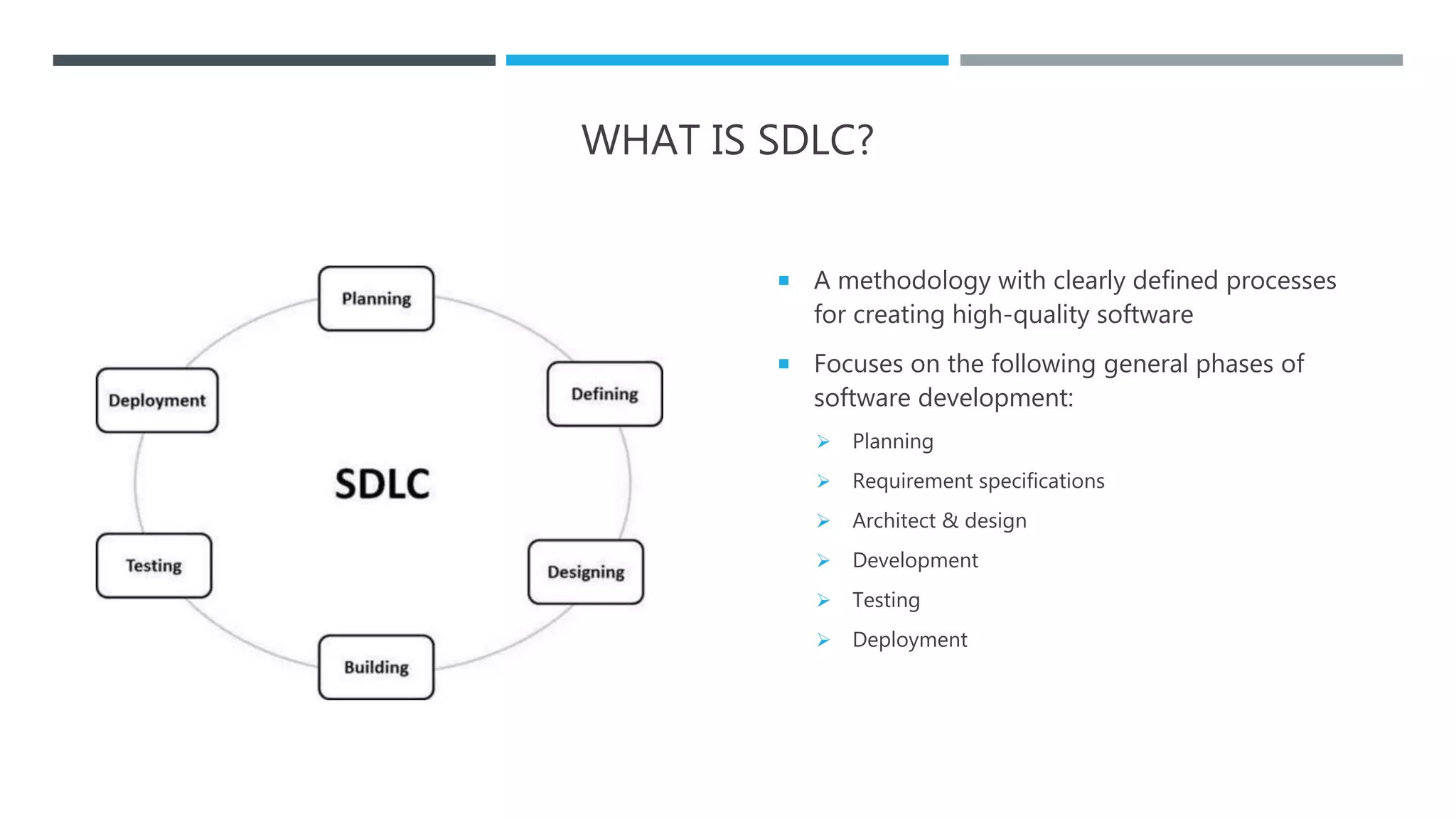
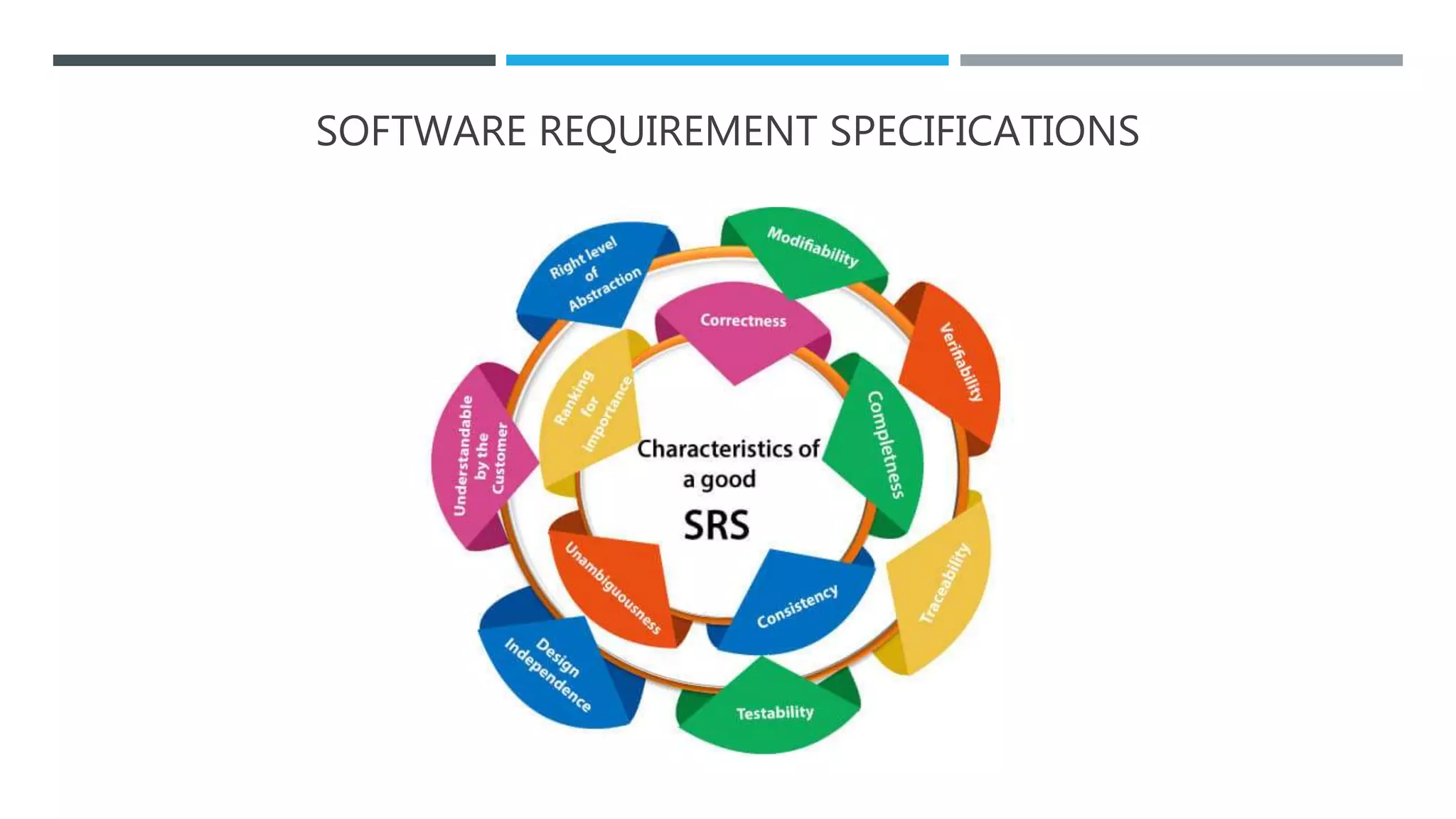
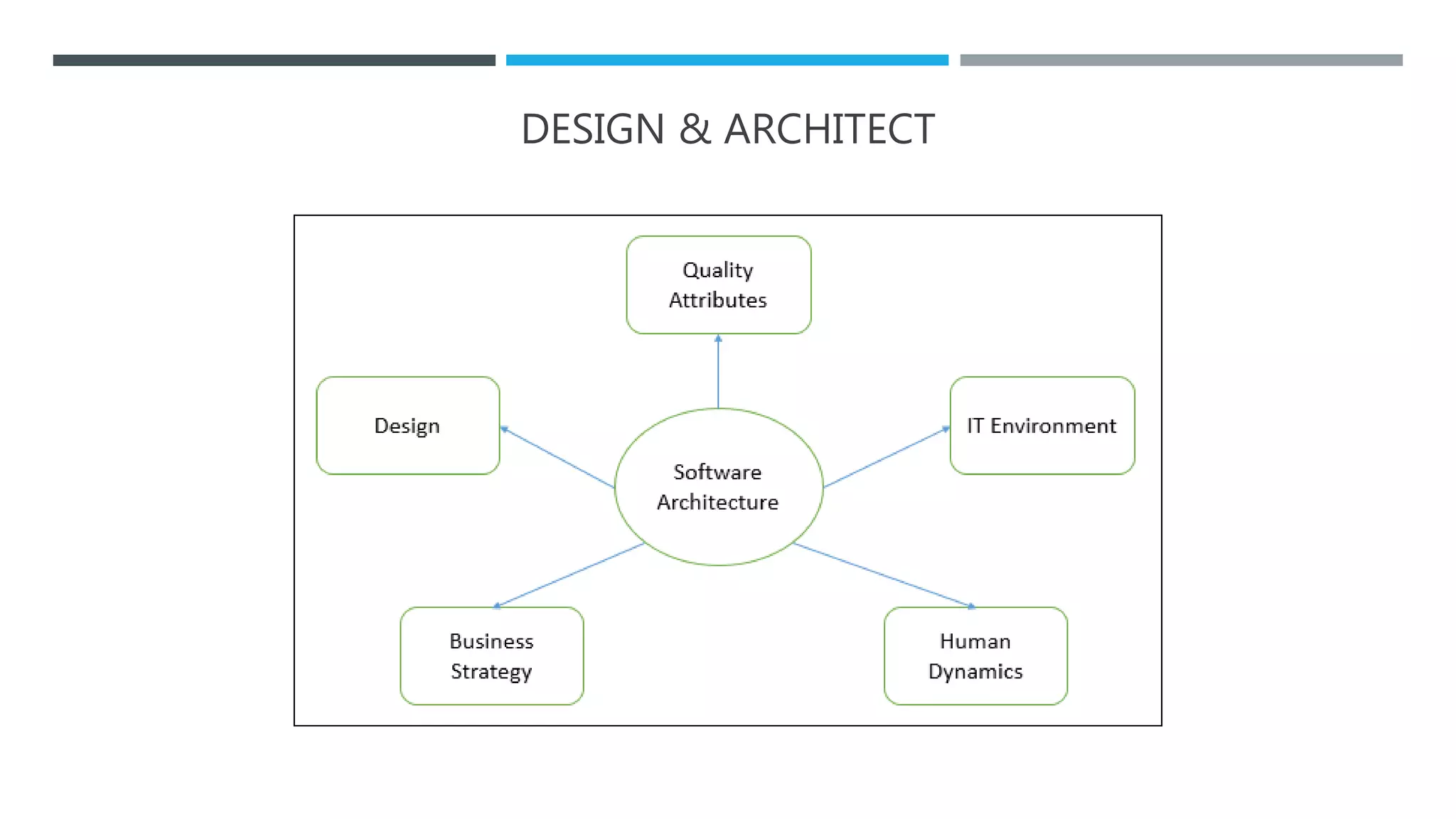
