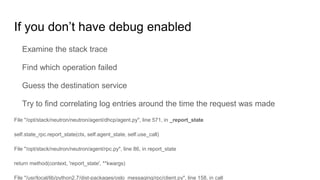
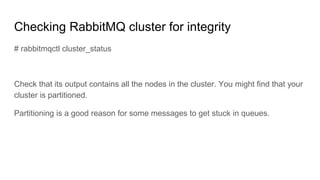
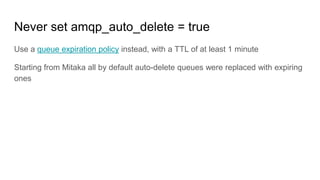
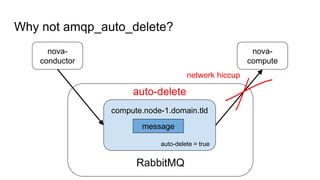
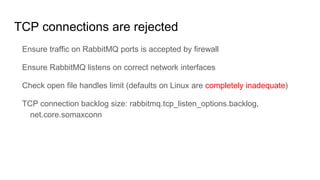
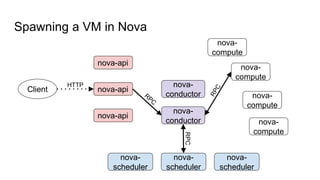
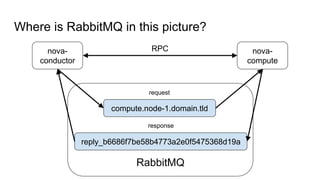
This document discusses common issues with oslo.messaging and RabbitMQ and how to diagnose and resolve them. It provides an overview of oslo.messaging and how it uses RabbitMQ for RPC calls and notifications. Examples are given of where timeouts could occur in RPC calls. Methods for debugging include enabling debug logging, examining RabbitMQ queues and connections, and correlating logs from services. Specific issues covered include RAM usage, unresponsive nodes, rejected TCP connections, TLS connection failures, and high latency. General tips emphasized are using tools to gather data and consulting log files.







![Spotting oslo.messaging logs
2016-04-15 11:16:57.239 16181 DEBUG nova.service [req-d83ae554-7ef5-4299-
82ce-3f70b00b6490 - - - - -] Creating RPC server for service scheduler start
/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/nova/service.py:218
2016-04-15 11:16:57.258 16181 DEBUG oslo.messaging._drivers.pool [req-
d83ae554-7ef5-4299-82ce-3f70b00b6490 - - - - -] Pool creating new connection
create /usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/oslo_messaging/_drivers/pool.py:109](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/austinsummit-oslo-160427202022/85/Troubleshooting-common-oslo-messaging-and-RabbitMQ-issues-11-320.jpg)





![Enabling the debug
[DEFAULT]
debug=true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/austinsummit-oslo-160427202022/85/Troubleshooting-common-oslo-messaging-and-RabbitMQ-issues-17-320.jpg)
![Enabling the debug
[DEFAULT]
debug=true
default_log_levels=...,oslo.messaging=DEBUG,...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/austinsummit-oslo-160427202022/85/Troubleshooting-common-oslo-messaging-and-RabbitMQ-issues-18-320.jpg)