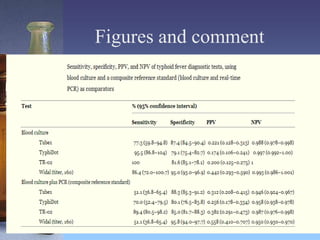
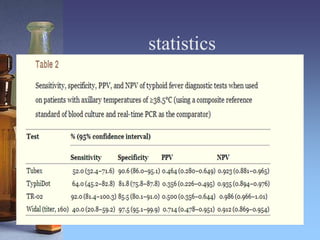
This document summarizes a study that evaluated rapid diagnostic tests for typhoid fever in Papua New Guinea. Samples were collected from 500 outpatients with fevers and tested using blood culture, PCR, and three rapid diagnostic tests (Tubex, TyphiDot, and TR-02 prototype). Based on the blood culture and PCR composite reference standard, 47 patients (9.4%) had typhoid fever. The Tubex and TyphiDot tests had low sensitivity and specificity, but the TR-02 prototype showed promising results. An axillary temperature of 38.5°C or higher correlated with typhoid fever. Using an accurate diagnostic test only on patients with high fevers could lower diagnosis costs while maintaining accuracy.