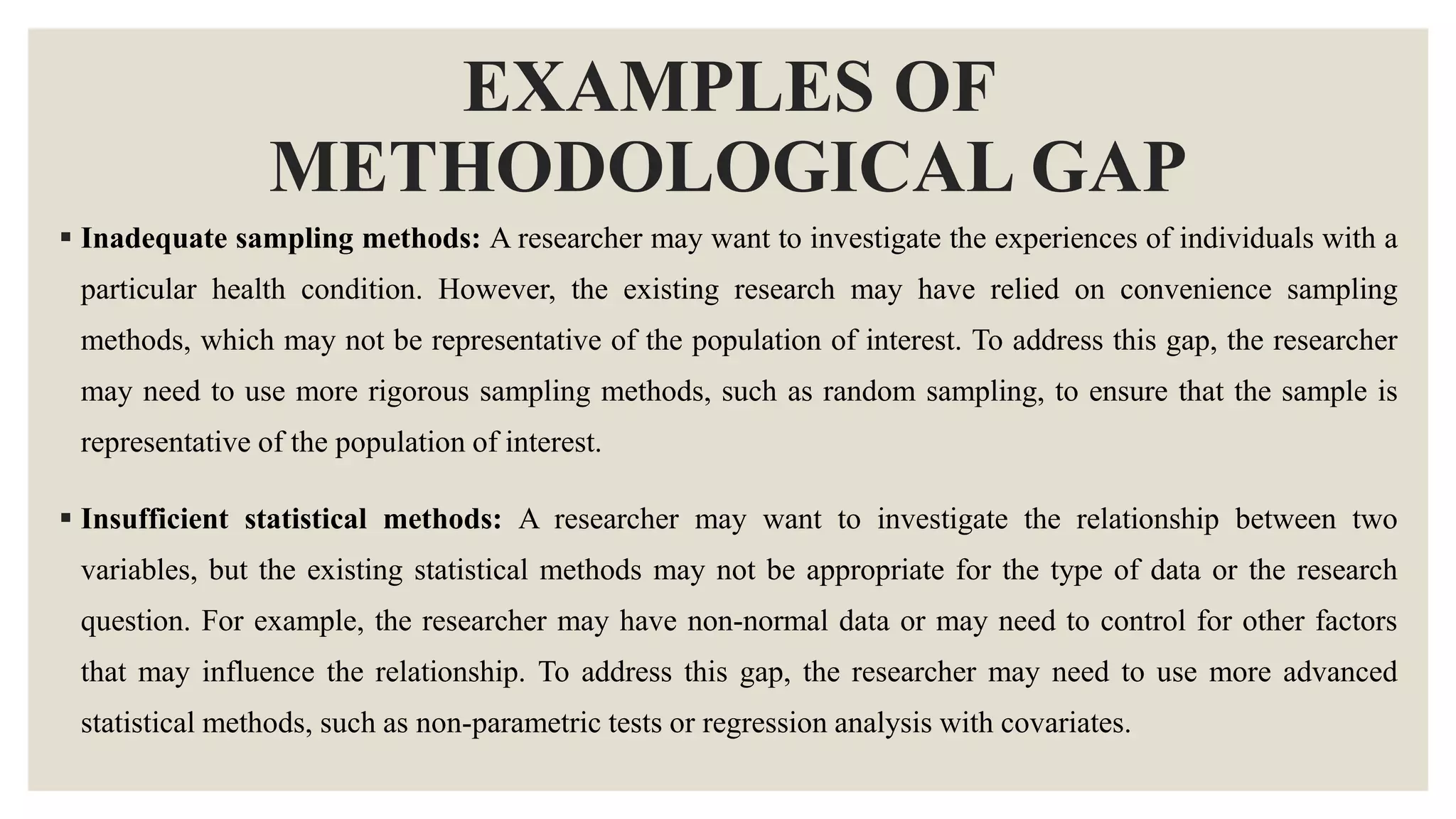
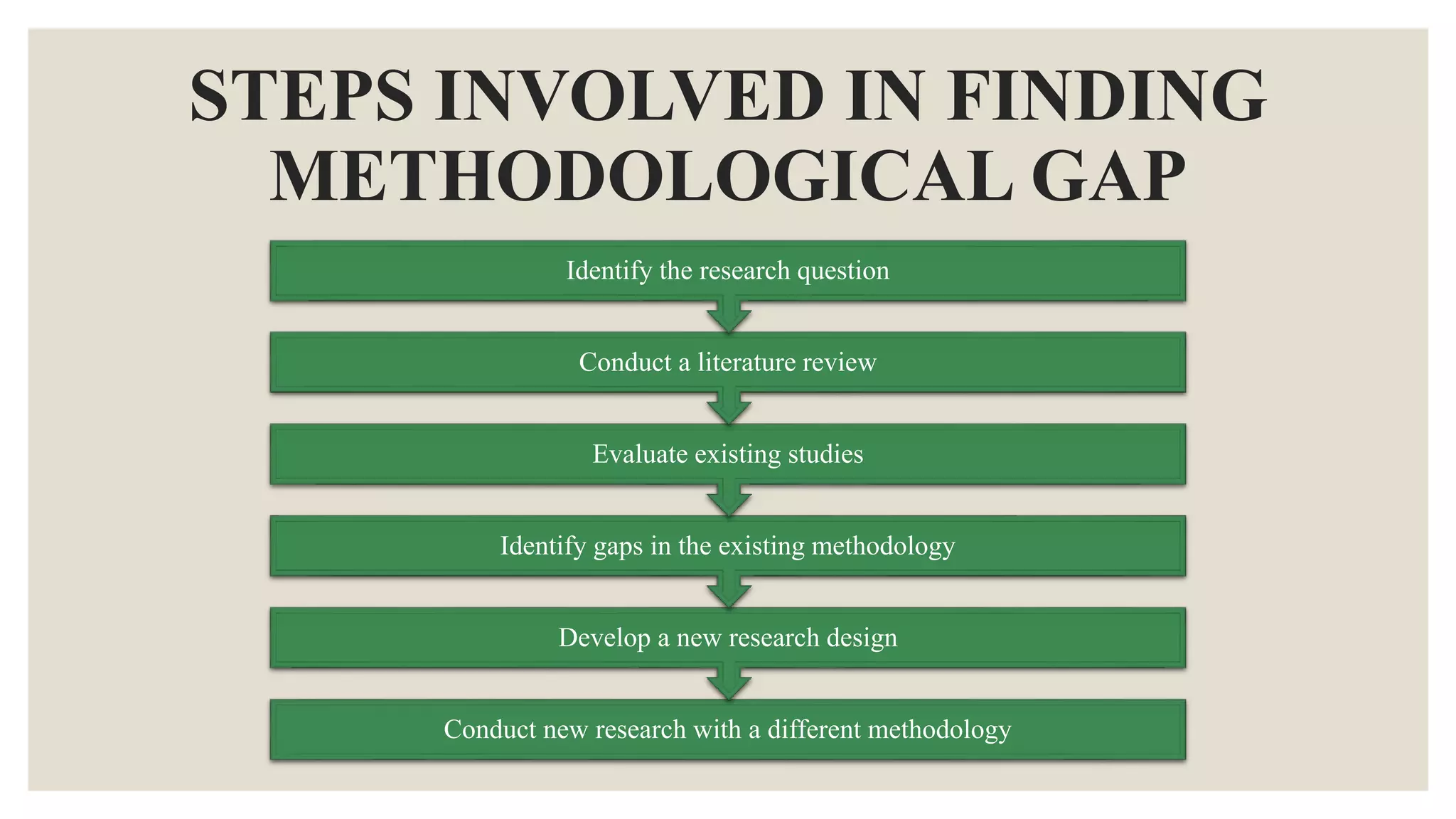
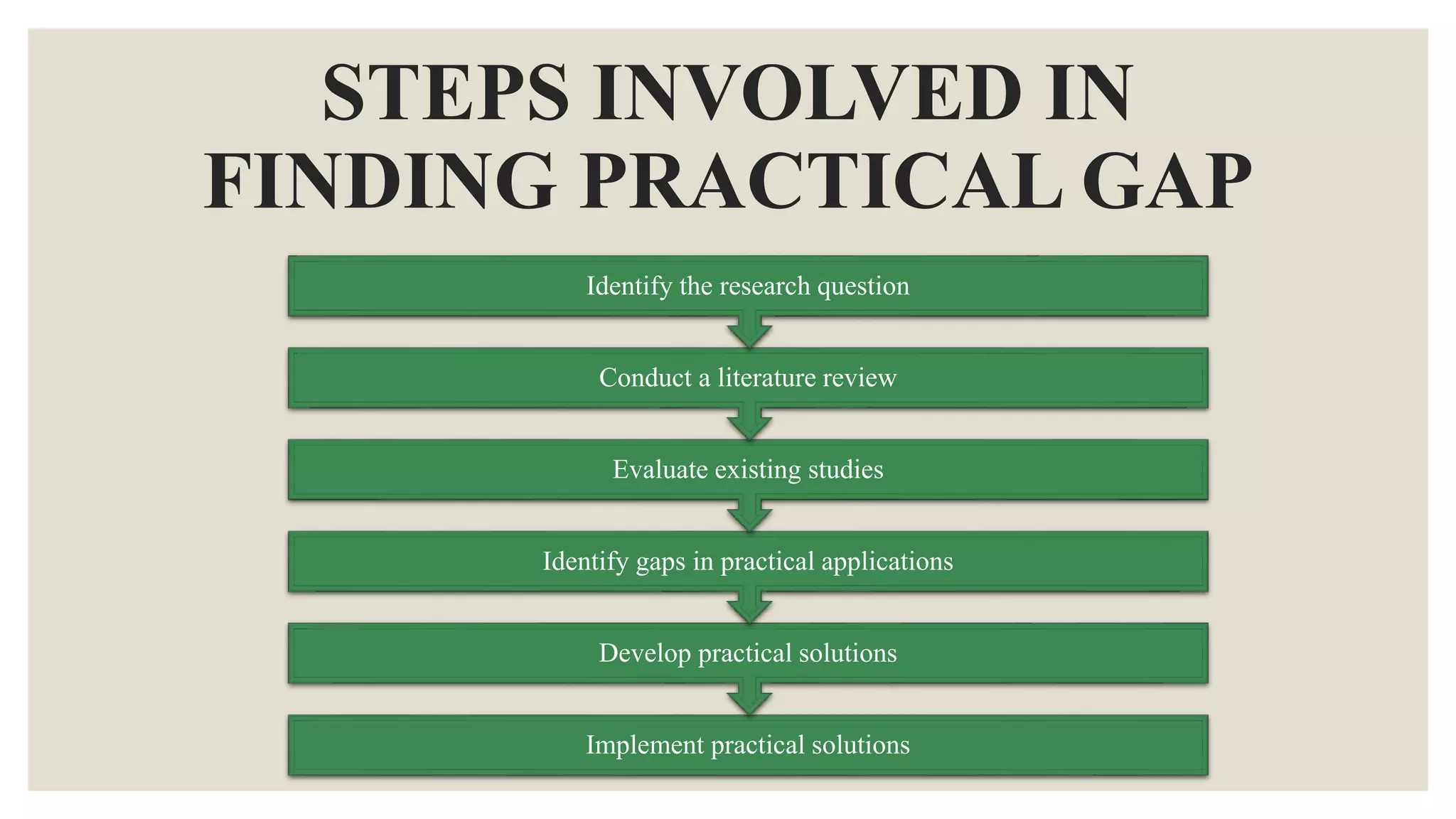
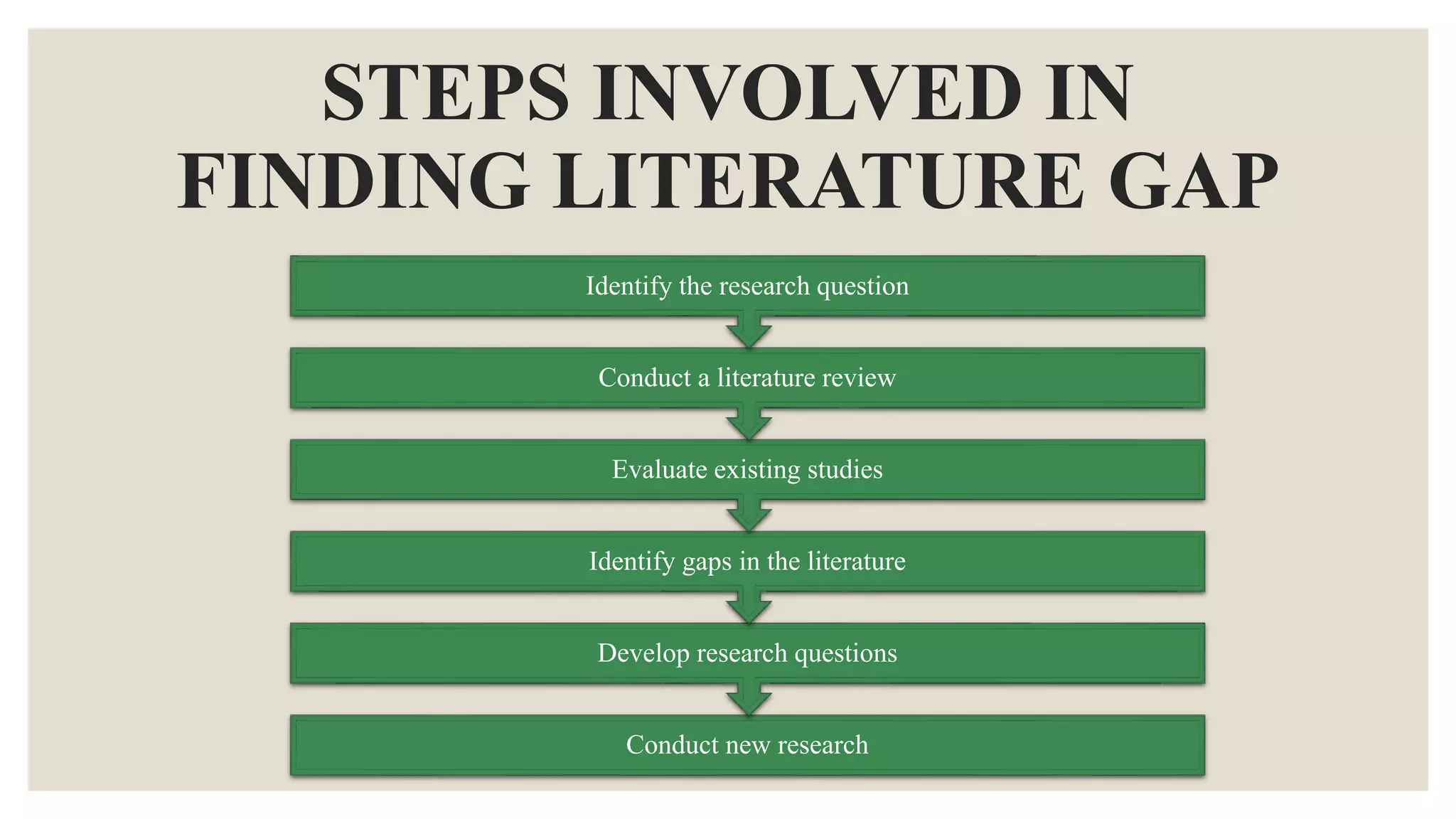
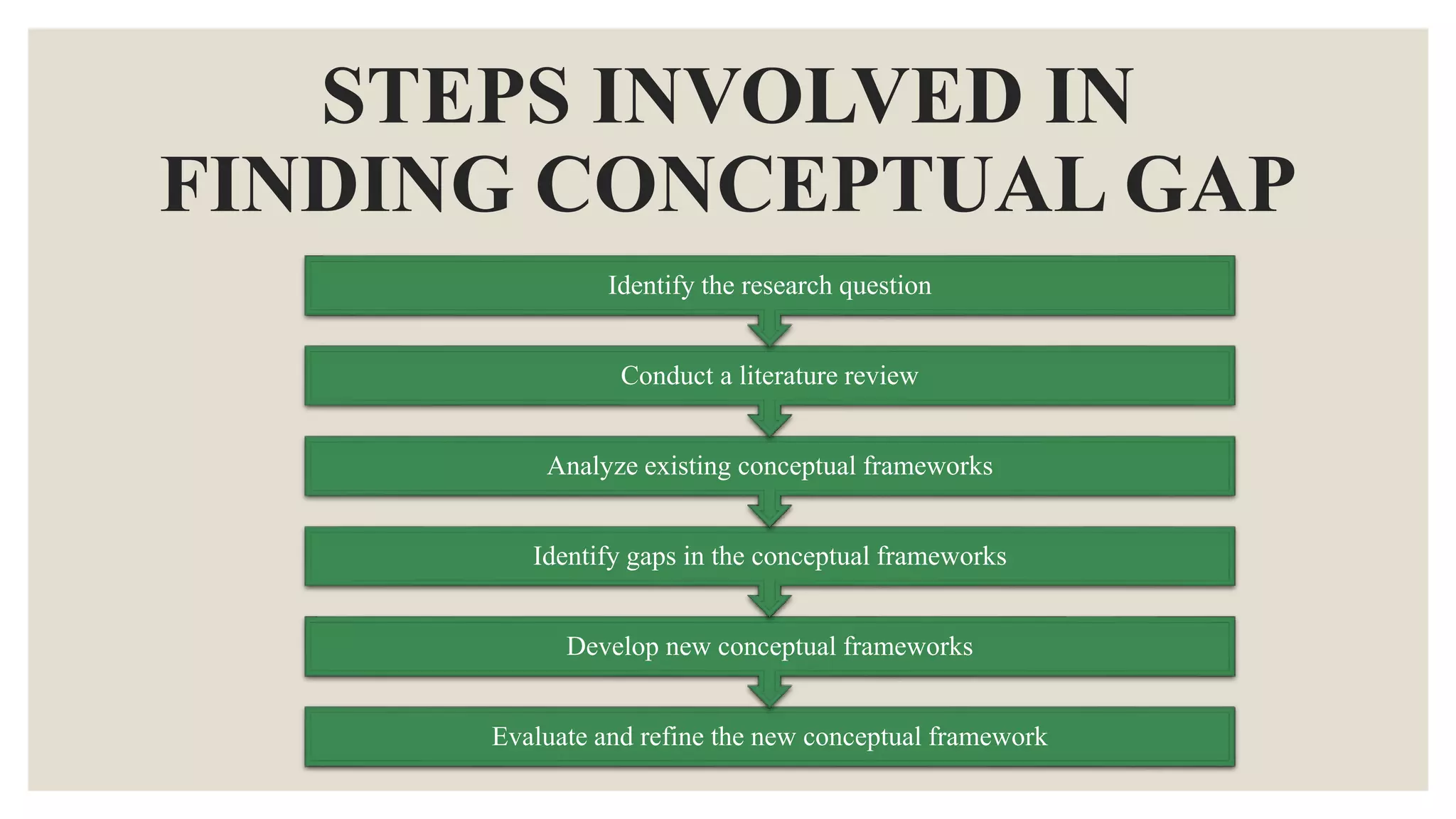
This document discusses different types of research gaps. It begins by defining a research gap as a missing or insufficient area of knowledge that has been identified through a literature analysis. Some common types of research gaps are then outlined, including theoretical, empirical, methodological, practical, literature, historical, cultural, and conceptual gaps. Each type of gap is defined and examples are provided. The document then goes on to discuss theoretical, empirical, and methodological gaps in more depth, providing definitions, examples, and steps to identify these specific types of gaps. In summary, the document categorizes and explains different types of research gaps to help researchers identify gaps in existing knowledge.