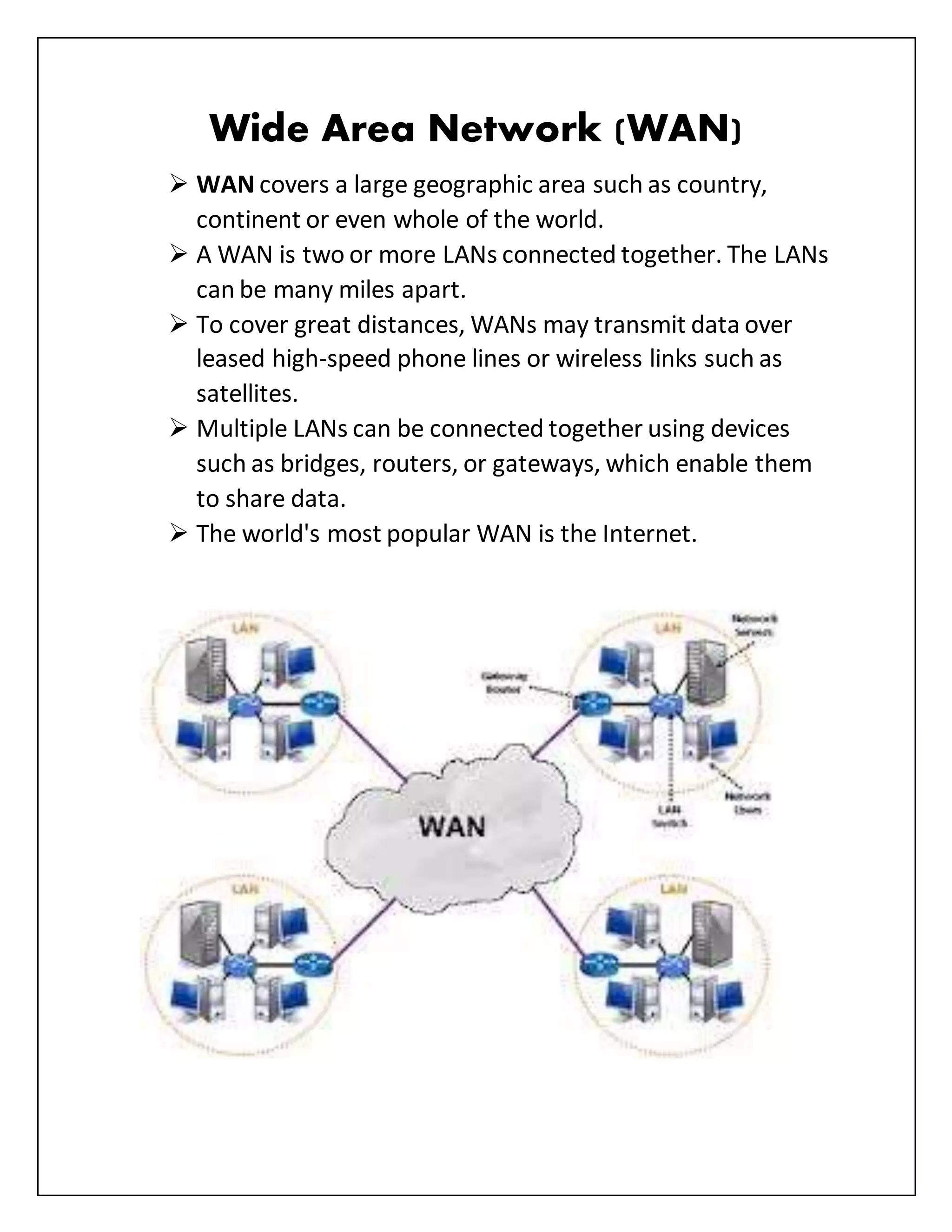
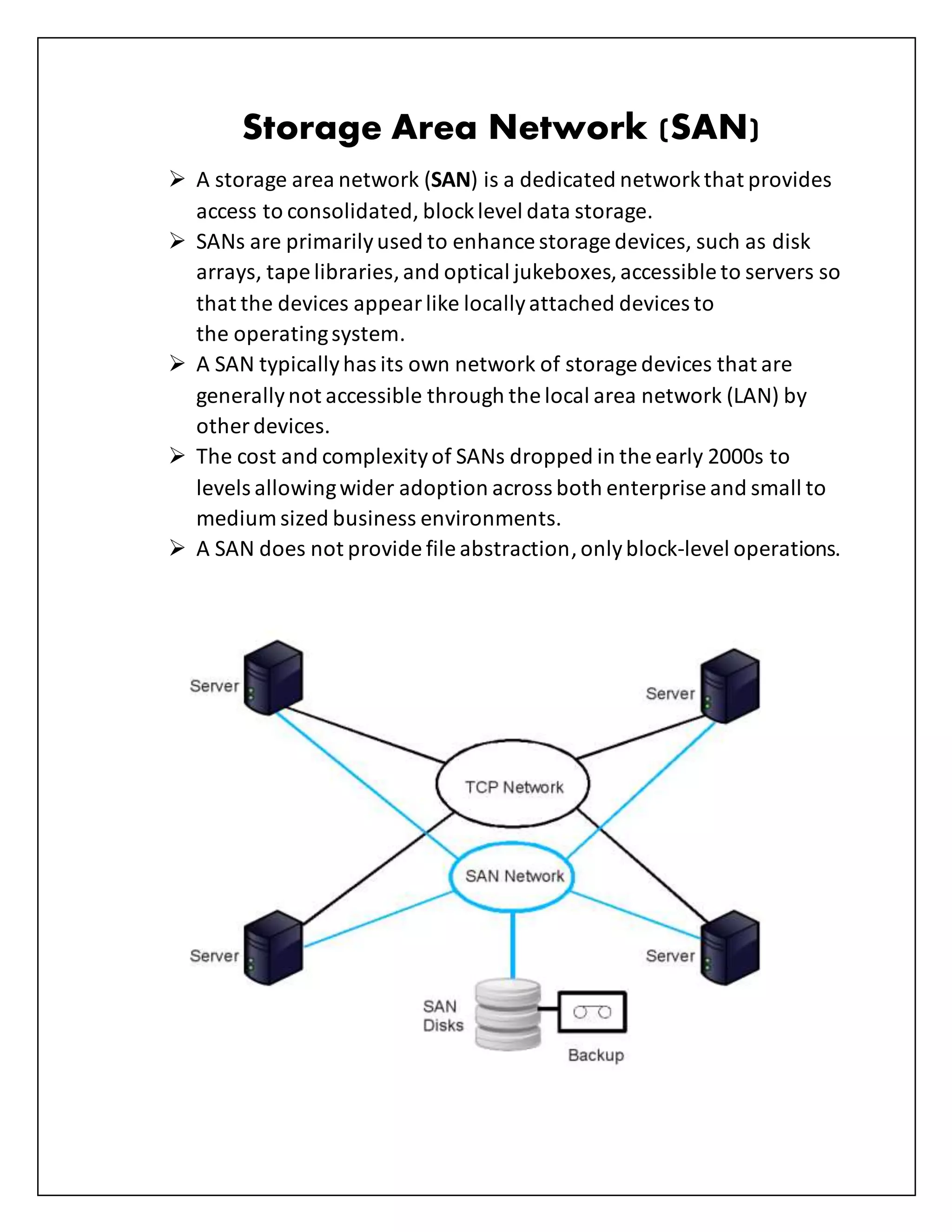
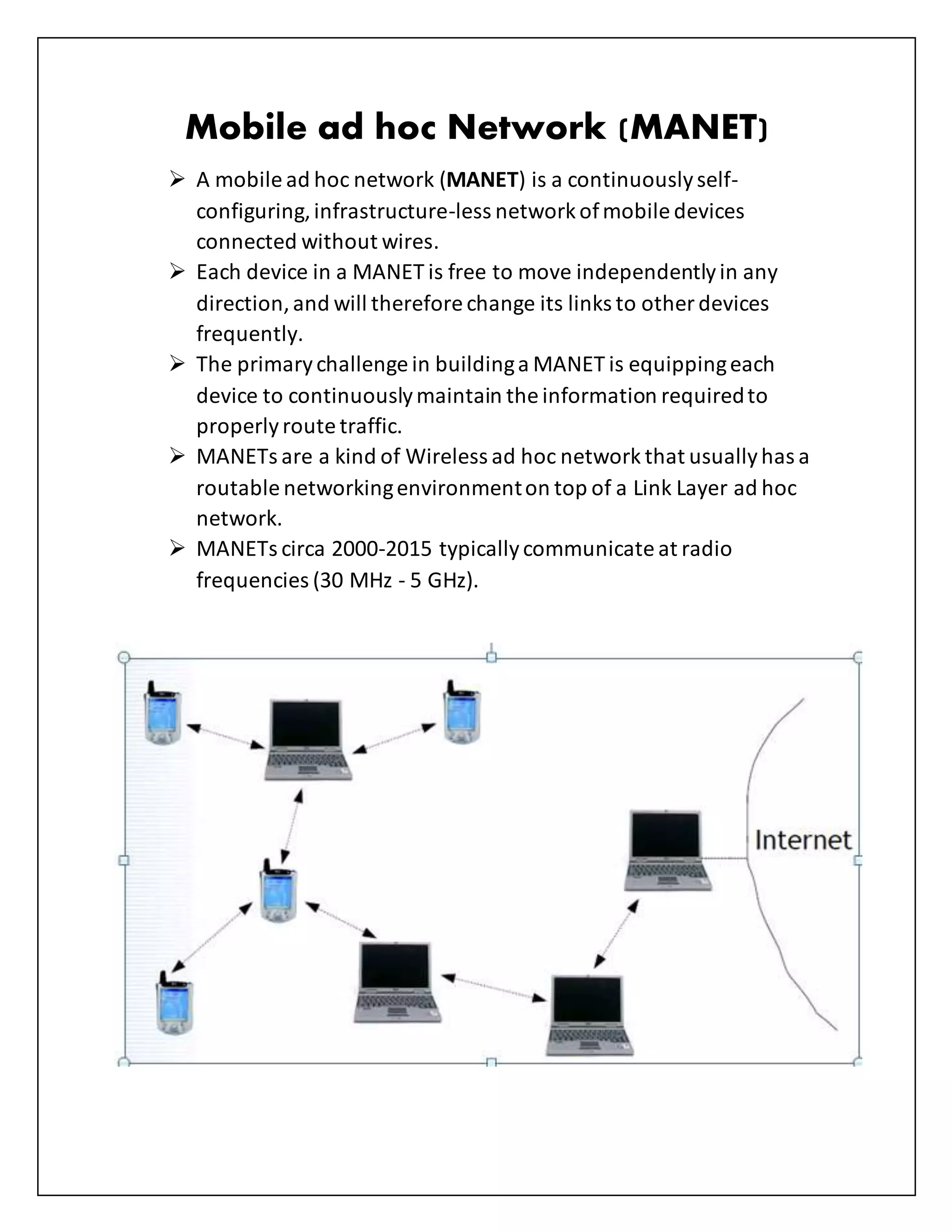
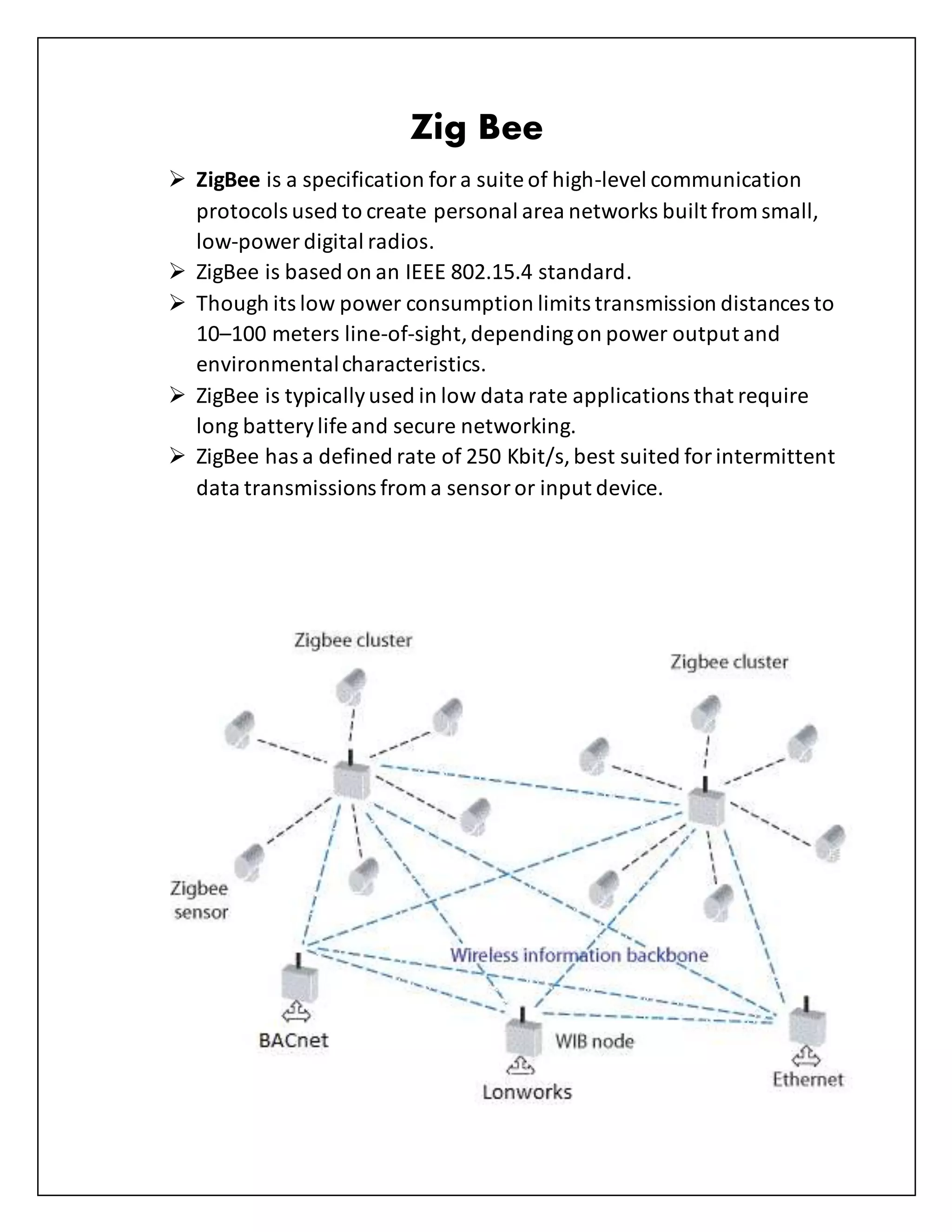
This document defines and describes several types of computer networks:
- Local Area Networks (LANs) connect devices within a small geographic area like a home or office building. Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) span larger areas like a city or campus. Wide Area Networks (WANs) can connect LANs over long distances, even worldwide.
- Personal Area Networks (PANs) connect devices in close proximity, within a few meters. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs) allow devices to connect within a LAN via wireless transmission. Storage Area Networks (SANs) provide block-level data storage access.
- Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) are infrastructure-less networks