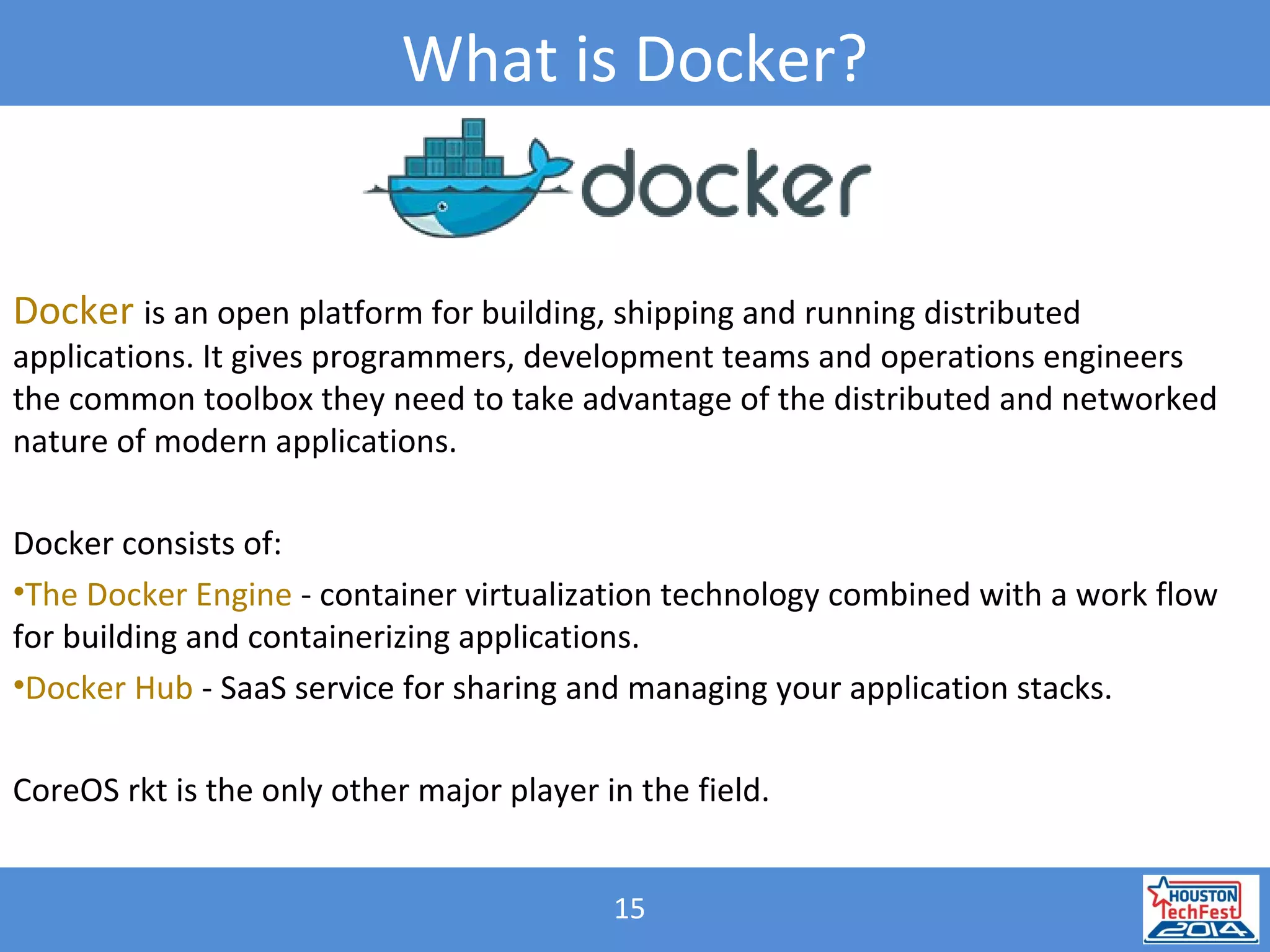
Lana Kalashnyk presented on transitioning to Java microservices on Docker. Key points included:
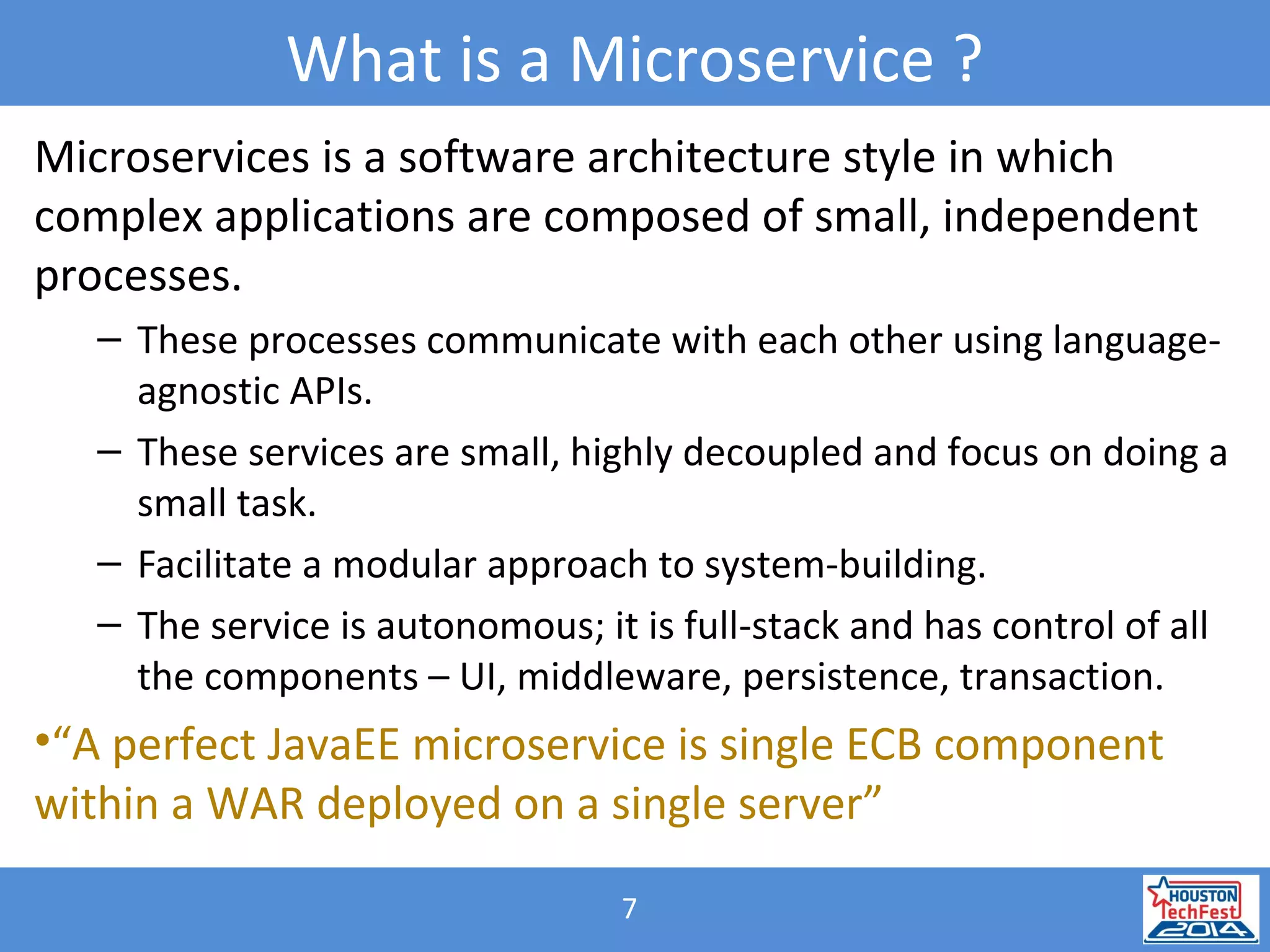
