This document provides contact details for Nangati T. Marshal and an overview of a lecture on production possibilities and opportunity costs. It includes:
1) Contact information for Nangati T. Marshal including email and phone number.
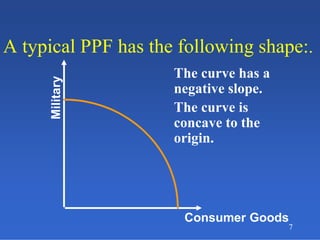
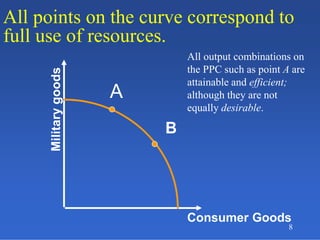
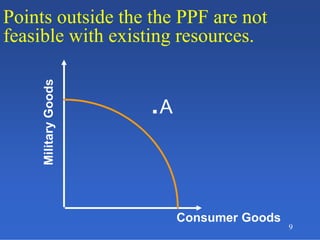
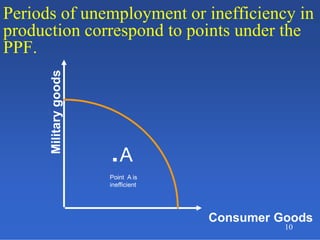
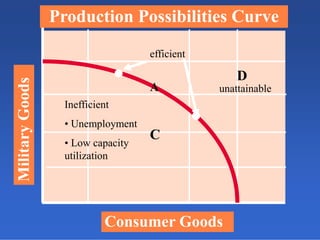
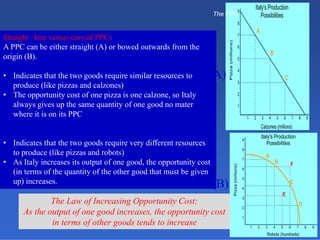
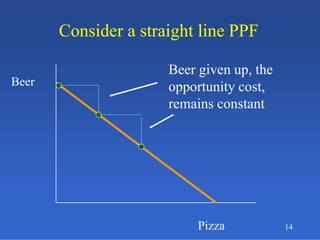
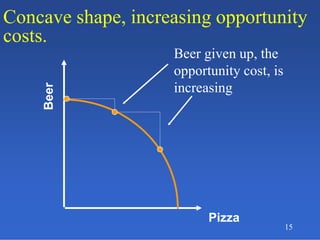
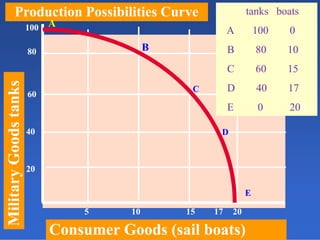
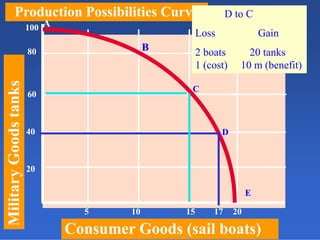
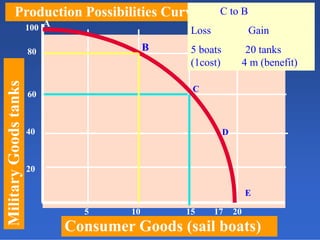
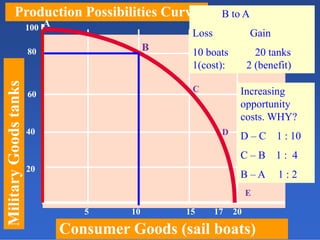
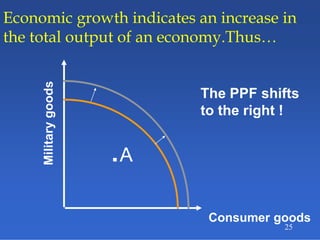
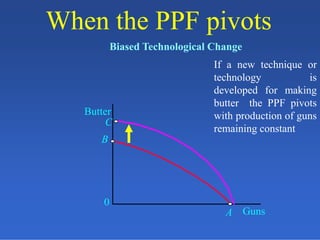
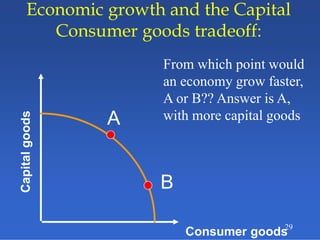
2) An introduction to the production possibilities frontier (PPF) as a graph showing the maximum combinations of goods that can be produced with limited resources.
3) Assumptions made in the PPF model including fixed resources, technology, and time period.