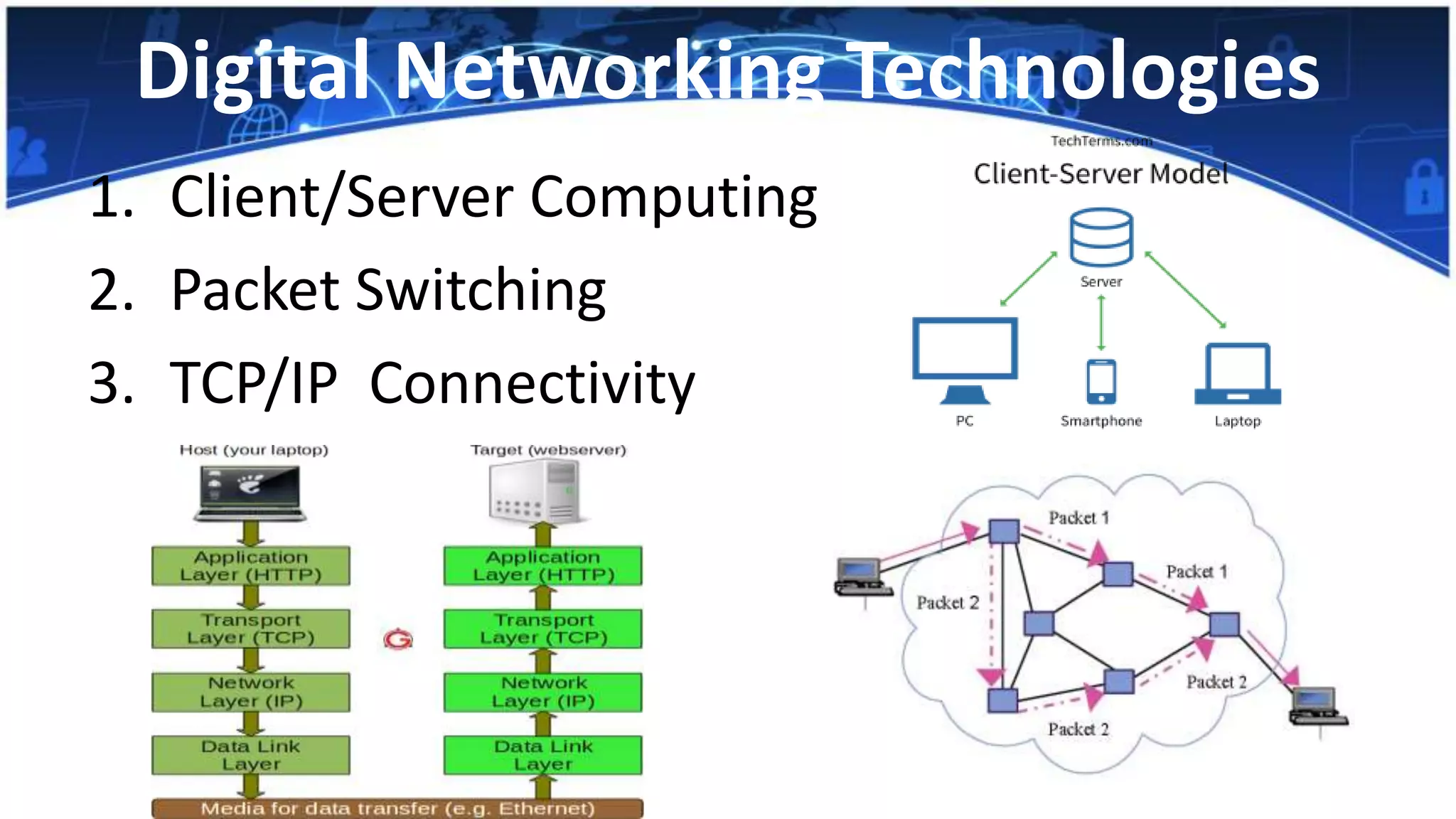
This document discusses different types of computer networks. It describes local area networks (LANs) that connect devices within a single building, wide area networks (WANs) that connect devices over longer distances, and other network types like campus area networks, metropolitan area networks, and home area networks. The document also discusses networks defined by their purpose, such as storage area networks, enterprise private networks, and virtual private networks. Large companies are described as using hundreds of interconnected LANs along with intranets, extranets, and other technologies. The document concludes that network connectivity, speed, and security will continue increasing significantly in the future.