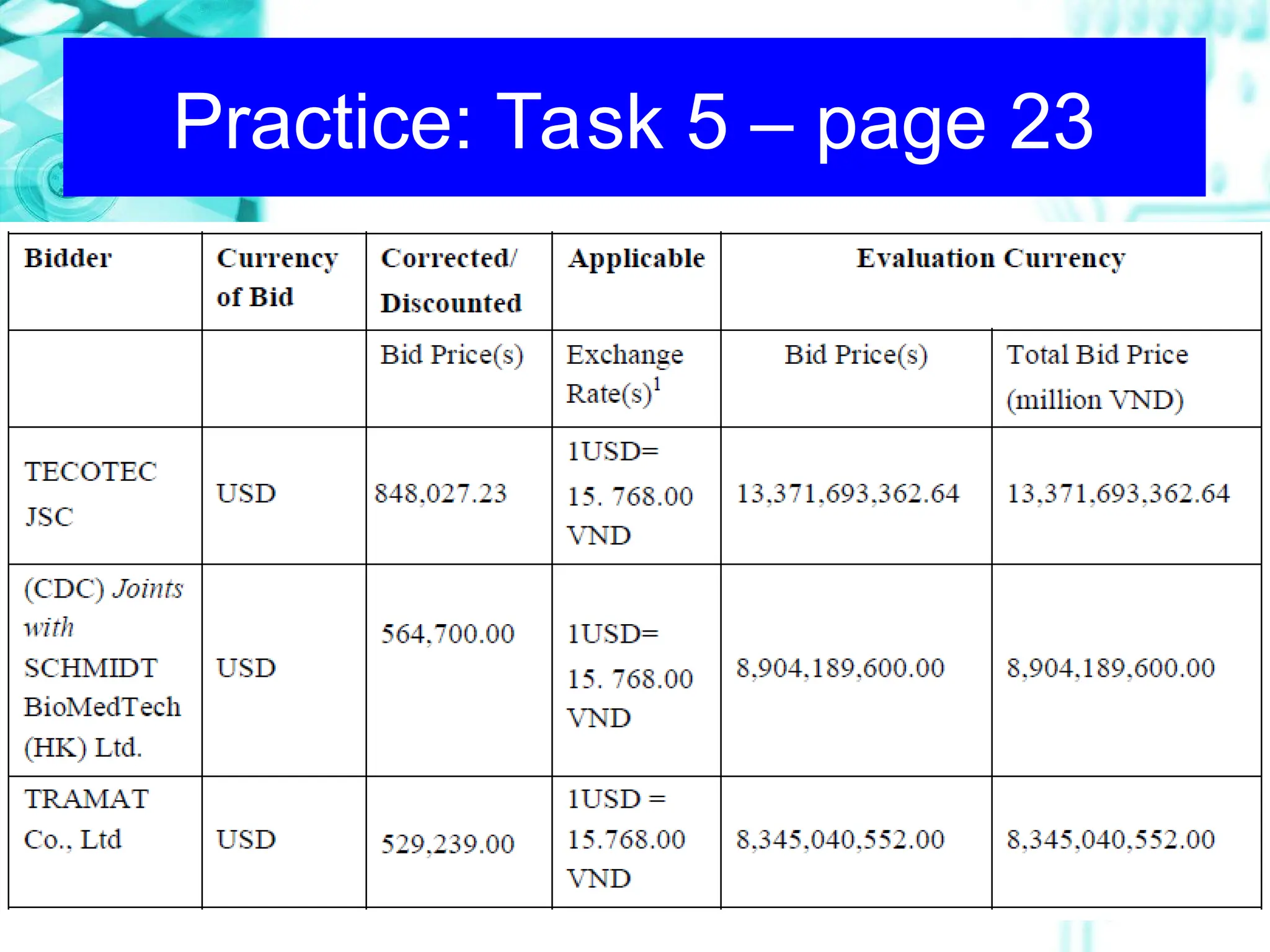
The document focuses on the importance and effective use of visual aids in presentations, outlining various types such as charts, models, and computer presentations. It offers design tips, including minimizing text, using color wisely, and ensuring clarity for the audience. Additionally, it emphasizes proper introduction, explanation, and interpretation techniques to engage the audience and convey messages effectively.