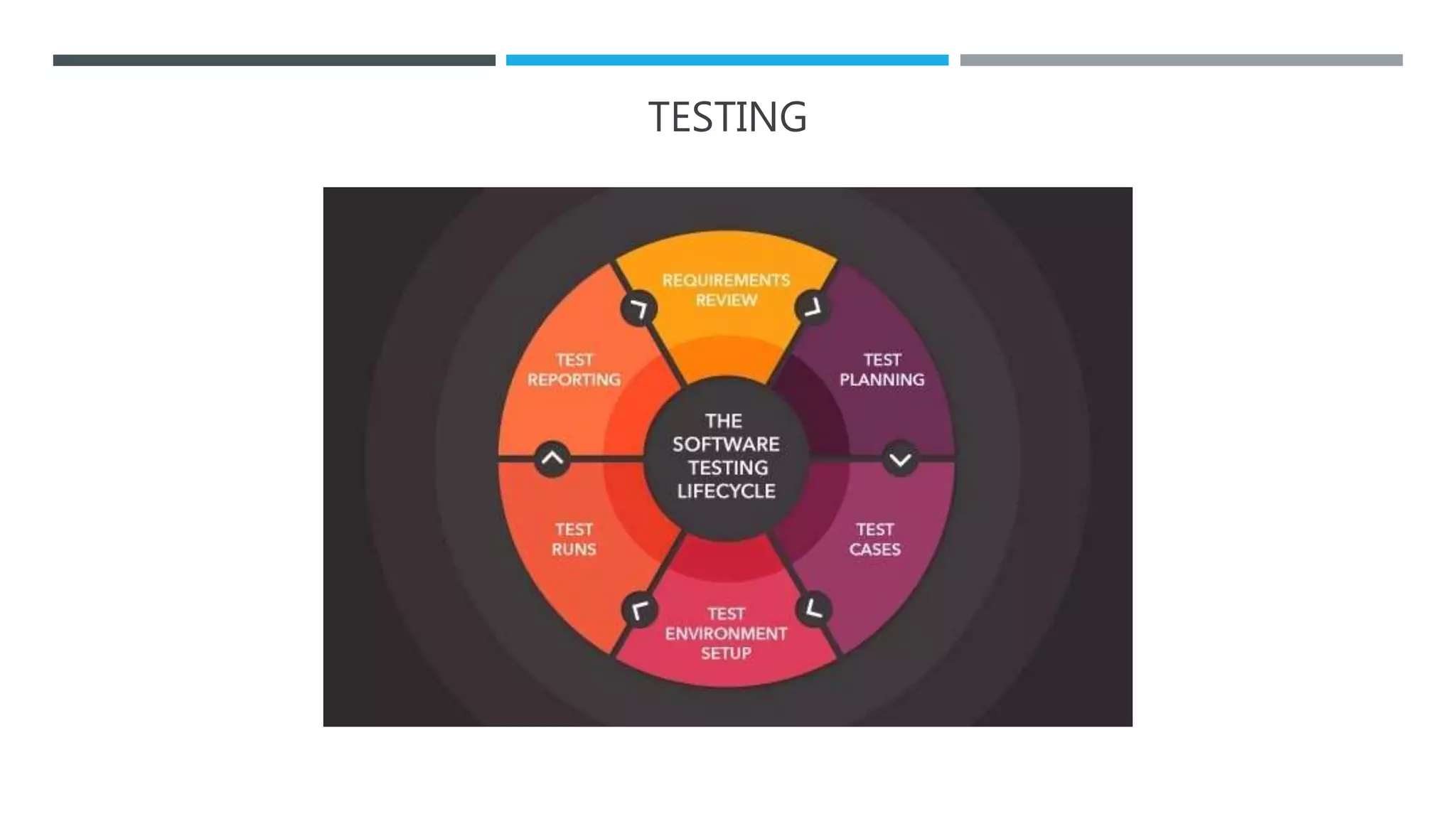
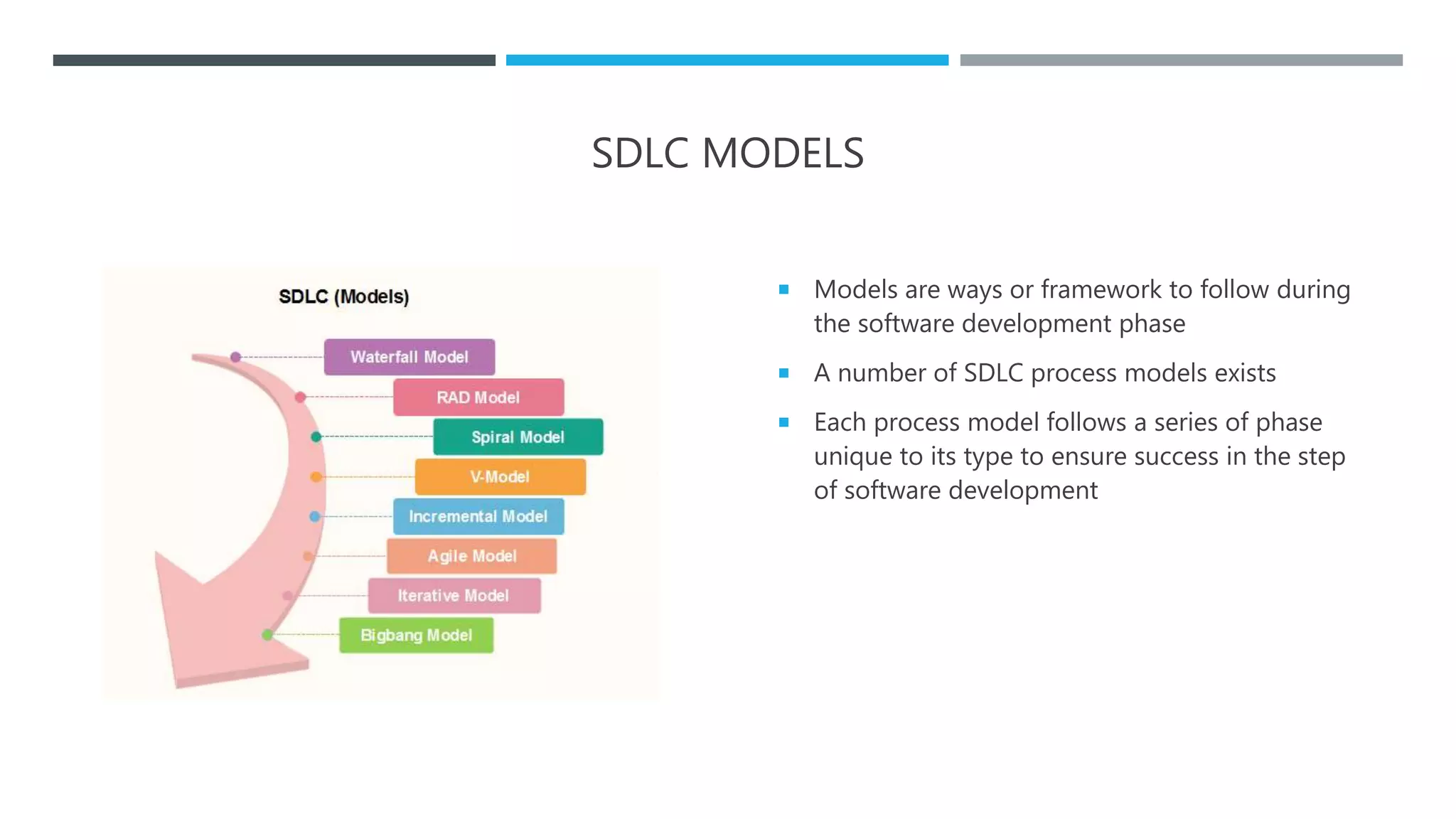
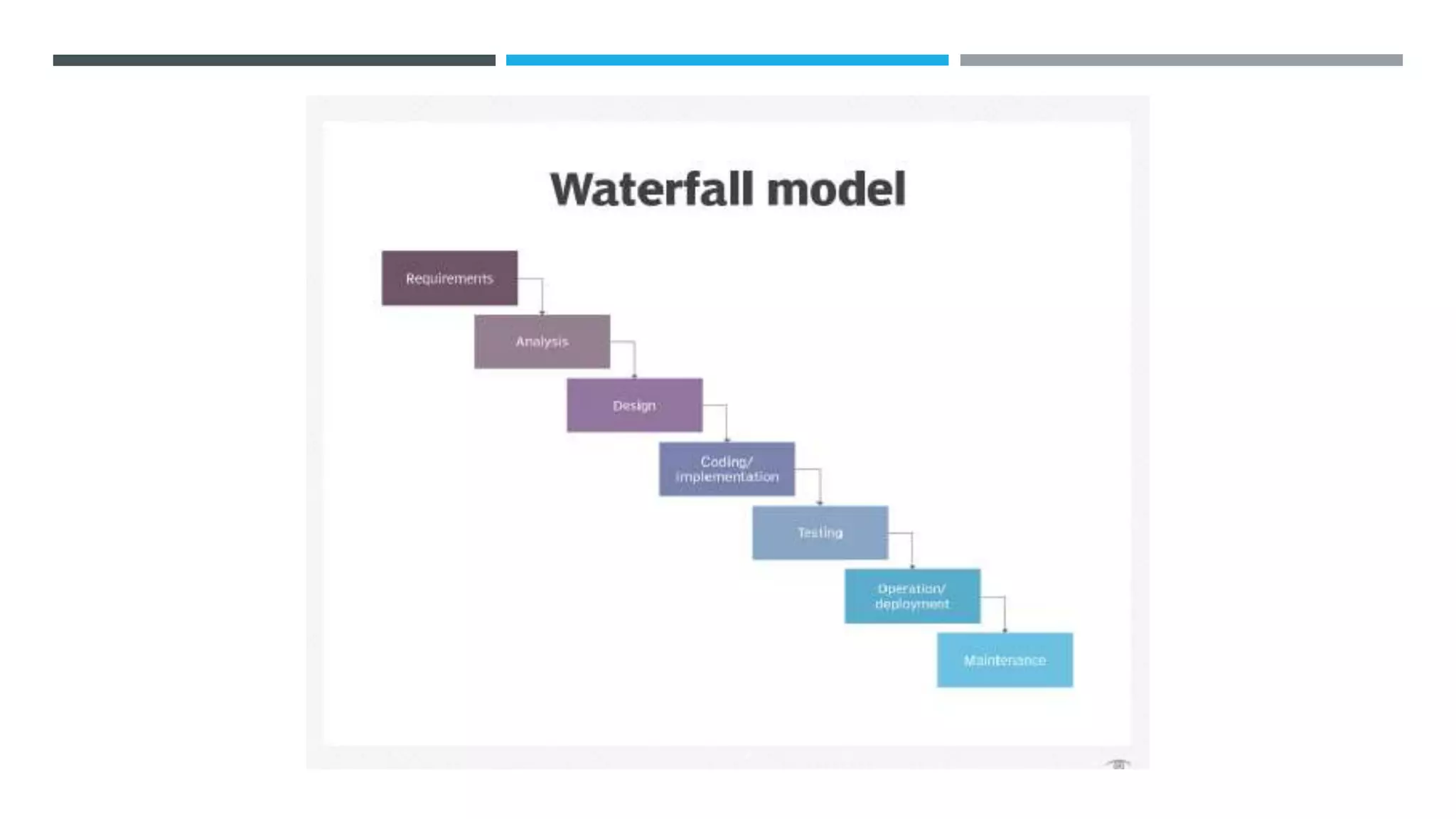
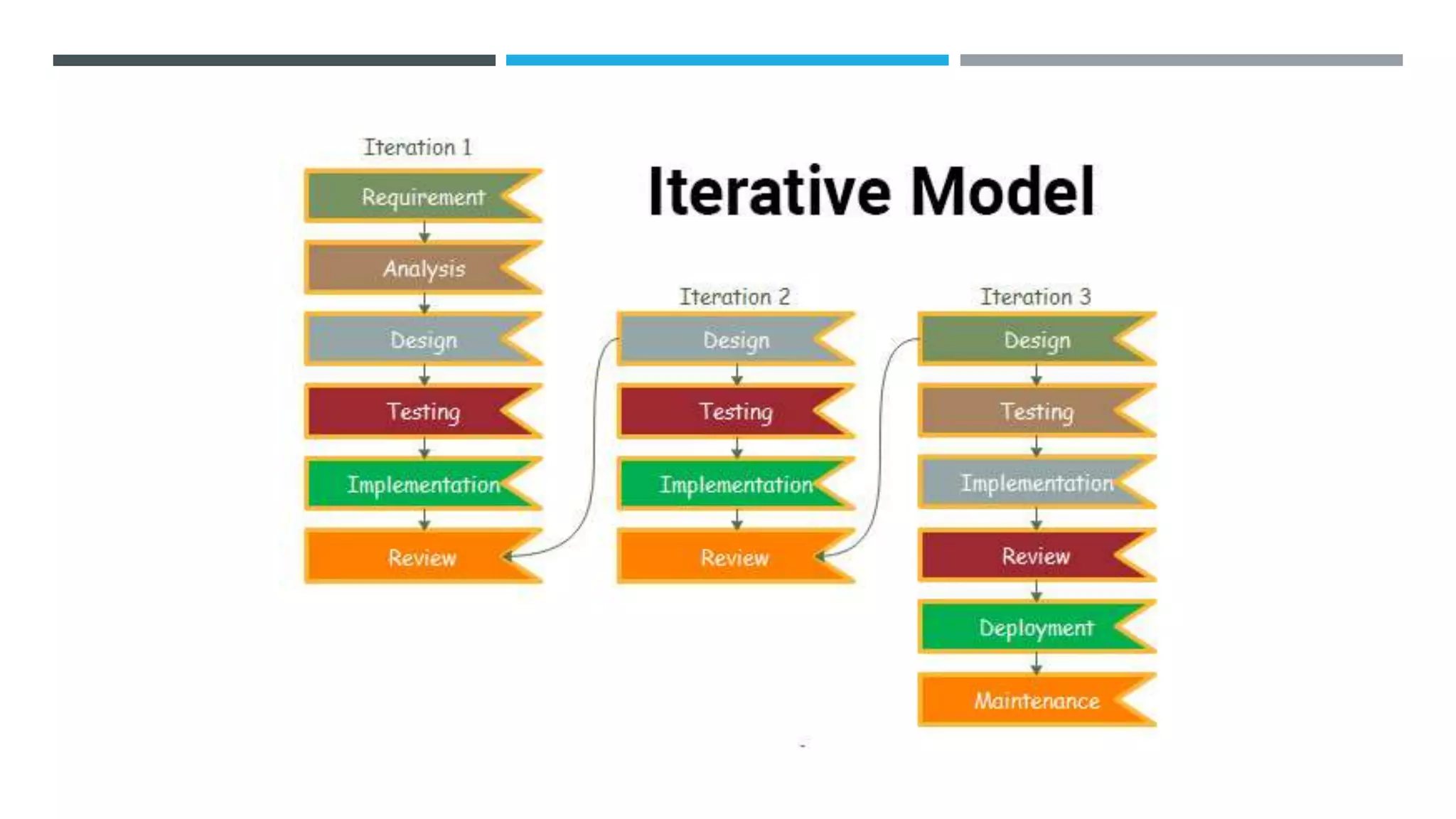
