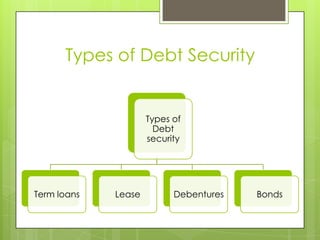
This document provides an overview of different types of debt securities including term loans, leases, debentures, and bonds. Term loans are monetary loans repaid with regular payments over a set time. Leases are contractual agreements where one party owns an asset and allows another party to use it for a period in exchange for periodic payments. Debentures are debt instruments issued by companies that offer to pay interest on borrowed money. Bonds are debt investments where an investor loans money to an entity for a defined period at a fixed interest rate.