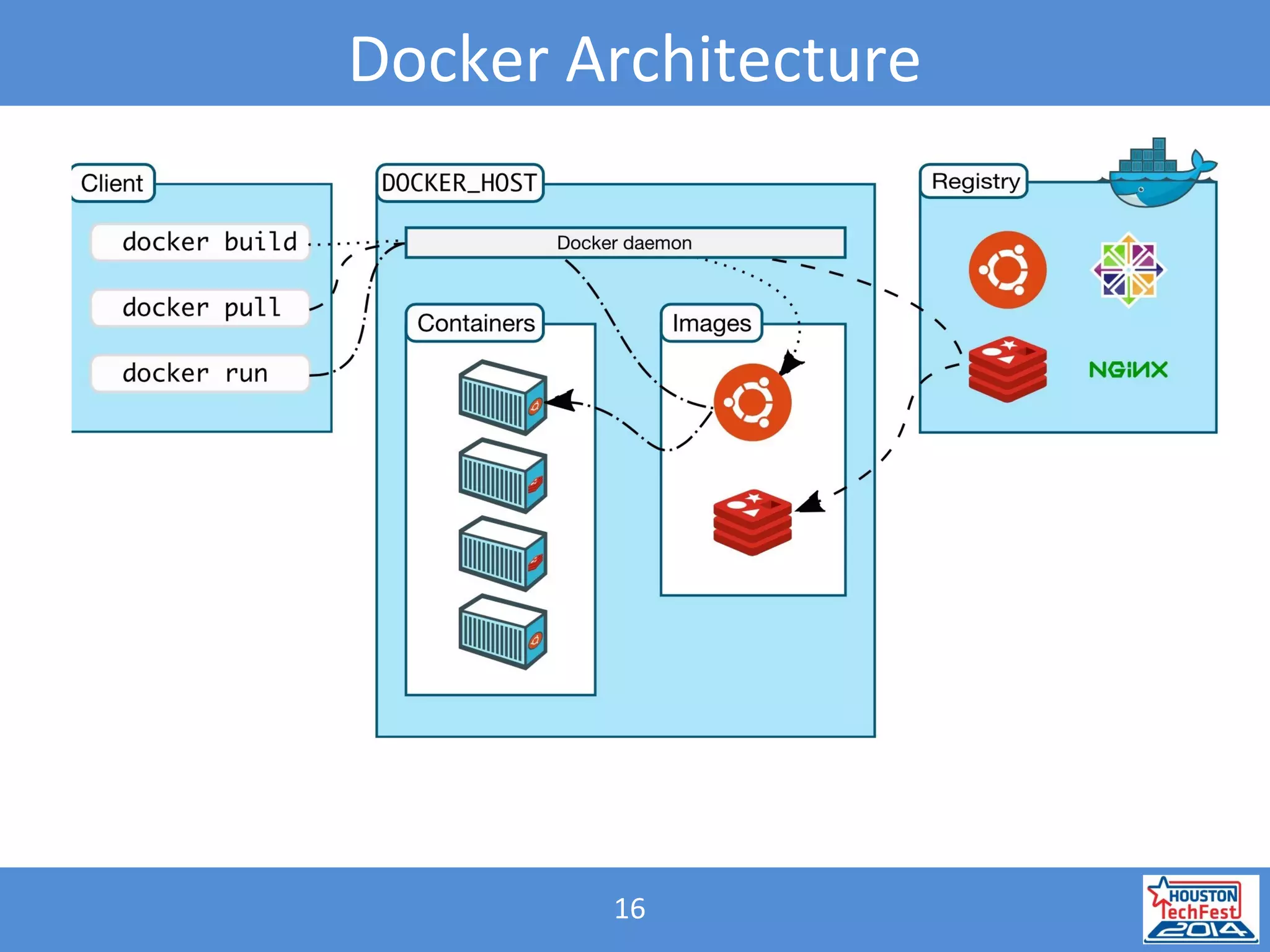
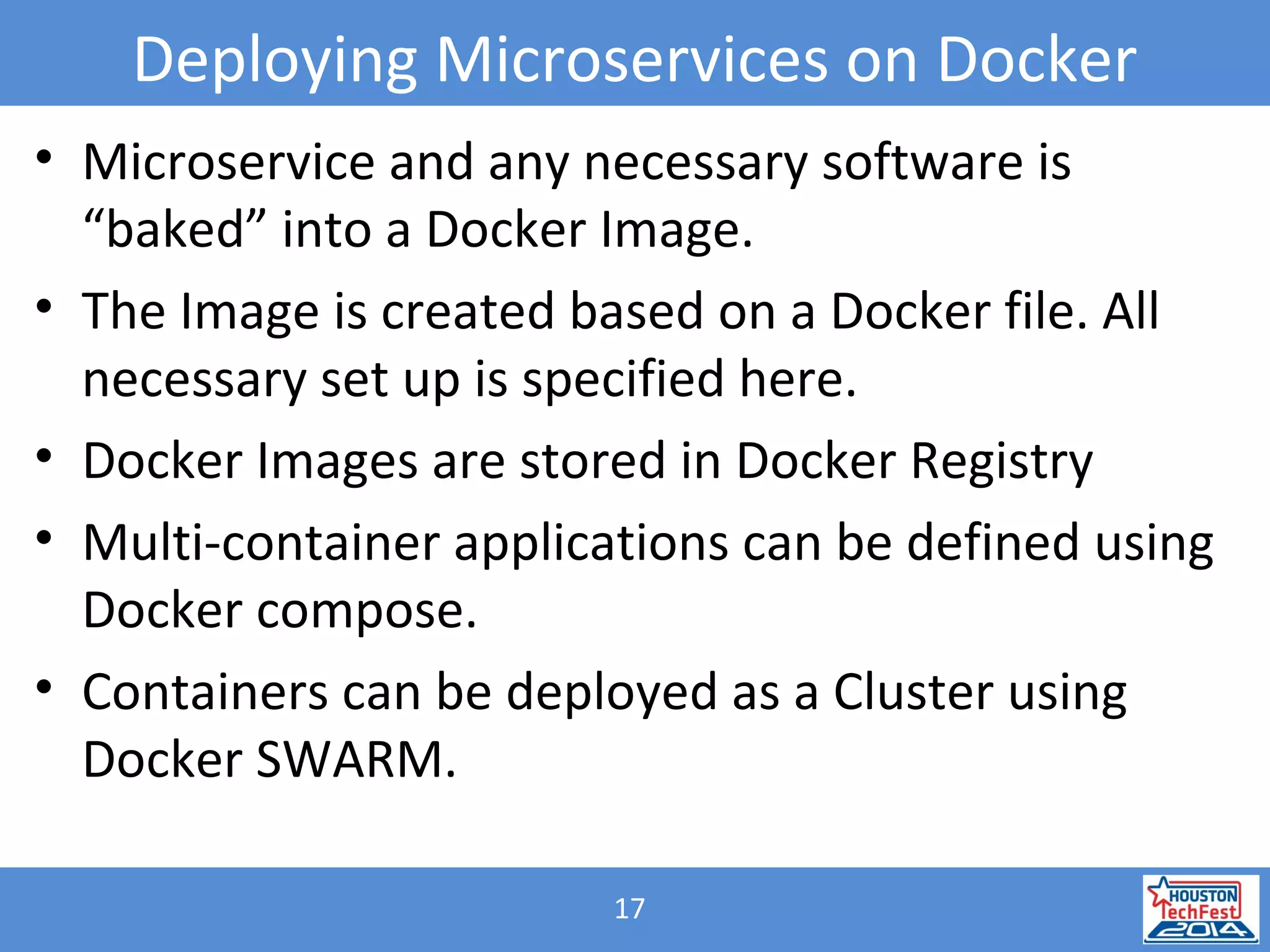
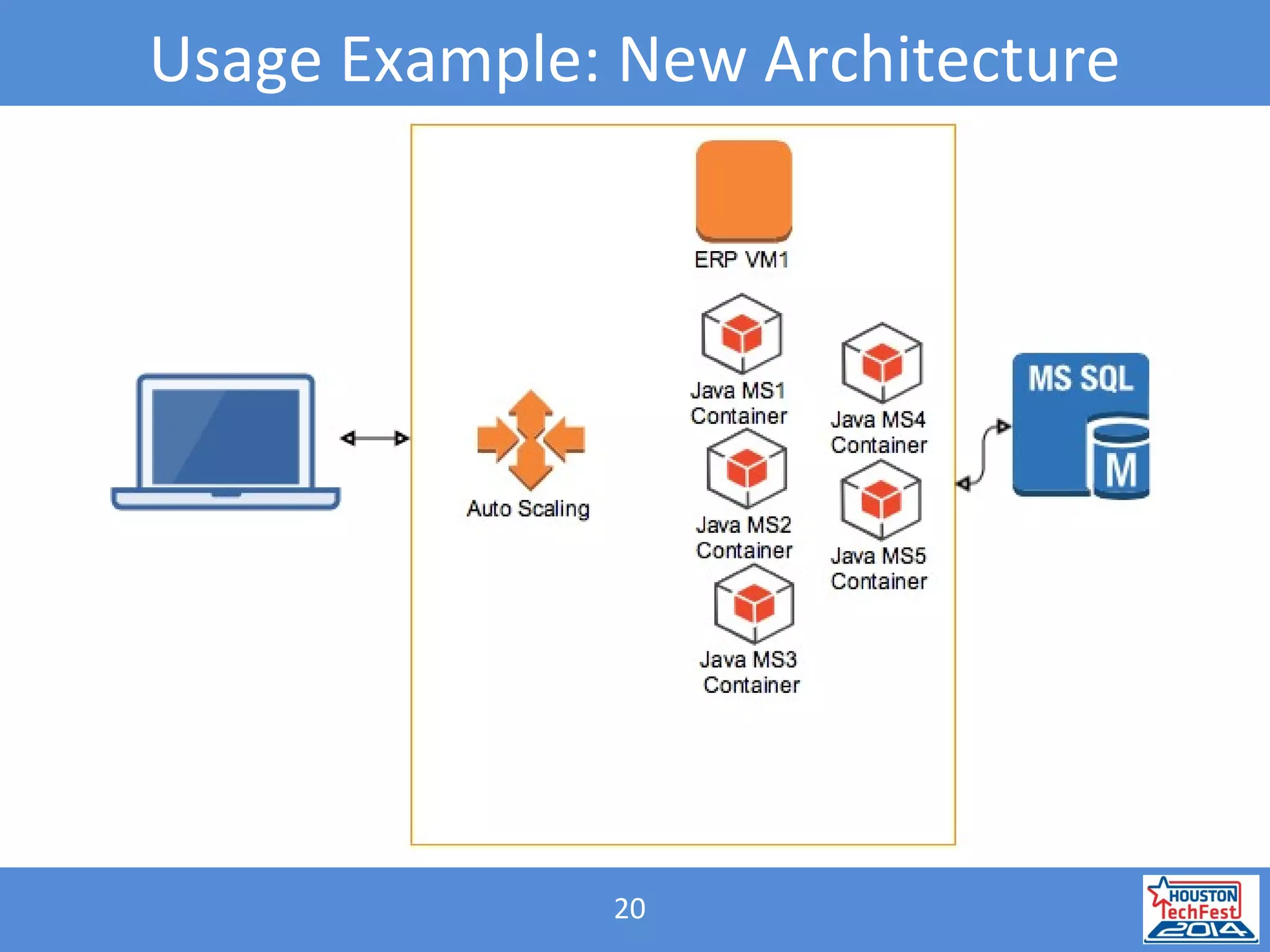
- Microservices involve breaking applications into small, independent