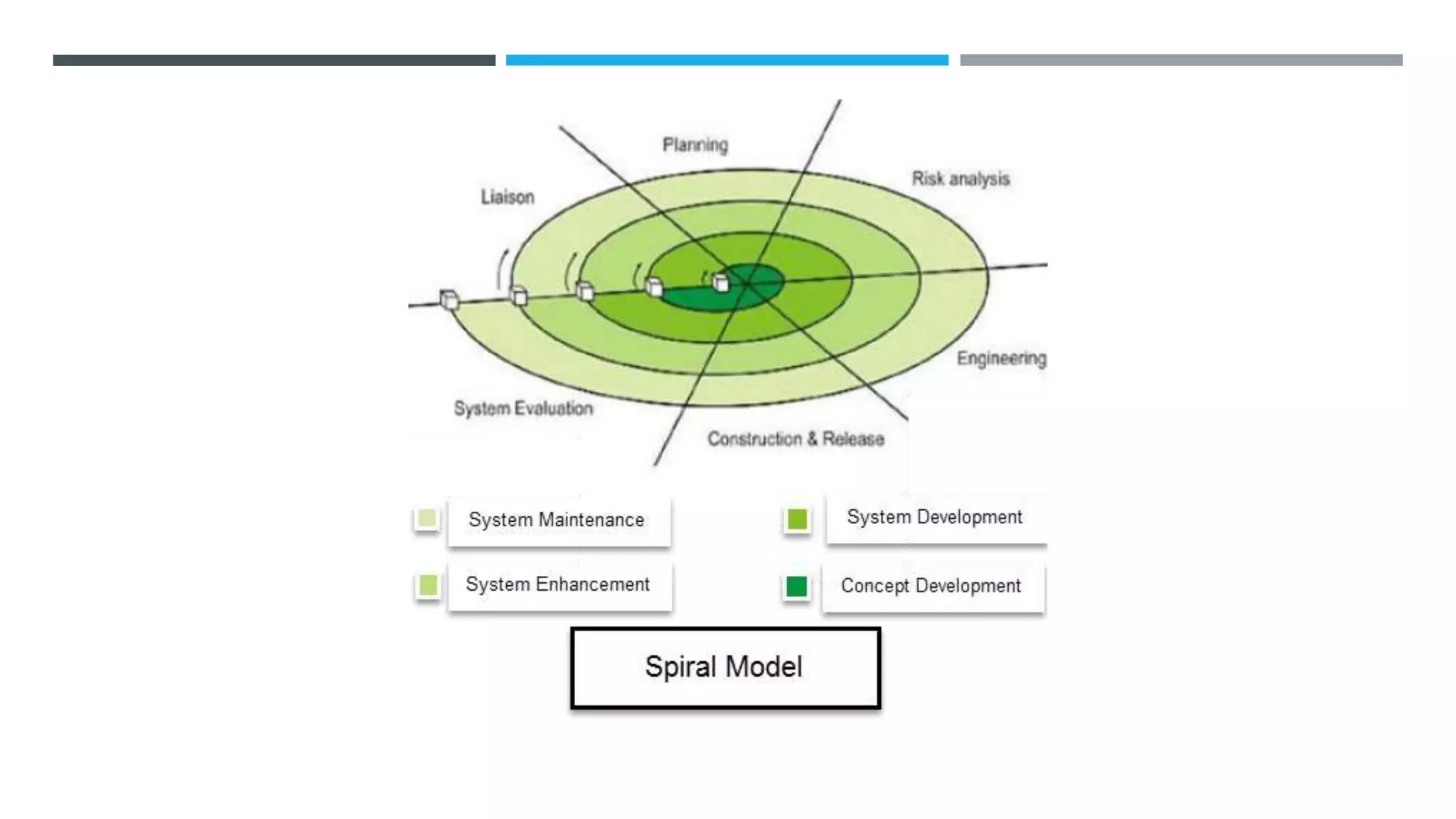
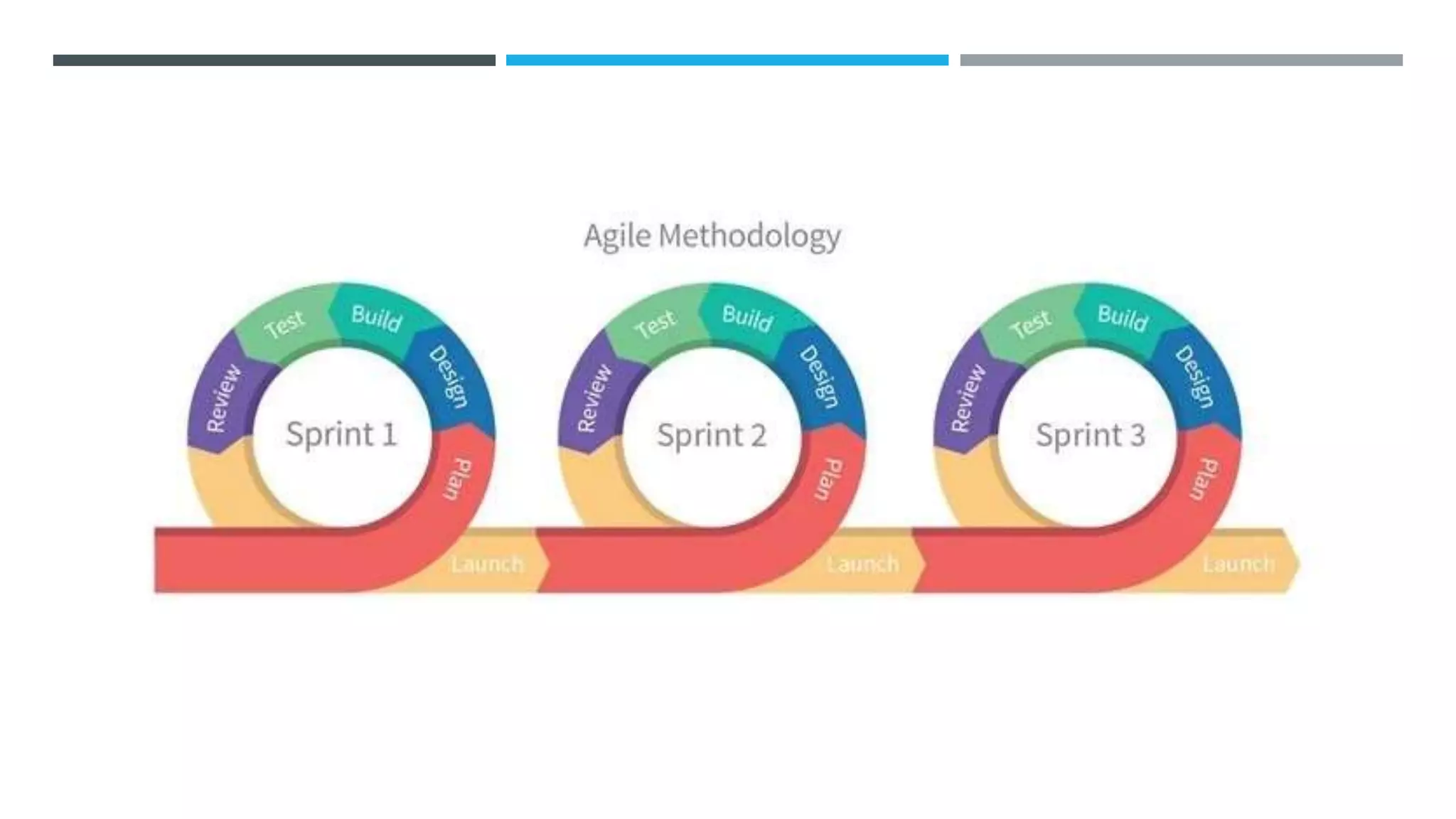
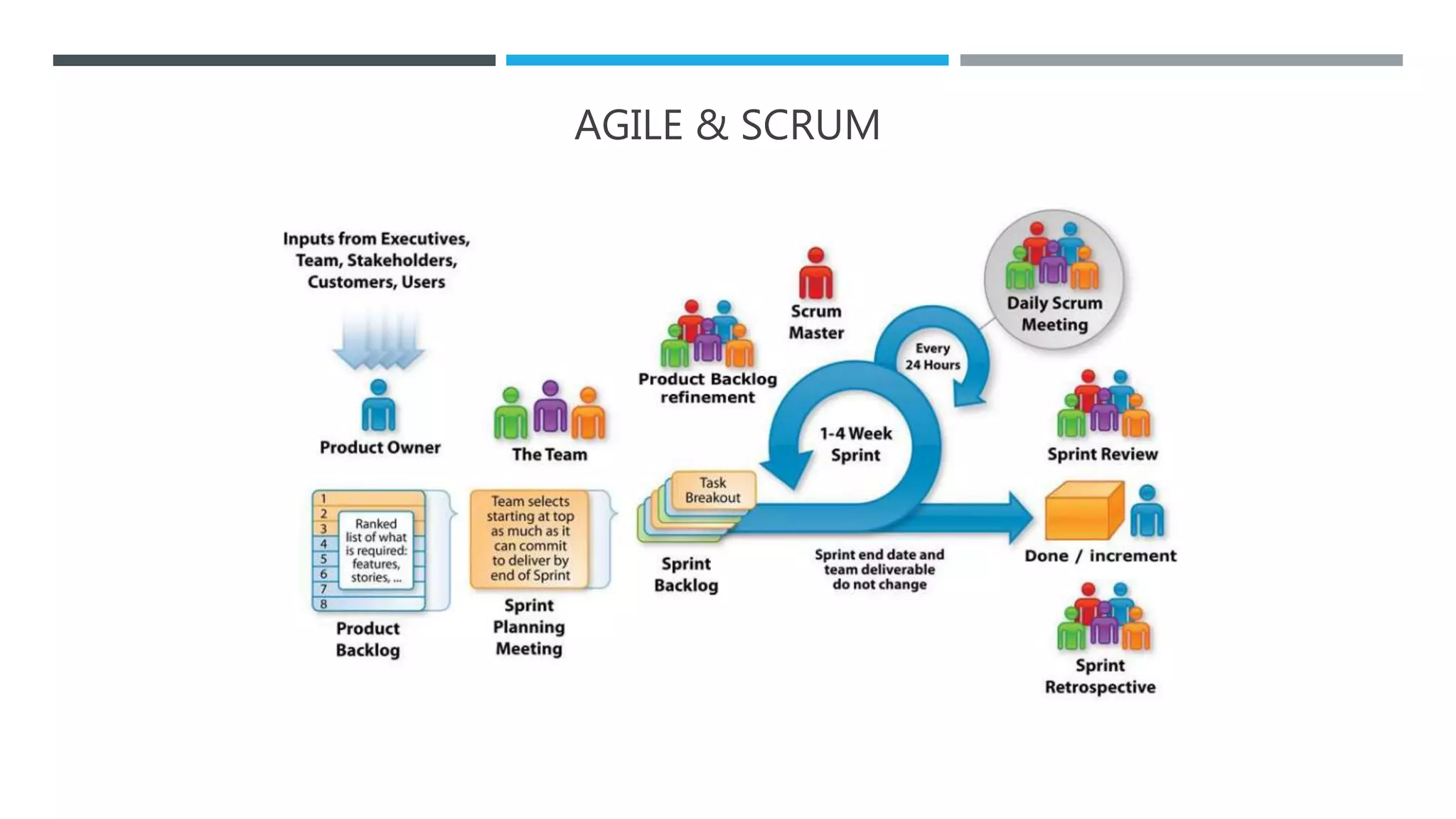
