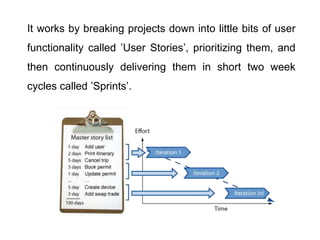
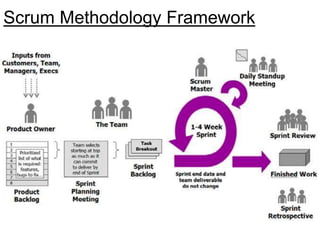
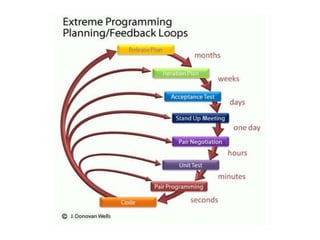
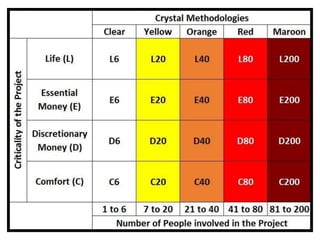
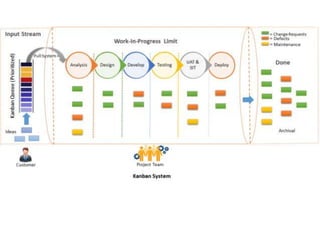
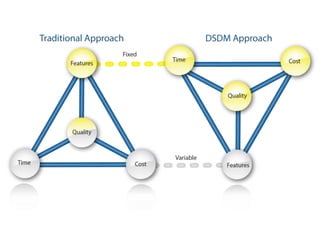
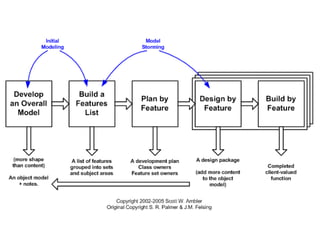
Agile is an iterative approach to software development that builds software incrementally from the start of the project. It breaks projects into small user functionality pieces called user stories that are prioritized and continuously delivered in short two week sprints. Popular agile methodologies include Scrum, Extreme Programming, Crystal, Dynamic System Development Method, Lean, Kanban, and Feature-Driven Development. Scrum uses product owners, cross-functional teams, and sprints to deliver potentially shippable increments. Extreme Programming emphasizes close customer involvement and rapid, frequent delivery of working software.