Asexual Reproduction in Plants: 6 Types Explained in 40 Characters
- 1. Asexual Reproduction in Plants
- 2. Asexual Reproduction in Plants 1. Involves only one parent, 2. Does not involve seeds or the fusion of gametes 3. Instead part of a plant’s stem, leaves or roots can become new plants, 4. Produces offspring / clones genetically identical to the parent, 5. Allows plants to be produced much faster then sexual reproduction. There are six types of a sexual reproduction. They are: 1) fission 2) budding 3) spore formation 4) regeneration 5) fragmentation 6) vegetative propagation
- 3. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS Fission Budding Spore formation Regeneration Fragmenta tion Vegetative propagation Multiple Fission Binary Fission BudLeafRootStem BulbRhizomeTuberRunner
- 4. There are two types Fission : In fission, unicellular organism splits to form new organisms. It is a process of reproduction in organisms such as protozoa and many bacteria. Binary Fission: In binary fission, the parent cell divides into two after reaching a point where it has fully grown. In this process, after splitting parent cell do not exist and two new organisms are formed. Examples of unicellular organisms that undergo binary fission are amoeba, paramecium, Leishmania etc.
- 5. Multiple Fission: Multiple fission is also a process of asexual reproduction in which parent cell splits to form many new organisms. This happens when cyst is formed around a unicellular organism. Inside this cyst the nucleus of an organism breaks in many smaller nuclei. When the favorable conditions come, the cyst breaks and the many daughter cells inside it are released. Plasmodium
- 6. Budding: The word bud means small outgrowth. In the process of budding, a small bud grows on the body of parent organism and when the time comes it detaches itself to form a new organism. Hydra and yeast undergoes the process of budding. Hydra reproducing by the method of budding. Yeast reproducing by the method of budding.
- 7. •Spore formation The method of spore formation occurs in both unicellular and multi-cellular organisms. This process takes place in plants. In spore formation, the parent plant produces hundreds of reproductive units called spores in its spore case. When this spore case of the plant bursts, these spores travel in air and land on food or soil. Here they germinate and produce new plants. EX: Fungi like Rhizopus, Mucor, etc., are examples of spore formation.
- 8. Regeneration Regeneration is an asexual method of reproduction. In this process, if the body of a parent organism gets cut, then each cut part can regenerate and form a whole new organism from its body parts. This happens because when the body of an organism that can undergo regeneration gets cut then the cells of cut body part divide rapidly and form a ball of cells. These cells then move to their proper places to form organs and body parts. Regeneration occurs in both plants and animals. EX: Hydra and planaria undergo regeneration. Regeneration in Planeria.
- 9. •Fragmentation Fragmentation occurs in multicellular organisms, be it plants or animals. In this process the multicellular organism breaks into two or more pieces on maturation. Each piece than grows into a new organism. Spirogyra which is a plant and sea anemones which is a sea animal undergoes the process of fragmentation.
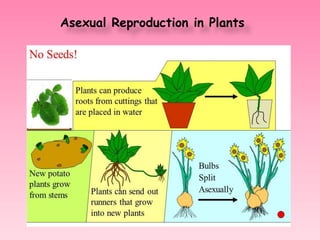
- 10. Vegetative Propagation: Vegetative propagation is a type of sexual reproduction in which the 1. Stems (Runner, tuber, rhizome and &bulb) 2. Roots, 3.Leaves 4.Buds give rises in to new plant. These are also called vegetative parts of the plants.
- 11. 1. Modified Stems (a) Runners • Horizontal stem which grows or runs over the soil surface. • The terminal bud sends up new shoots & down new roots from it. Ex: Strawberries
- 12. B. Rhizomes- Modified stems that grow under the soil, produce new roots from stem. Ex- Grasses
- 13. C. Tubers-: shorter, thicker stems that produce an “eye” which is capable of producing a new plant. Ex-Potato
- 14. D. Bulbs: Stem covered with modified leaves which can produce a new plant. Ex: Onion E. Food Storing Roots Roots which are capable of producing a new plant Ex: carrots & beets
- 15. 3. Modified Leaves • Some plants produce Plantlets along the edges of the leaves. • When they reach a certain size, they fall off and grow into new plants. Ex: Cacti
- 16. 4. Modified Buds Bulbs : A bulb (an underground bud) has a reduced stem, roots, fleshy leaves swollen with stored food and a main bud in the centre which grows into a new plant Ex: Onion, Daffodil, Tulip
- 17. Vegetative Propagation Artificial Method of Asexual reproduction most used in agriculture 1. Cuttings- pieces of stem cut from parent kept in water, moist soil or sand Will put out new roots. Ex:-Many garden plants like
- 18. Grafting- Buds or sections are cut from one plant is attached to another that is already rooted in the soil. Ex- Roses, Fruit Trees
- 19. 3. Layering : A branch of a plant is bent over and pinned down into the soil at a node. It is covered over with soil & eventually new roots & shoots develop useful for the propagation of woody plants. Ex: blackberry, gooseberry.
- 20. 4.Tissue culture- pieces of the center of stem are removed placed in flasks with growth medium a whole new plant will develop
- 21. Advantages of artificial vegetative propagation •The new plant will have exact features as that of parent plant. •Fruit trees grown by grafting bear fruit much earlier. •Plants need less attention in their early years. •Many plants can be grown from just one parent. •Can get seedless plants. Thank you, Nanditha Akunuri B.Sc, B.Ed, M.sc, M.A, M.Ed, (P.hD)
Editor's Notes
- 2. Rhizomes- modified stems that grow under the soil, produce new roots from stem. Ex- Grasses 3. Tubers- shorter, thicker stems that produce an “eye” which is capable of producing a new plant. Ex-Potato