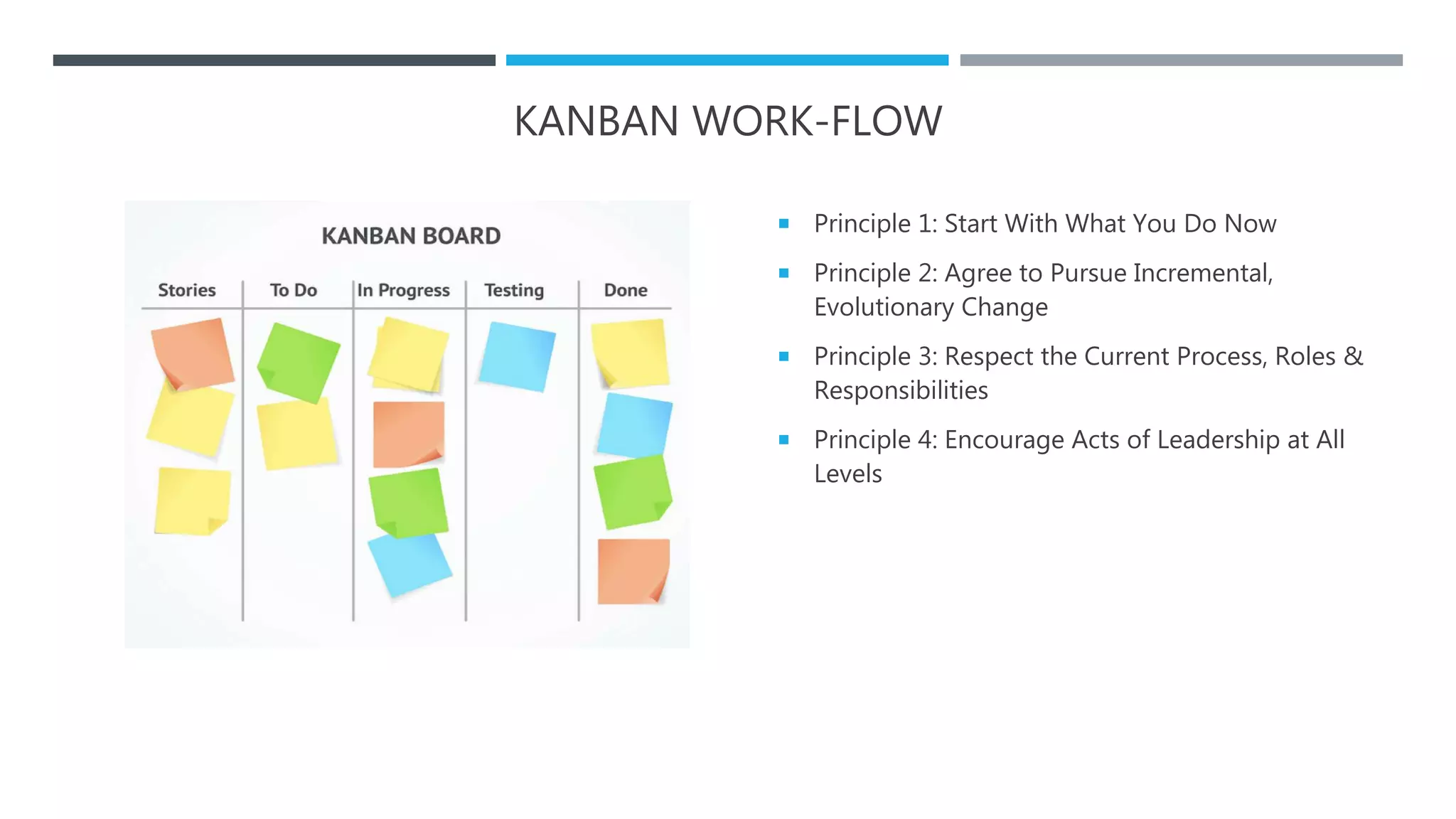
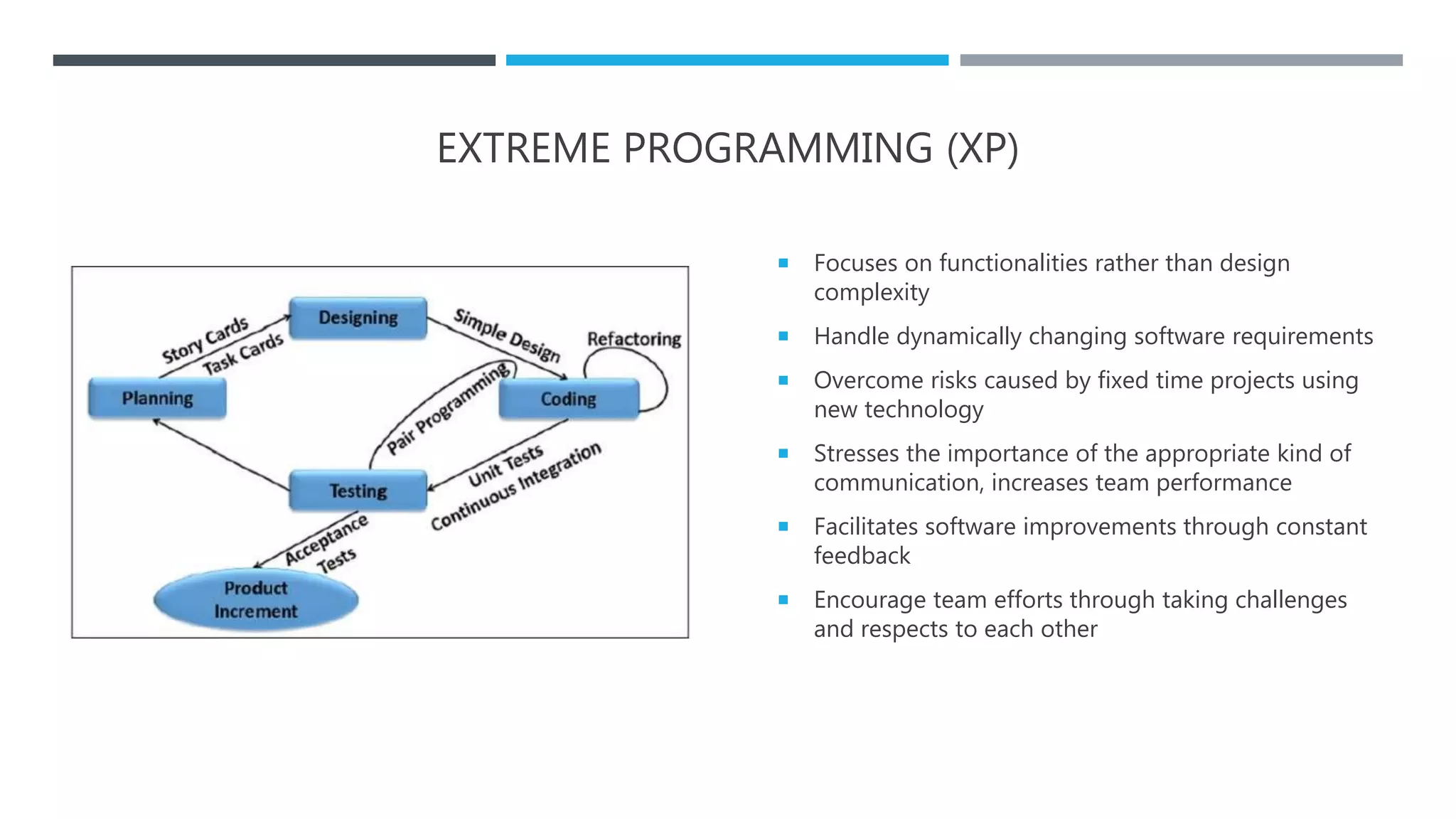
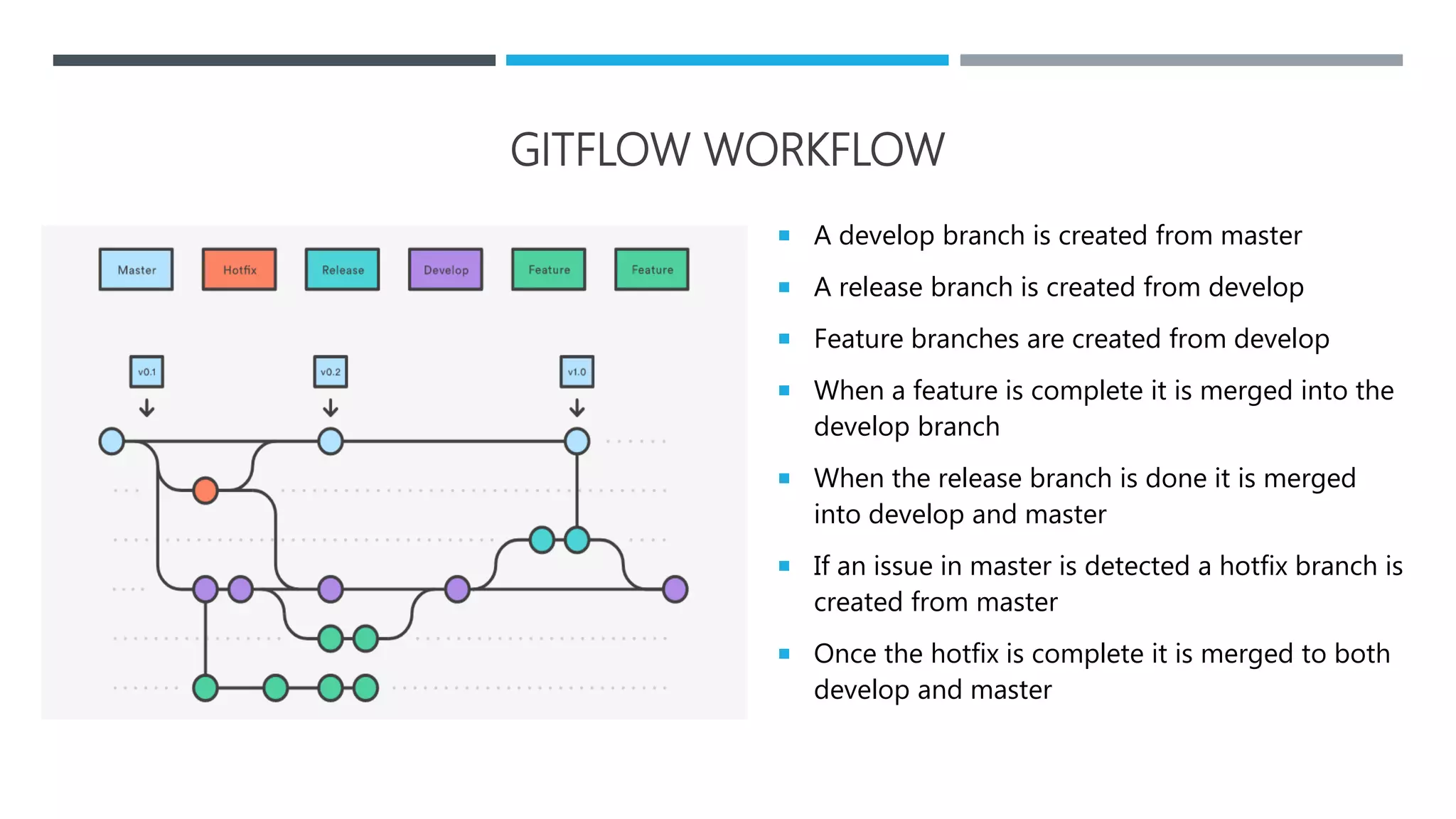
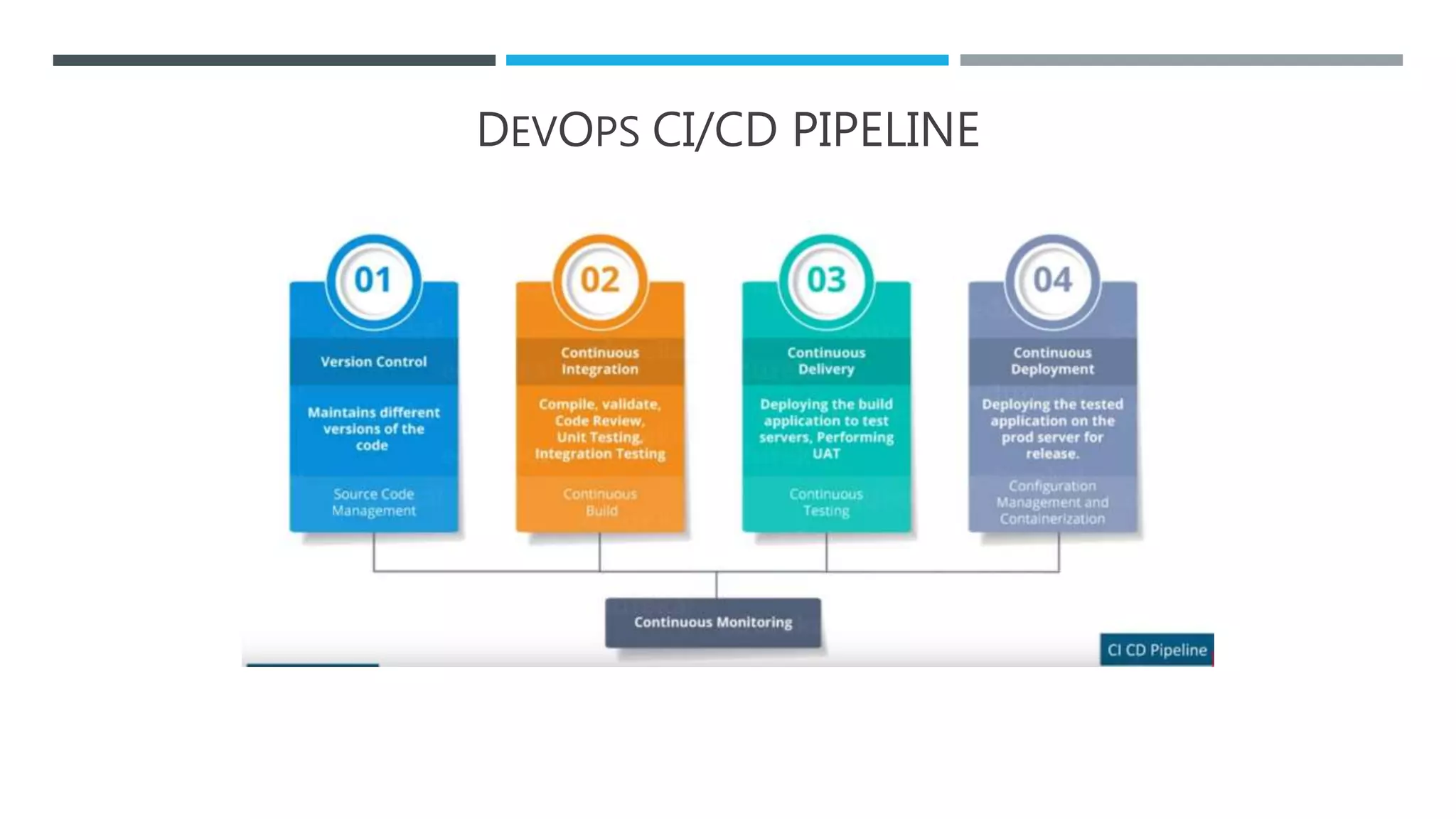
