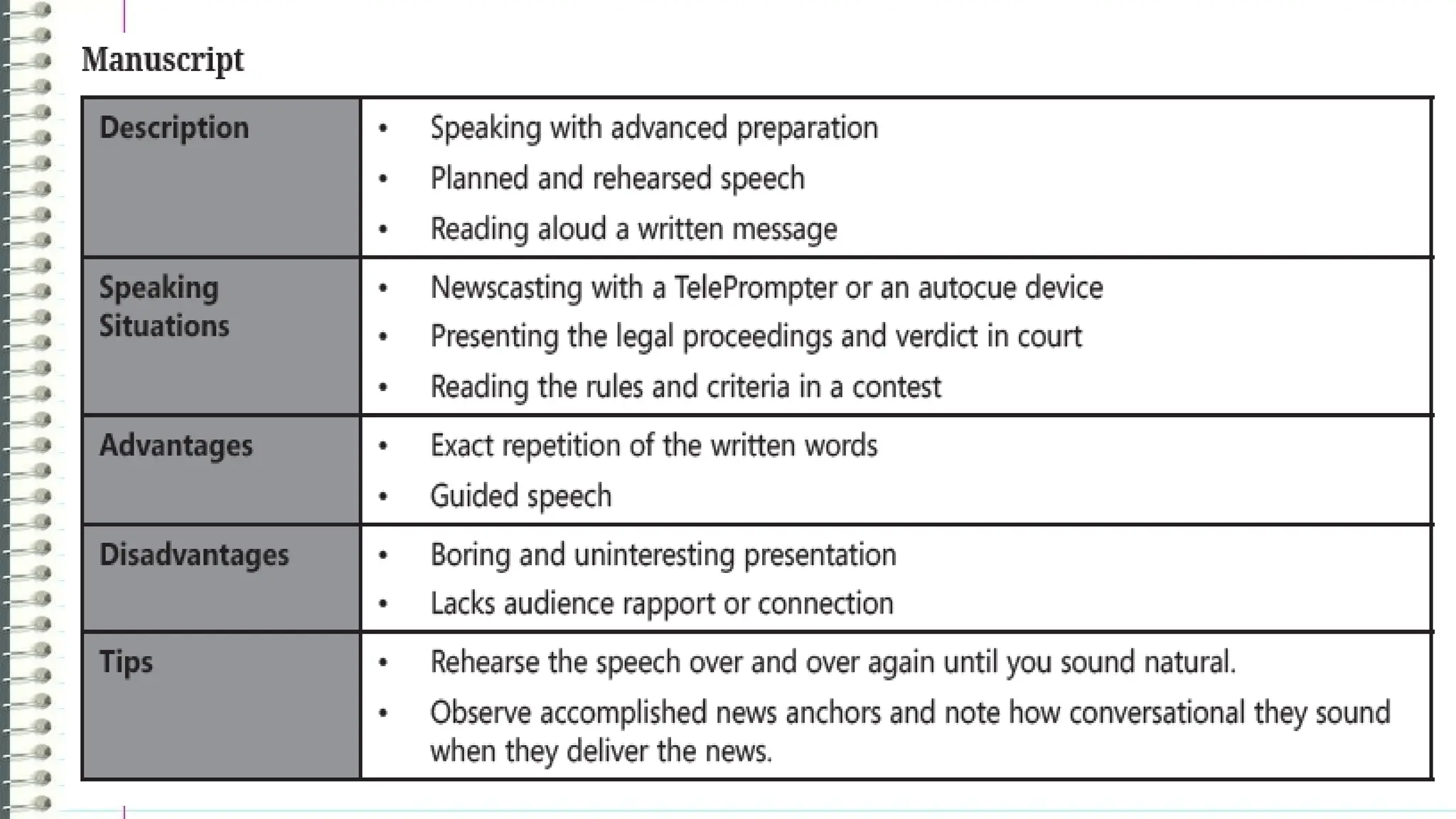
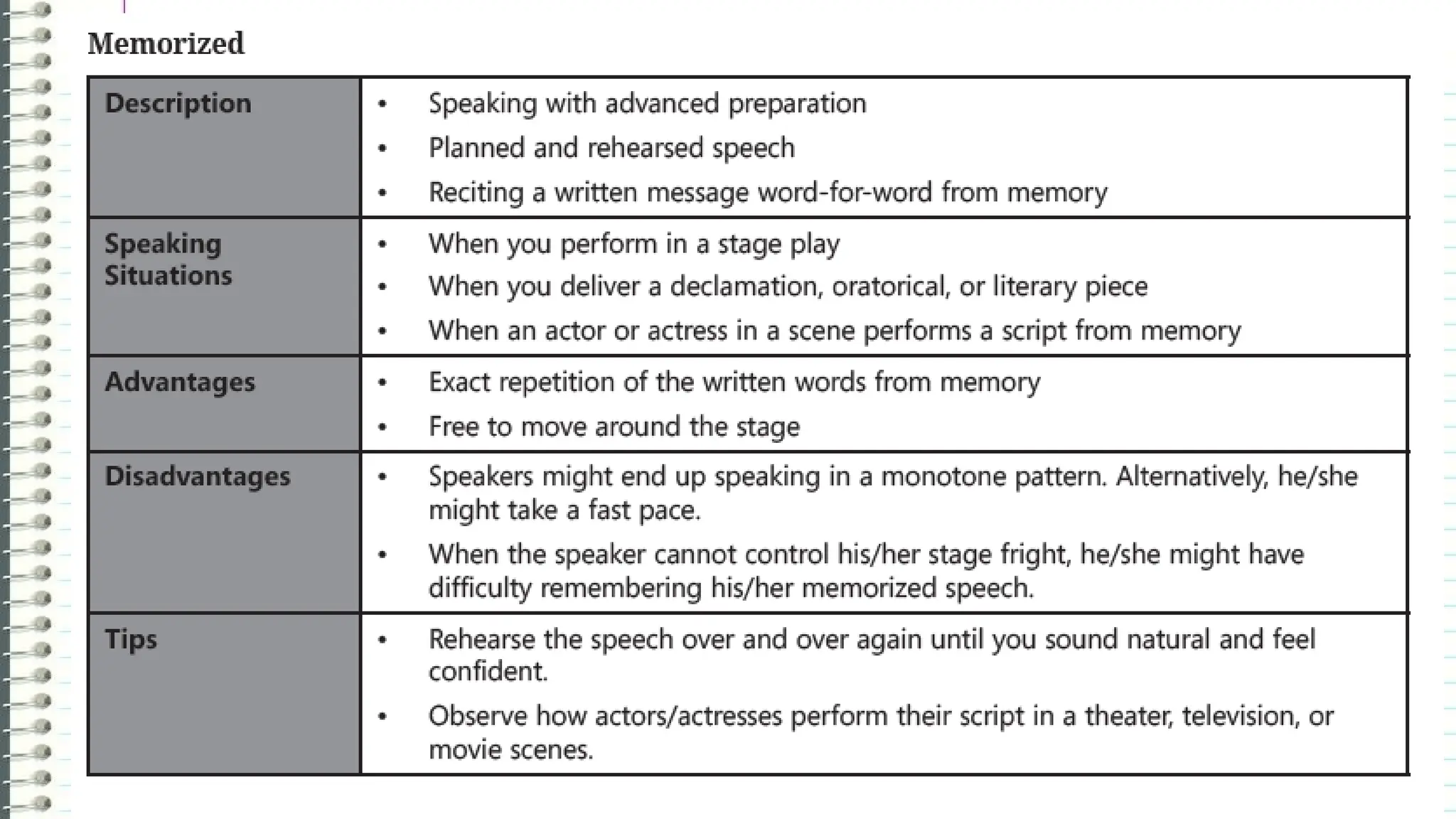
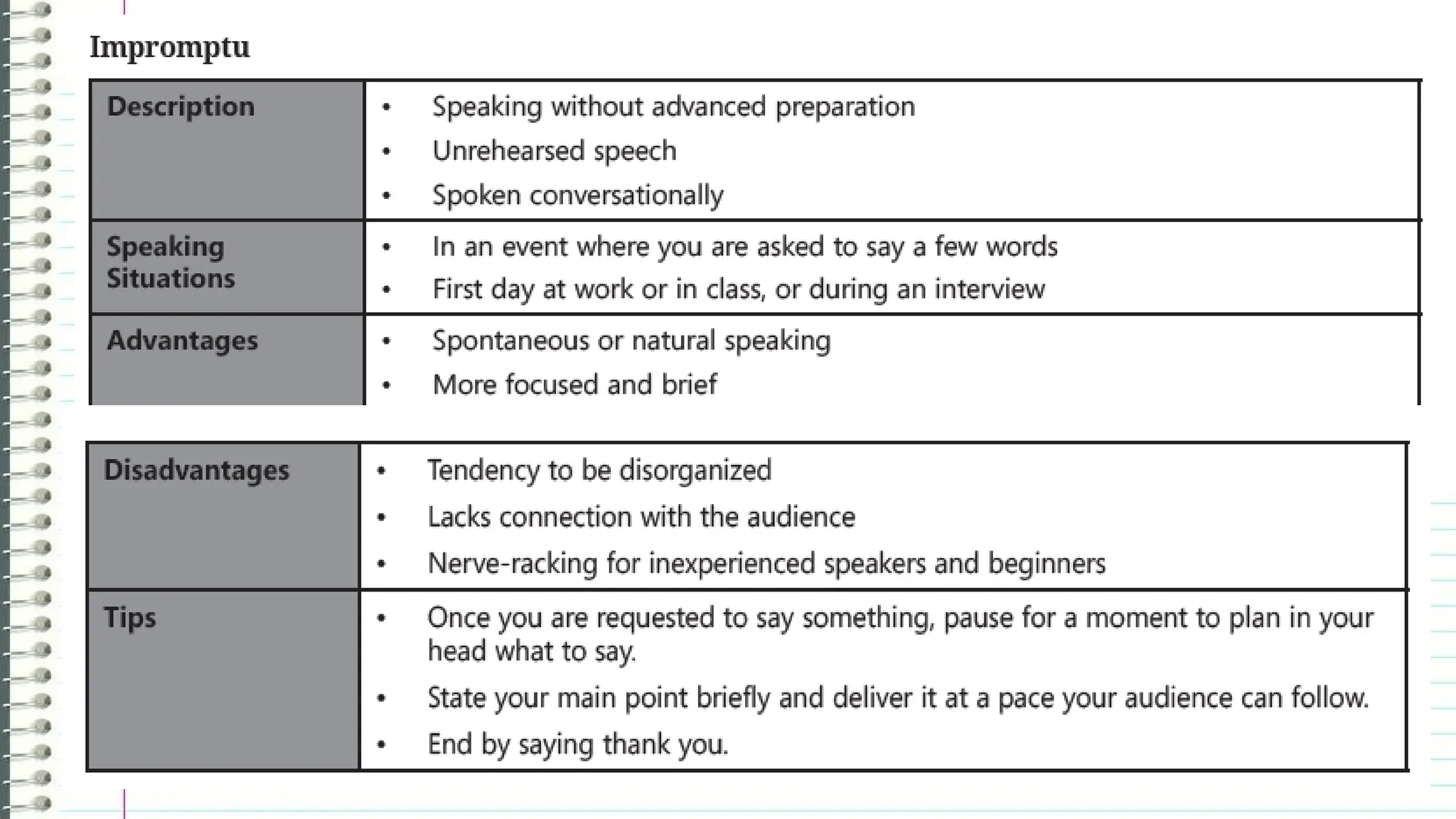