services that communicate via APIs. Docker containers help deploy and manage microservices.
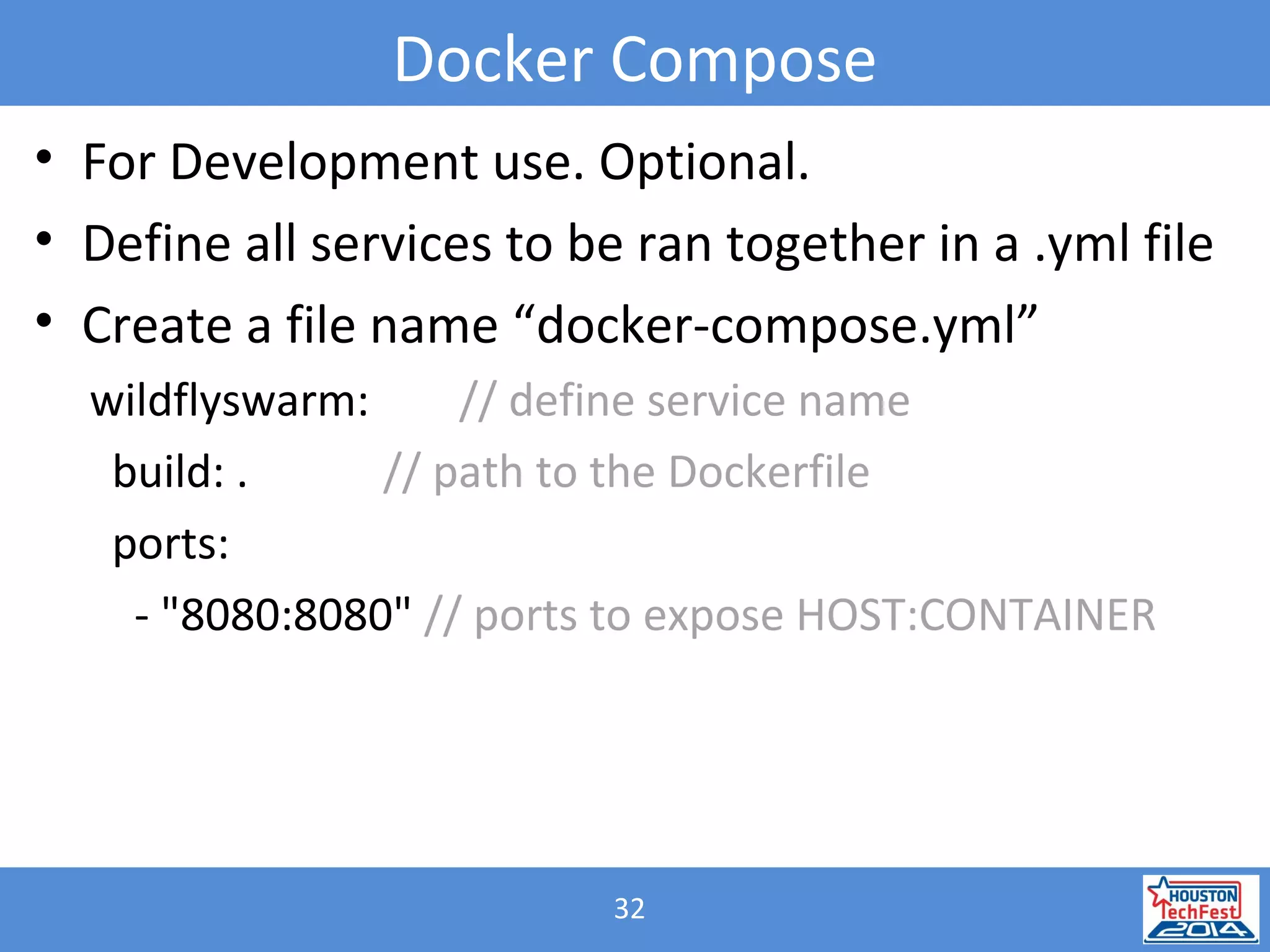
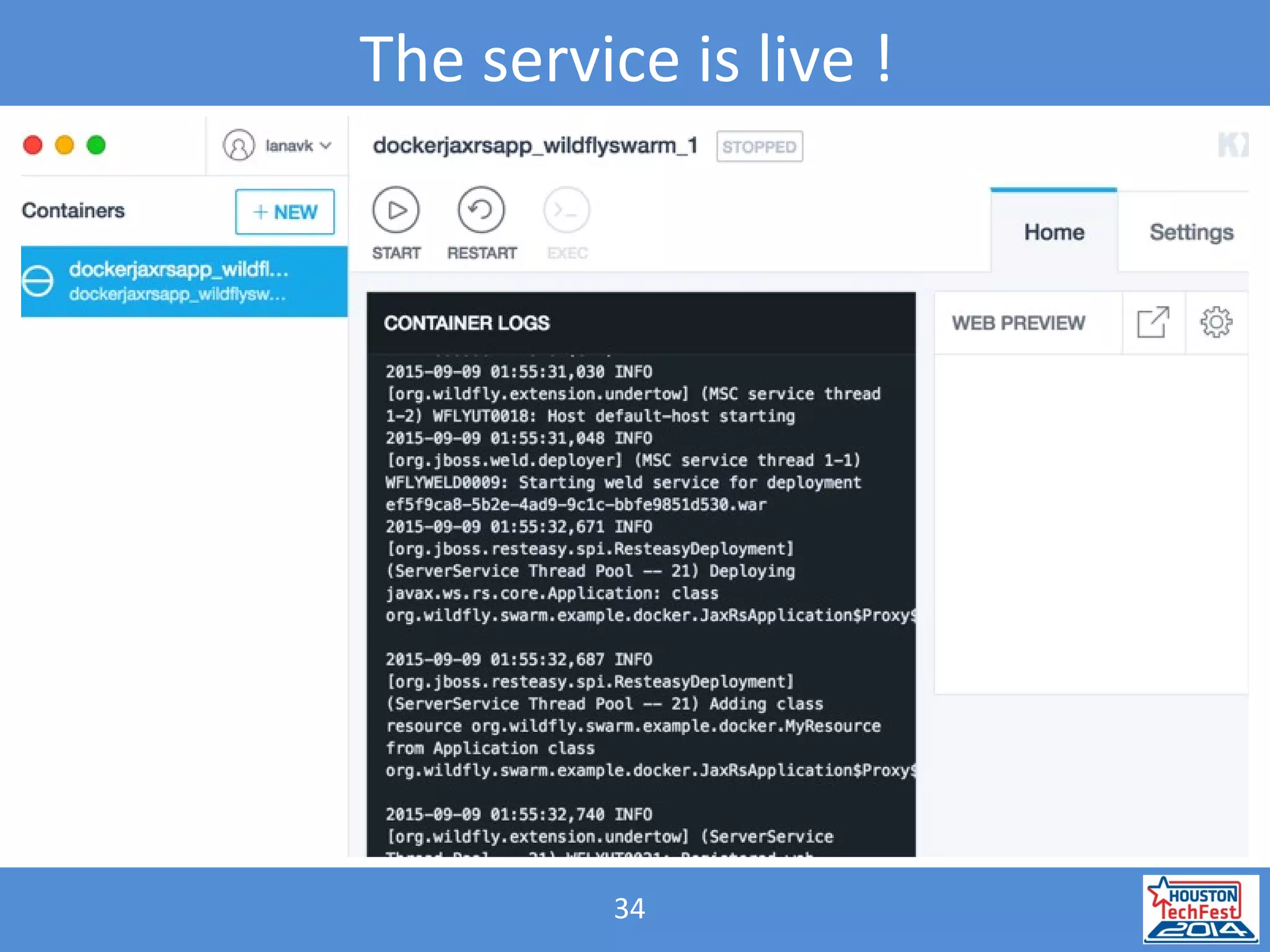