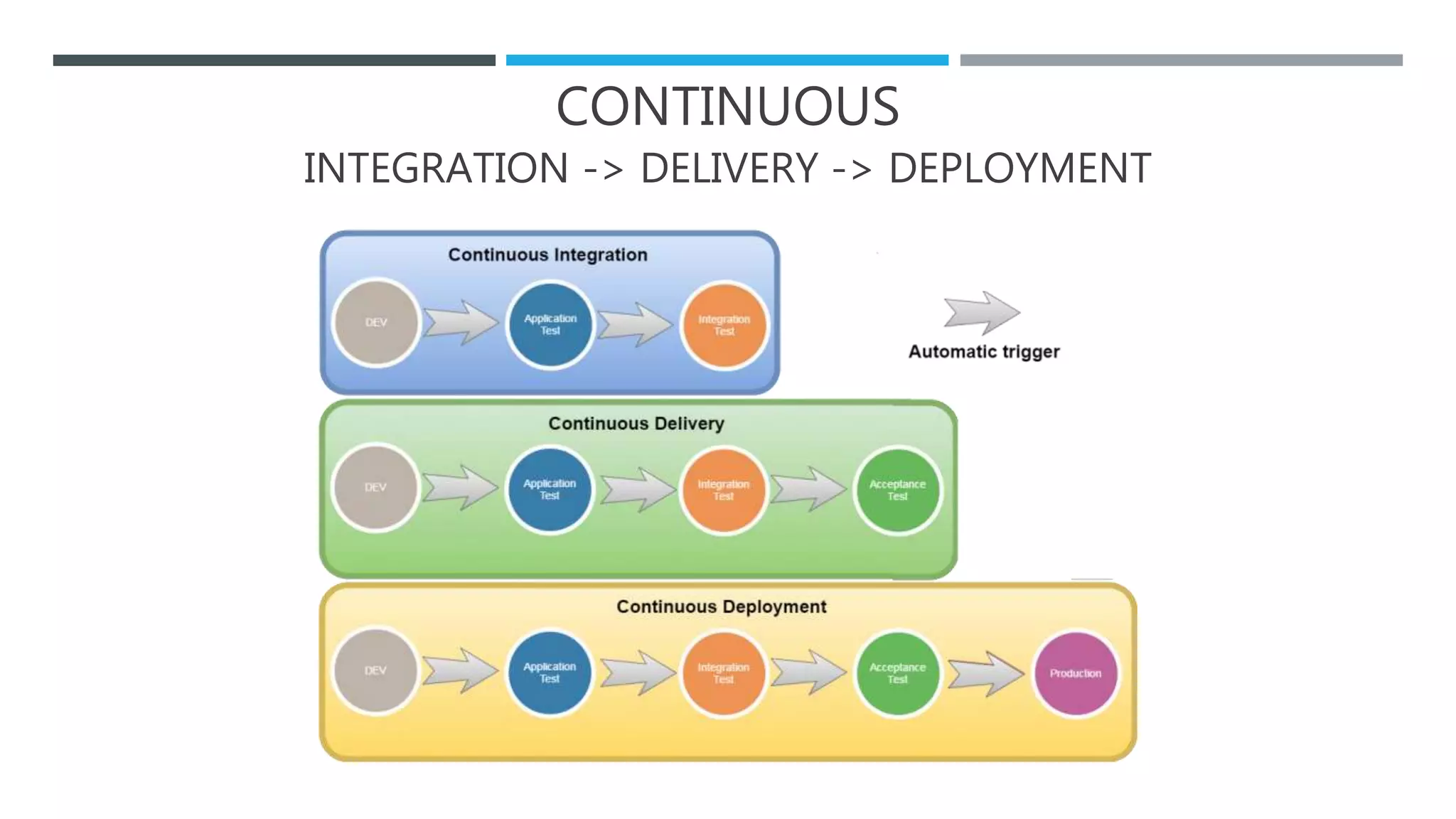
The document outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), detailing traditional approaches, popular models, and methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and Kanban. It emphasizes the phases of software development from planning to deployment, explaining the importance of continuous delivery and adaptation to evolving requirements. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as Extreme Programming (XP) and DevOps CI/CD, highlighting practices for code review and integration.