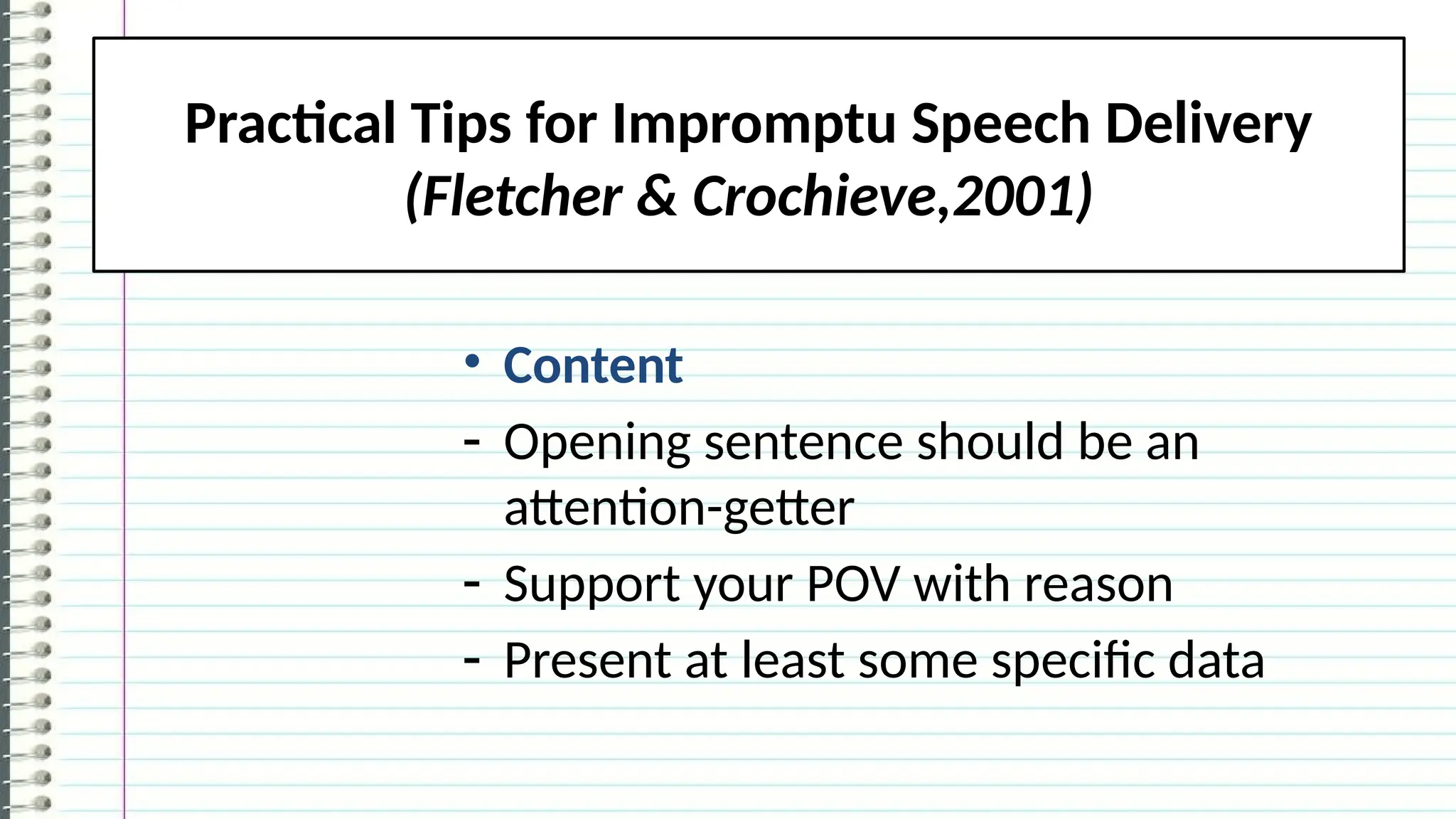
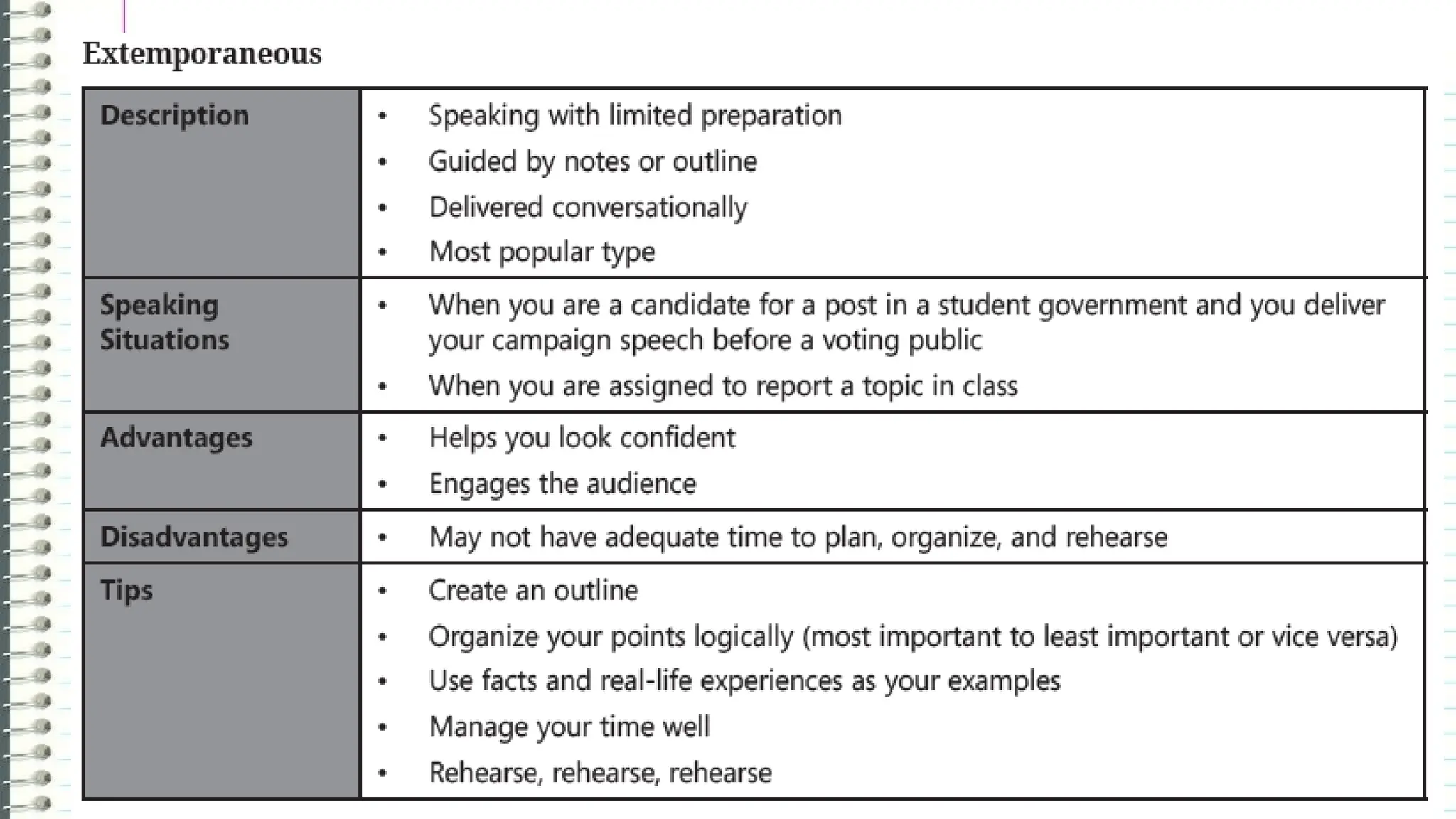
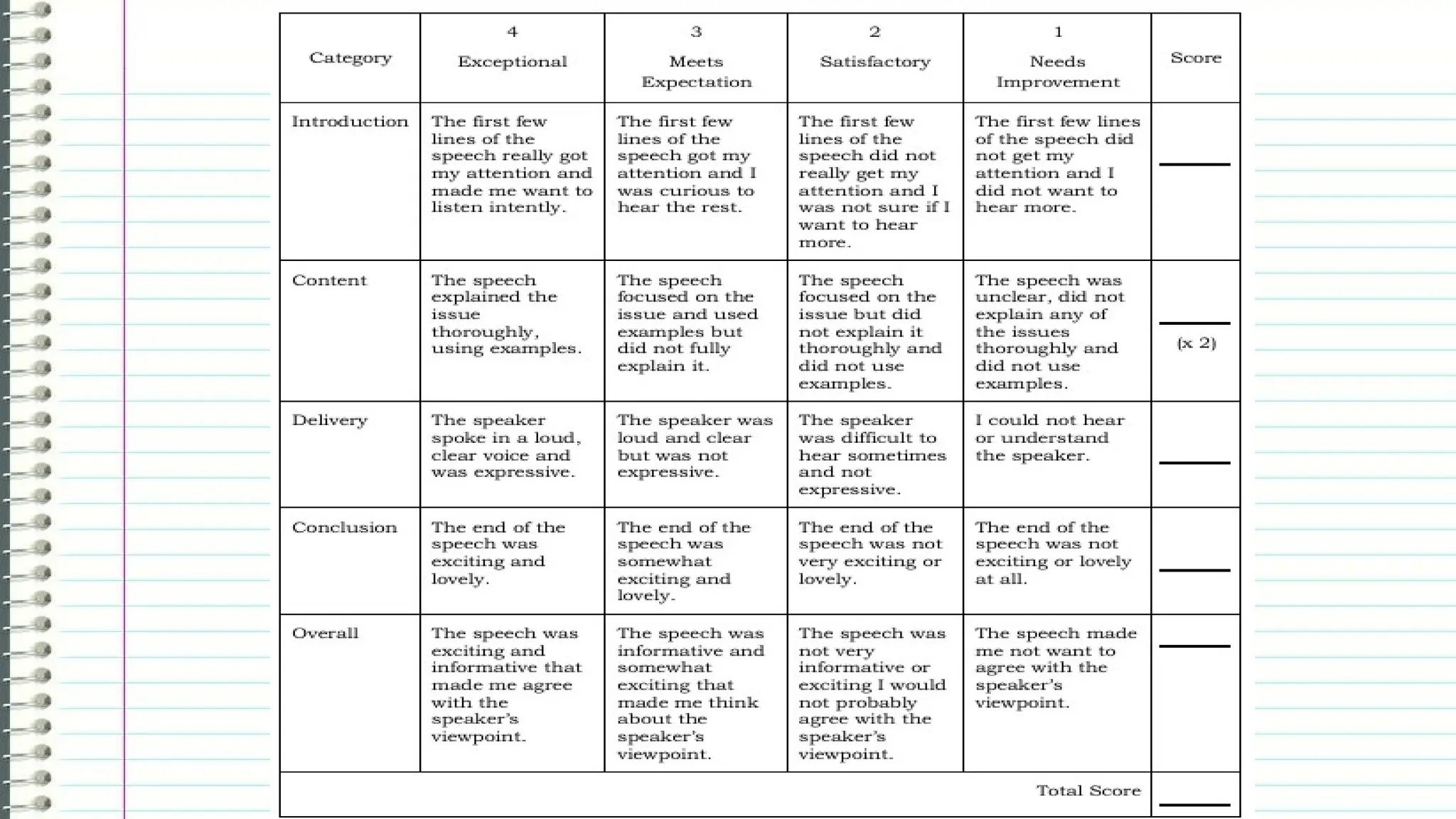
The document outlines the different types of speeches categorized by purpose: informative, persuasive, and entertaining, along with ways to deliver them, including impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized forms. It emphasizes the importance of speeches as formal communications meant to convey significant messages. Additionally, it encourages learners to practice delivering their own speeches, particularly in a life coaching context, to assist those affected by the COVID-19 pandemic.