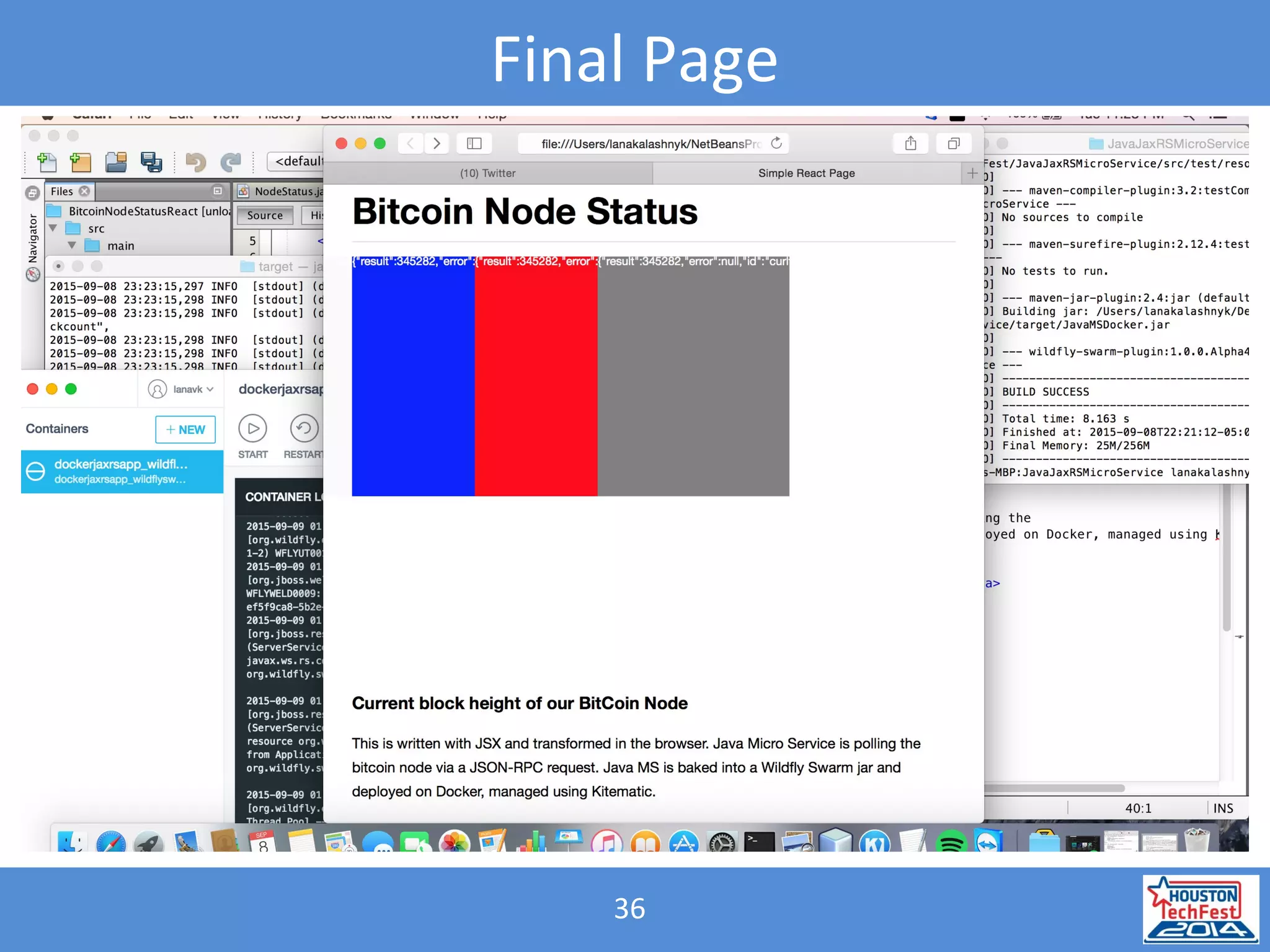
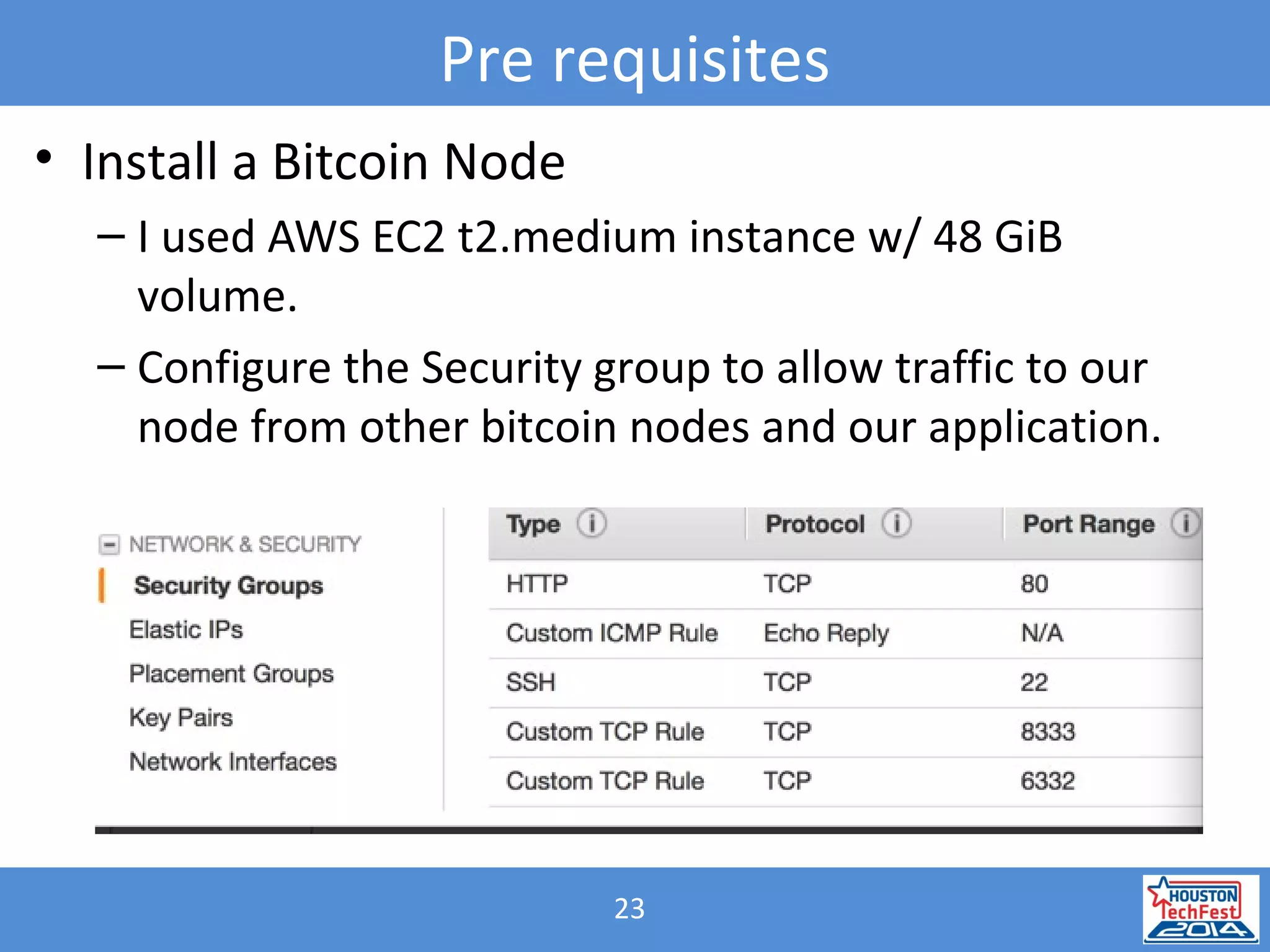
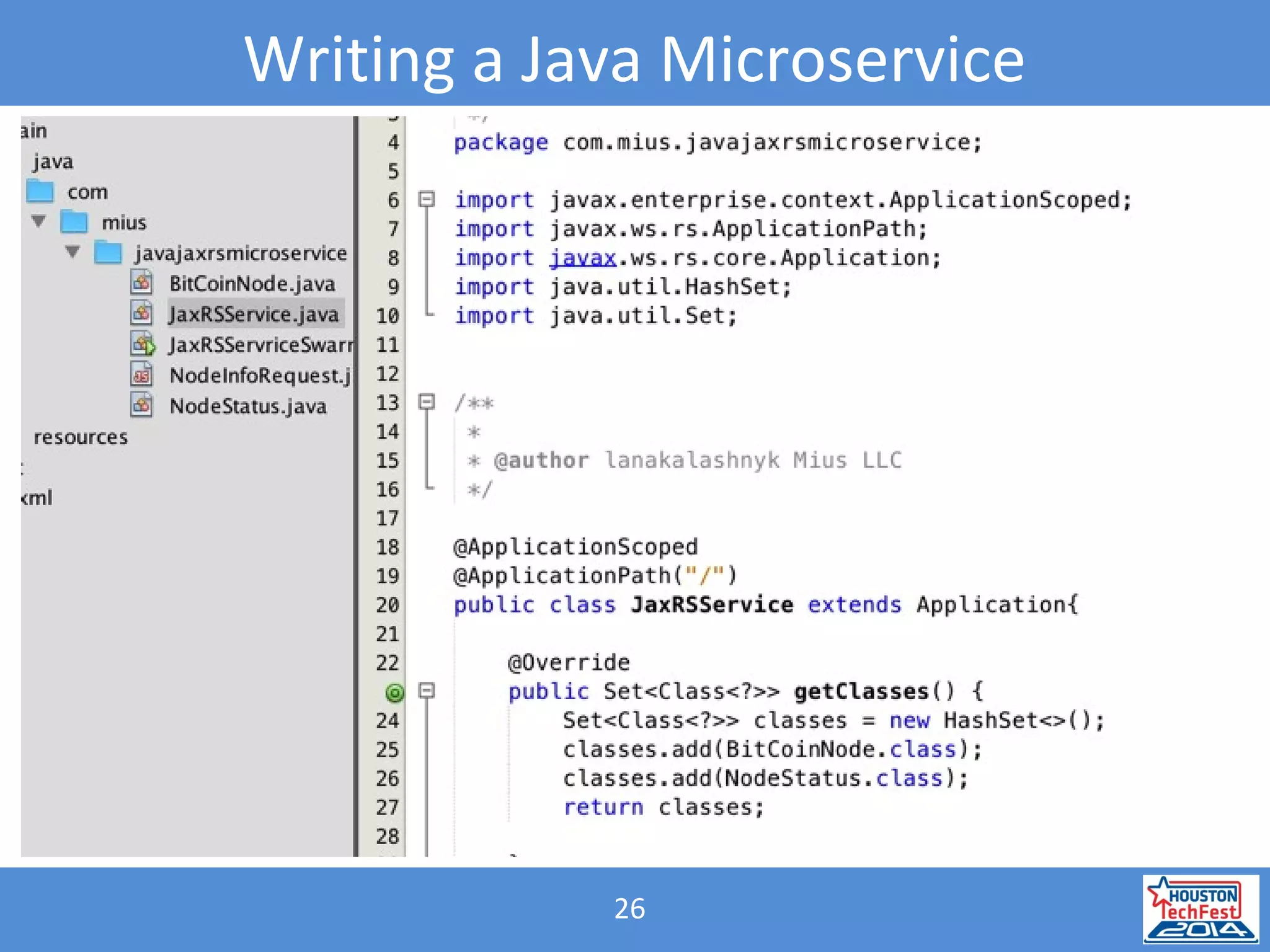
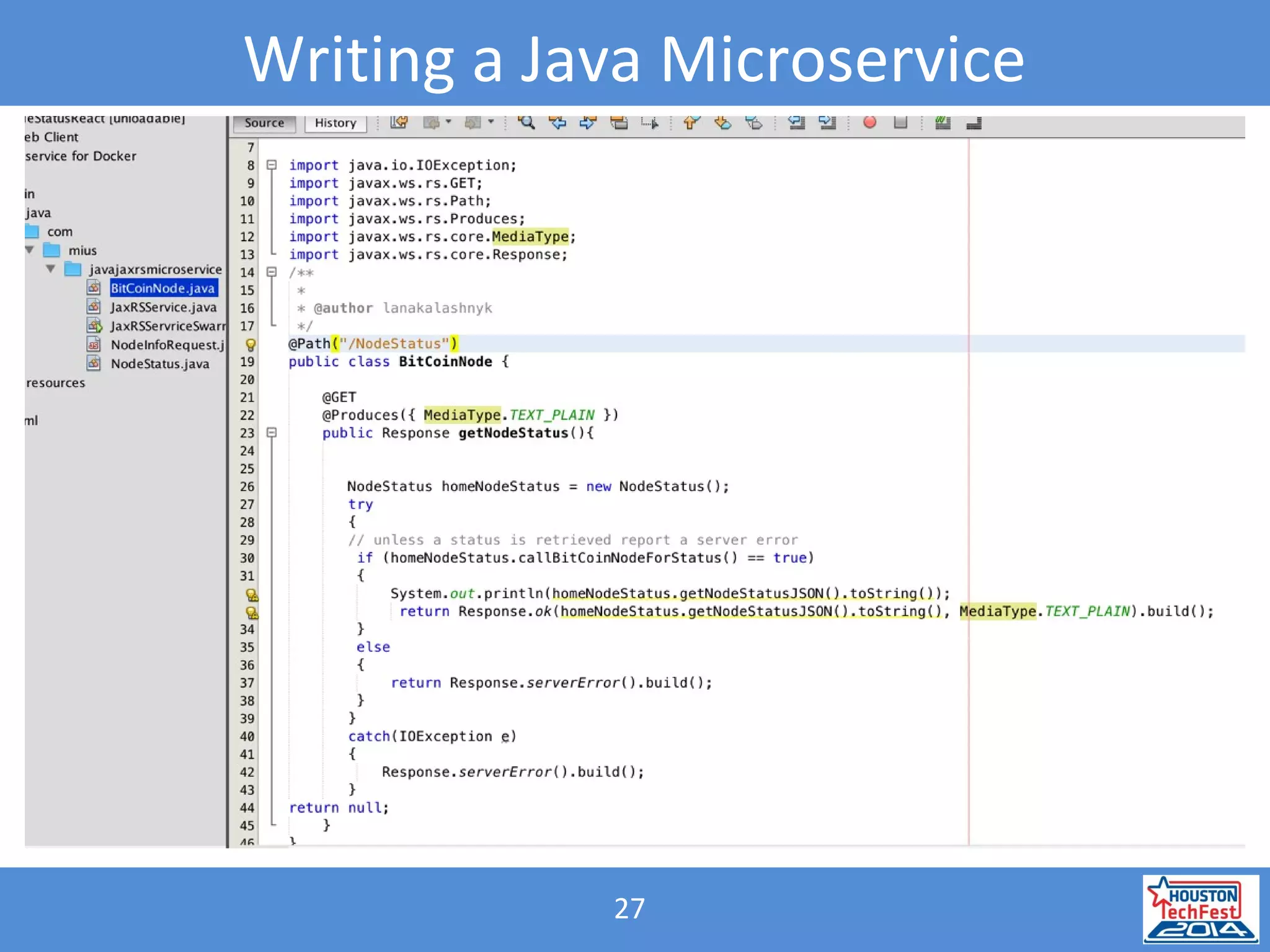
