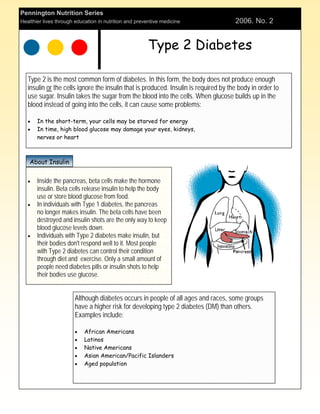
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or ignores the insulin produced. Left untreated, high blood glucose can damage organs. The document summarizes diabetes complications like hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, their causes and treatments. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels to control diabetes and prevent related health issues.