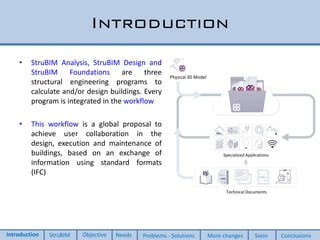
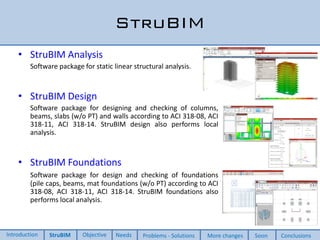
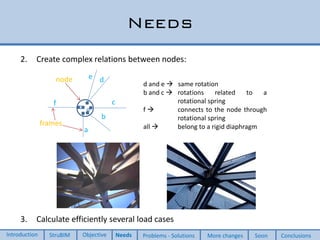
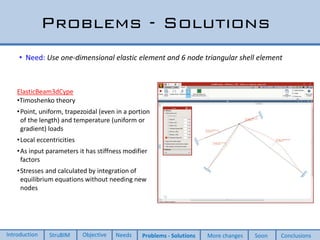
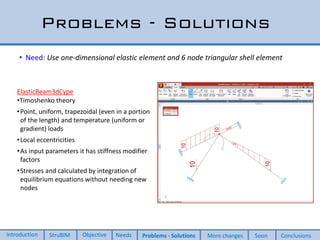
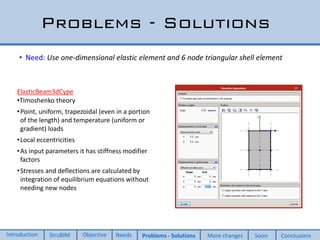
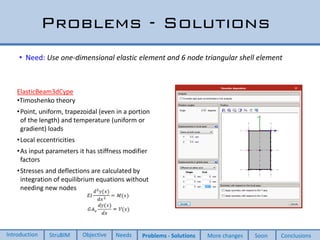
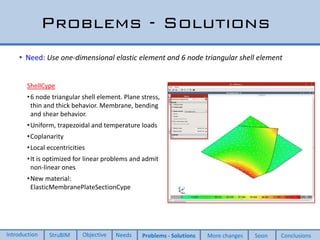
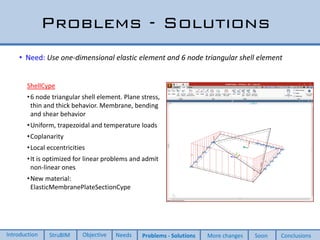
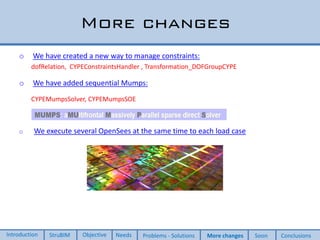
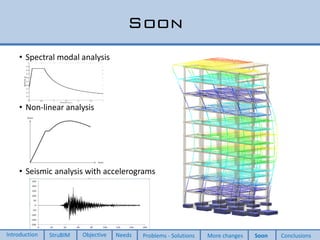
This document discusses two new elements added to OpenSees for structural analysis. The first is an ElasticBeam3dCype element that uses Timoshenko beam theory and can apply various load types and account for eccentricities. The second is a ShellCype element that is a 6-node triangular shell element capable of membrane, bending, and shear behavior under different load cases. The additions also include a new constraint handler and implementation of sequential MUMPS to allow OpenSees integration into BIM workflows and perform dynamic nonlinear analysis in the future.