- The presentation demonstrated a Java microservice that polls a Bitcoin node for block height updates. It was packaged into a Docker container using Wildfly Swarm and exposed via REST APIs.
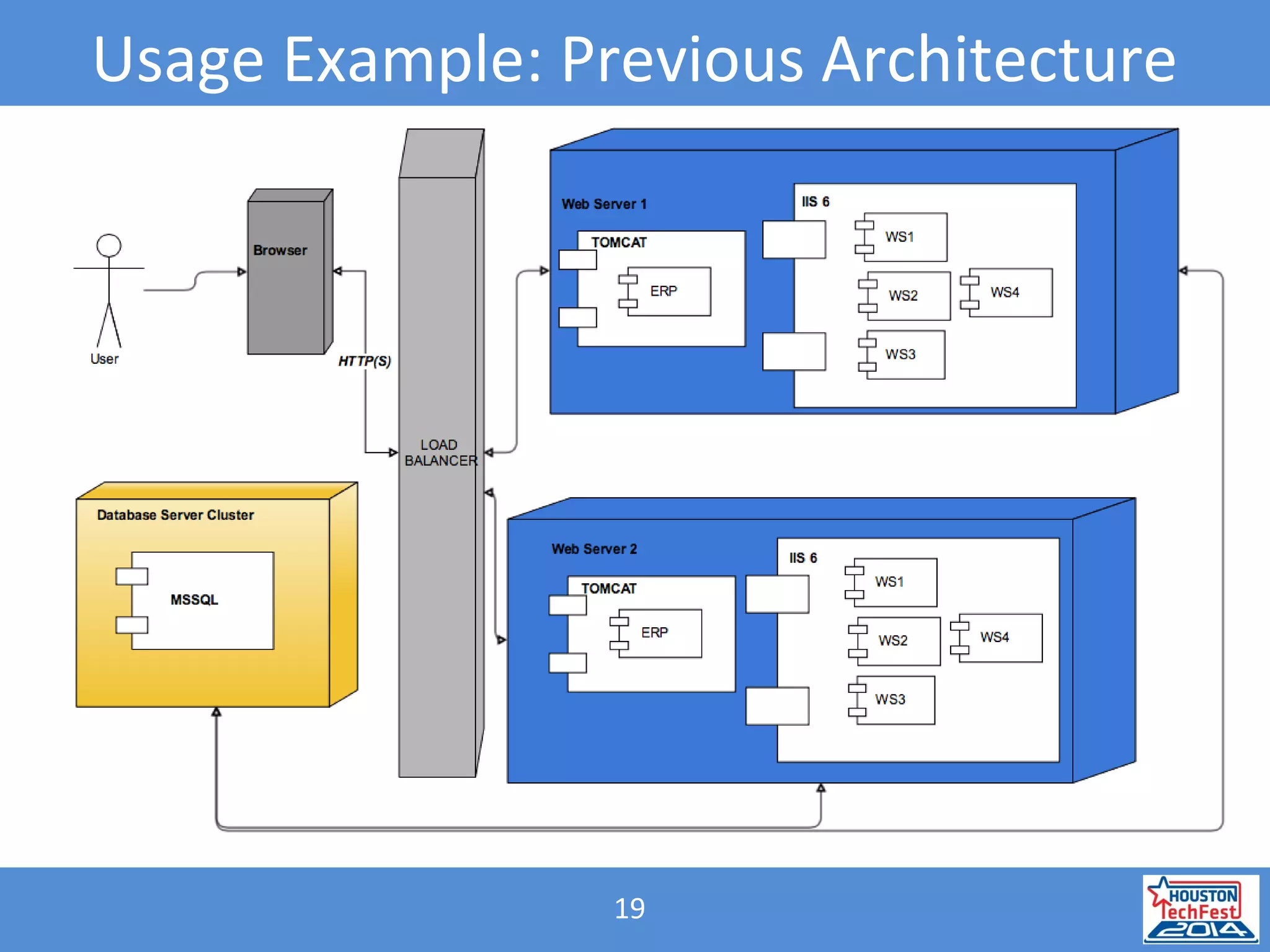
- A React web page displayed the data from the microservice. This illustrated how microservices and containers could replace outdated .NET web services.
