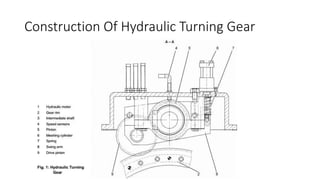
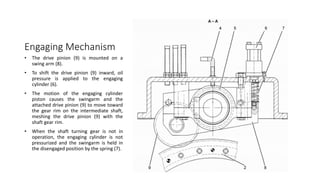
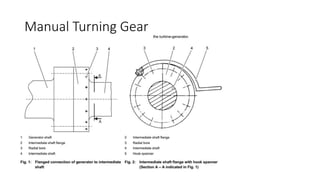
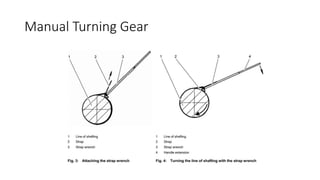
The document discusses shaft turning gear, which rotates the turbine shaft and other equipment at low speed after shutdown to ensure uniform cooling. This prevents issues like bending. It is also used to slowly break inertia during cold starts. There are two main types: hydraulic and manual. The hydraulic type uses a hydraulic motor supplied with lube oil to rotate the shaft at 120 rpm. It has an engaging mechanism that uses oil pressure to move a drive pinion into mesh with a gear rim to engage the turning gear. The manual type uses a hand-operated mechanism to manually rotate the shaft.