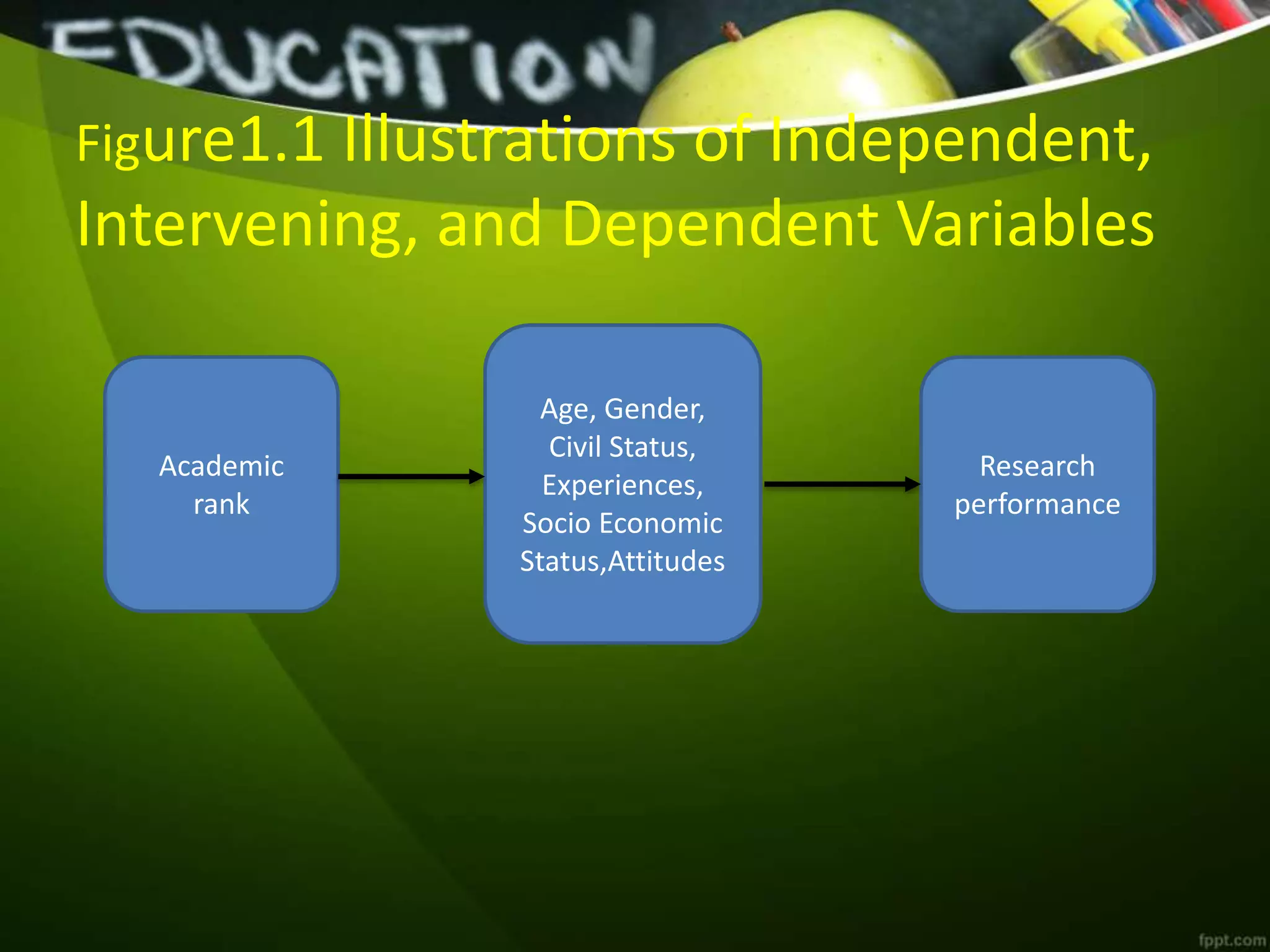
The document outlines various research methods, including basic, applied, and developmental research, as well as their classifications such as library, field, and laboratory research. It also defines variables (independent, dependent, moderator, control, and intervening) and describes the components of the research process, difficulties encountered, characteristics of good research, and qualities of a good researcher. Key elements include the importance of empirical and analytical approaches in research, along with traits such as efficiency and creativity.