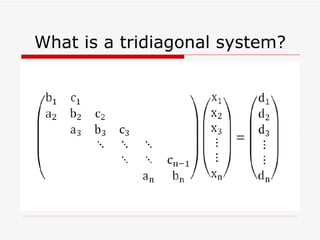
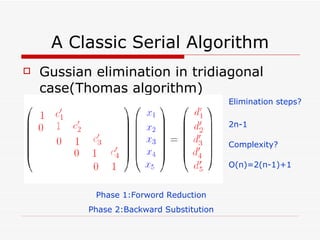
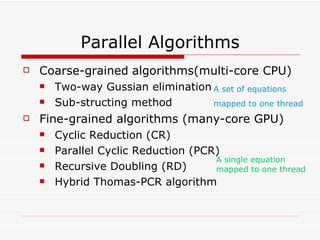
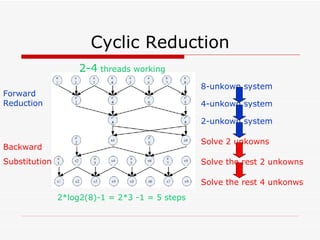
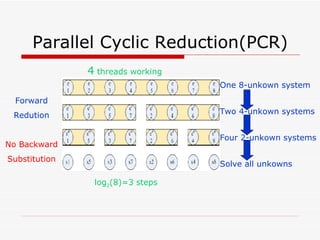
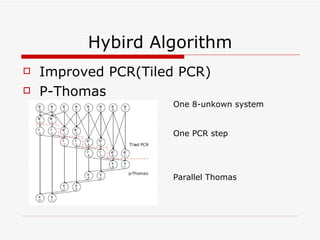
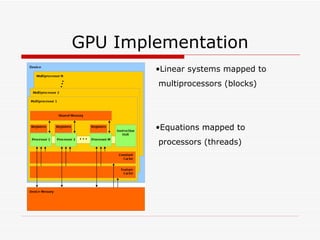
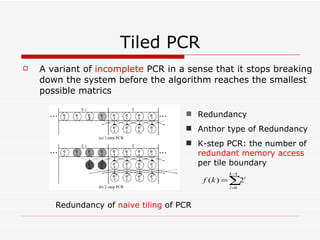
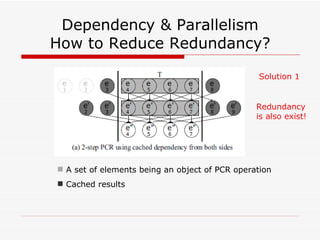
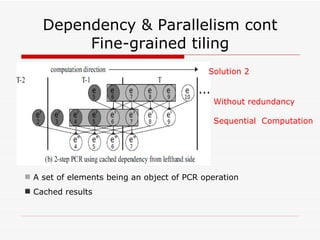
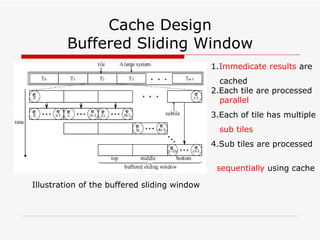
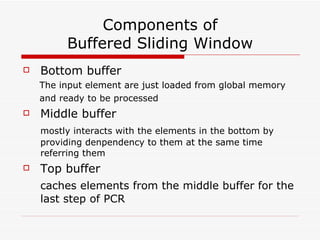
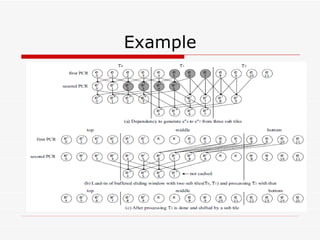
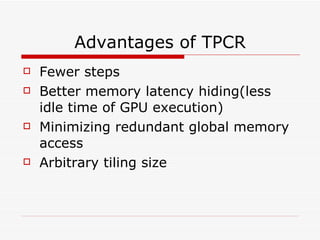
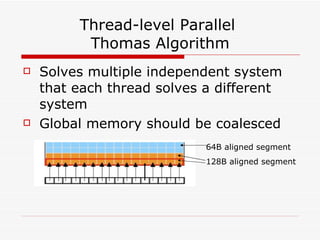
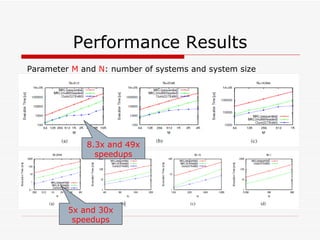
This document summarizes algorithms for solving tridiagonal systems on GPUs. It introduces classic serial and parallel algorithms like Gaussian elimination and cyclic reduction. It then presents a hybrid tiled parallel cyclic reduction (TPCR) algorithm that minimizes redundant memory access through caching. The TPCR algorithm is implemented and tested on a GPU, achieving speedups of 8.3x-49x over a CPU. Factors like cache size, memory access, and synchronization overhead determine the TPCR algorithm's performance.