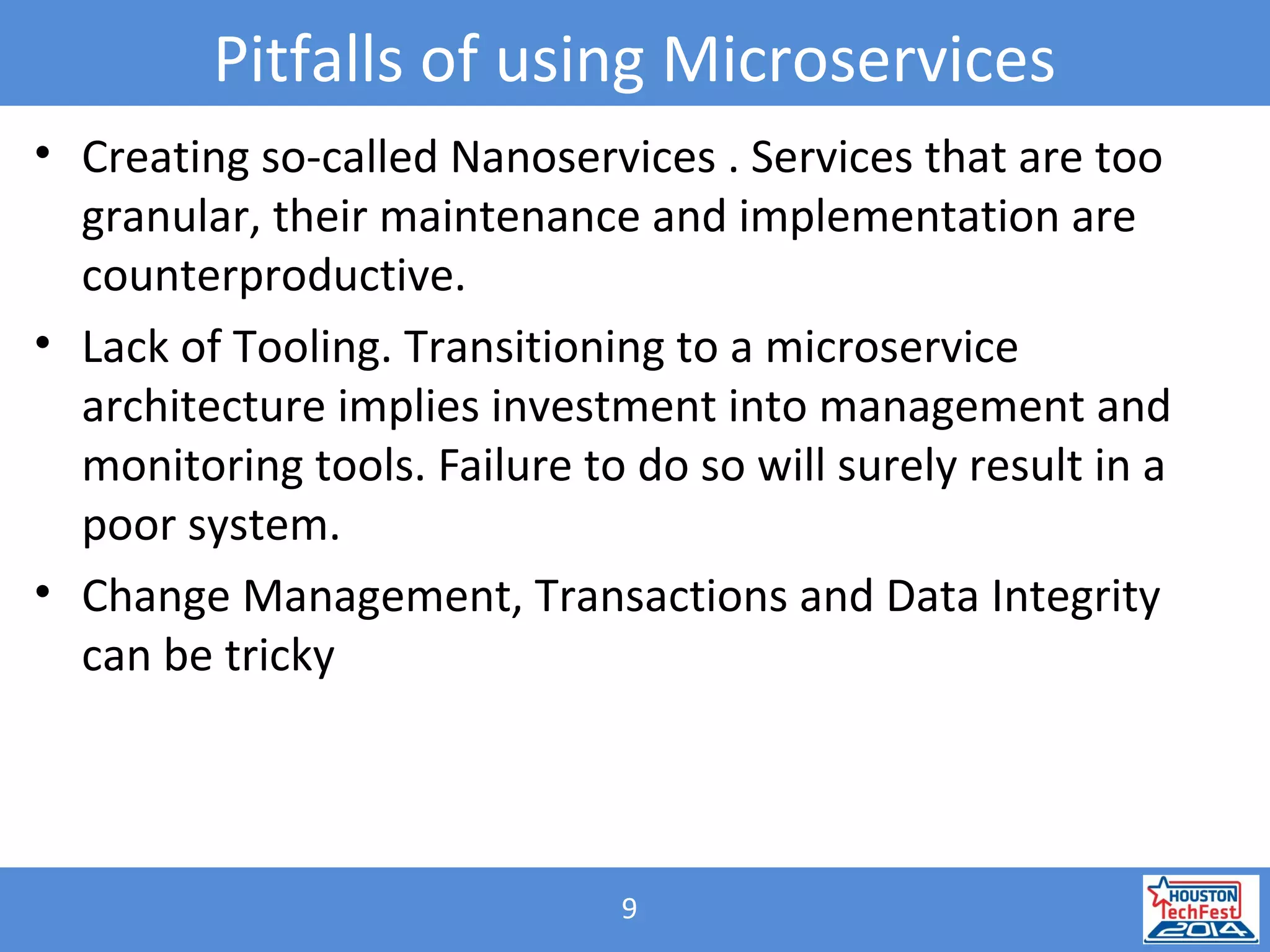
- Benefits of microservices include independent deployability, fault isolation, and infrastructure automation using containers. Challenges include managing transactions and data




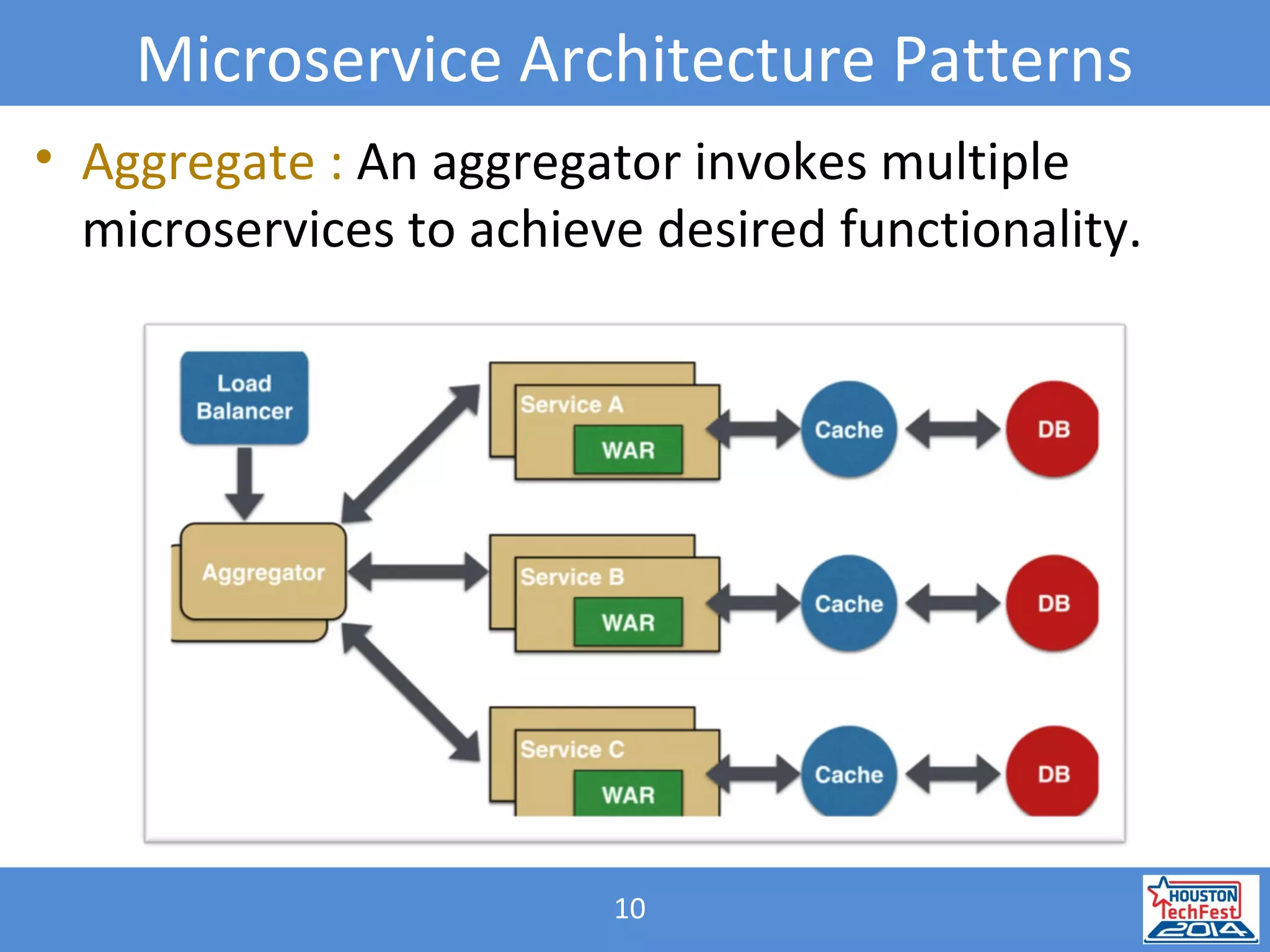
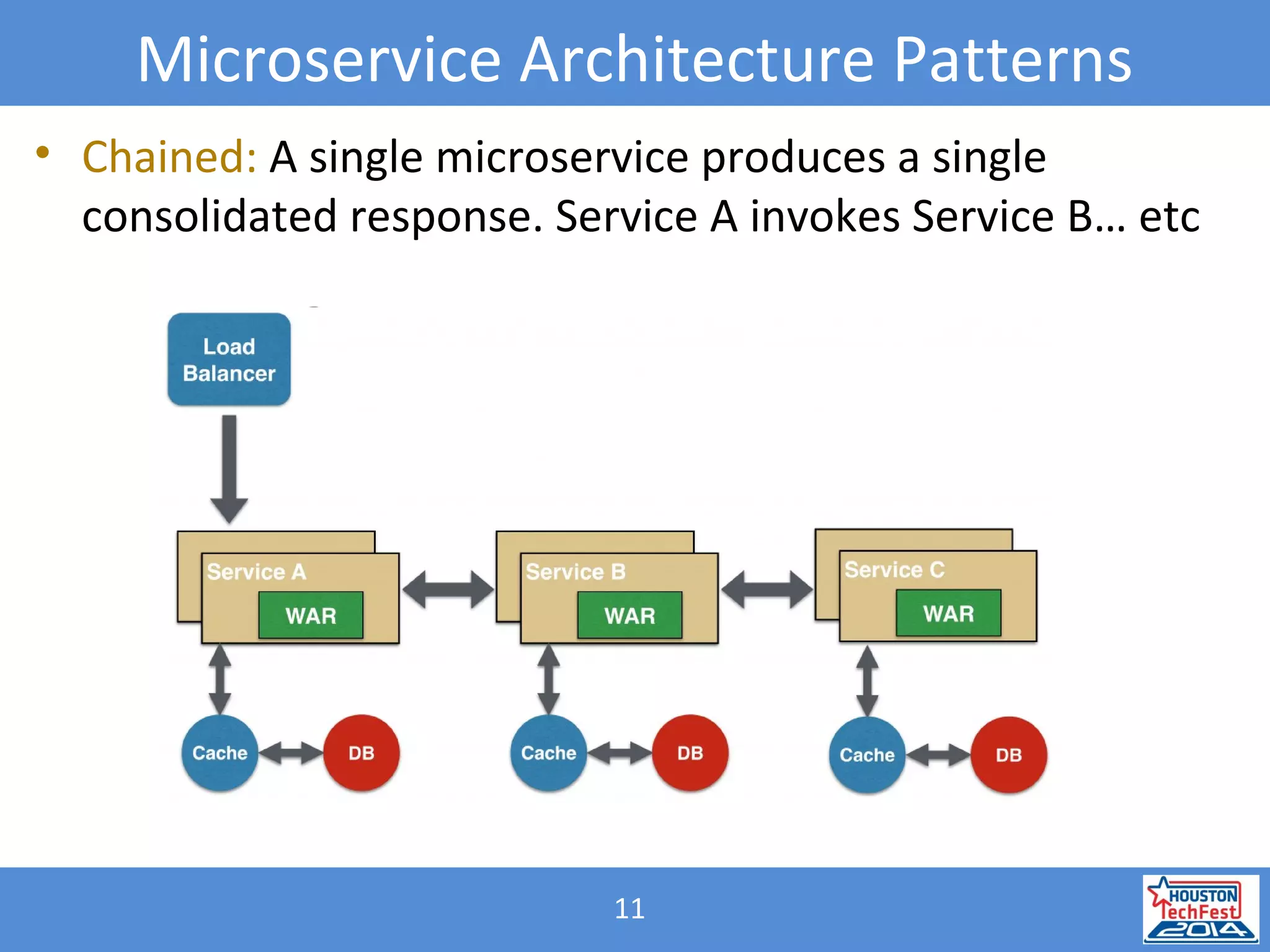
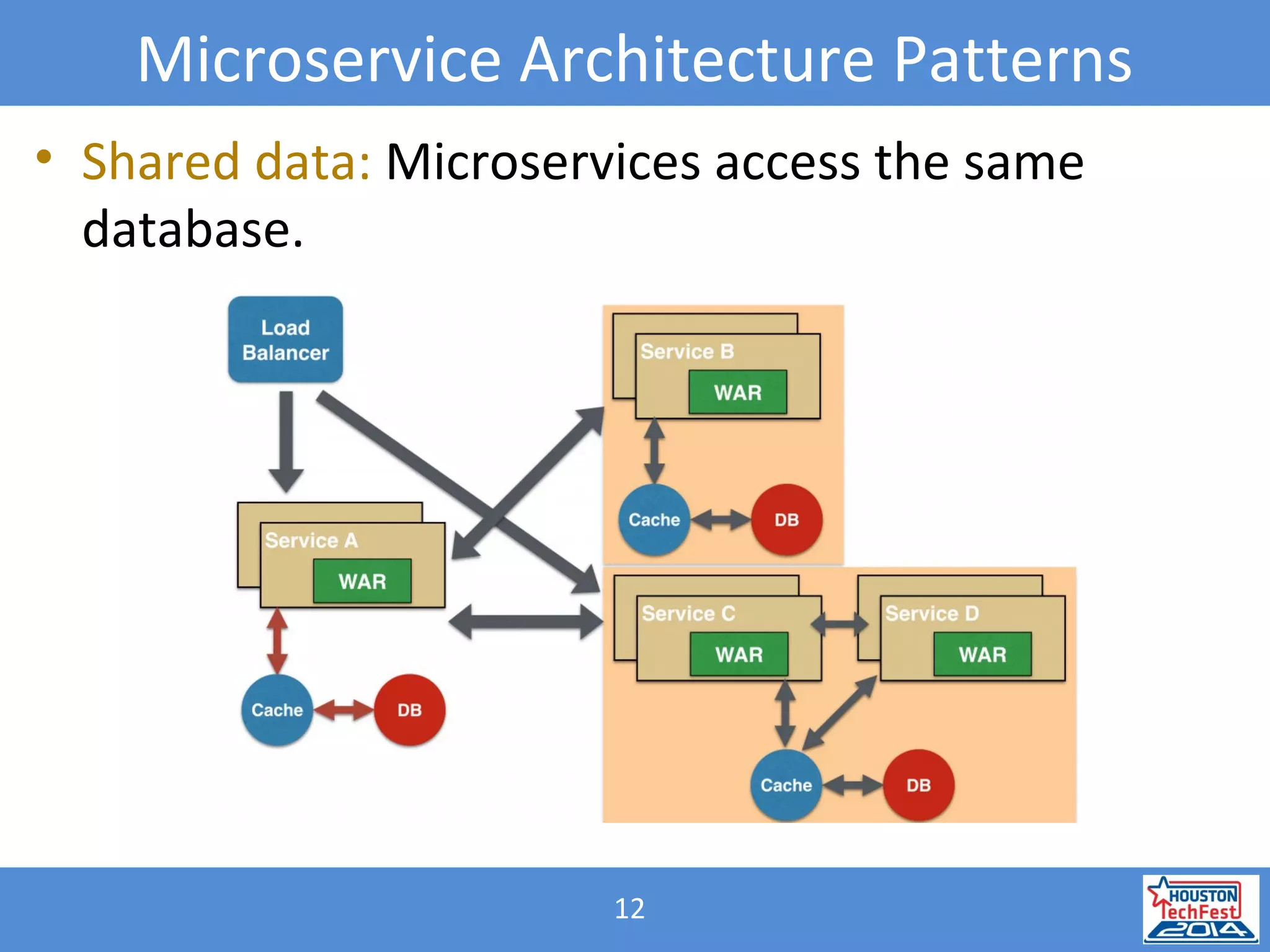








![31
Create a Docker File
• Create a file name “Dockerfile”
– Specify the base image
• FROM java:openjdk-8-jdk
– Copy over your files into the container
• ADD target/JavaMSDocker-swarm.jar /opt/JavaMSDocker-
swarm.jar
– Open port 8080 for our Service
• EXPOSE 8080
– Configure the container to run as an executable
• ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/opt/JavaMSDocker-
swarm.jar"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e3e35c44-a55c-4963-9381-41690d3c6b1f-151004185031-lva1-app6891/75/TransitioningToMicroServonDocker_MS-31-2048.jpg)