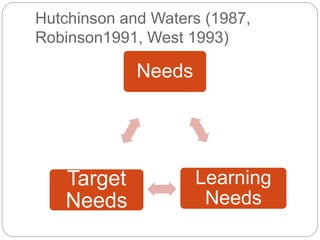
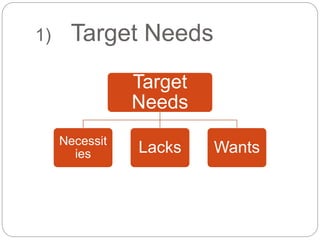
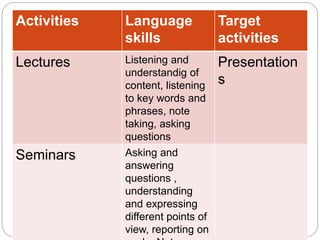
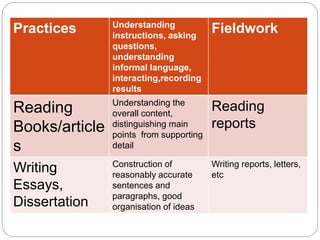
This document discusses different types of needs that should be considered when developing an English for Specific Purposes course, including target needs, learning needs, and constraints. Target needs refer to the language requirements of learners' target situations and include necessities, lacks, and wants. Learning needs involve determining how learners will meet the target needs through considerations like course format, materials, and learner characteristics. Constraints refer to non-pedagogical limits on course planning, such as policies and budgets. A thorough needs analysis considers all of these factors to design a course that addresses learners' language requirements and learning process.