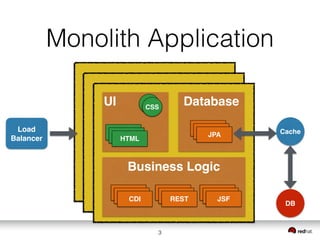
The document discusses the transition from monolith applications to microservices and containers in Java EE applications, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each architecture. It emphasizes microservices' benefits, such as easier development, faster deployments, and improved fault isolation, while also addressing challenges like operational complexity and coordination of deployments. Additionally, the document covers container technology, particularly Docker and Kubernetes, detailing their roles in enhancing application portability, isolation, and management.
























![“If you can't build a [well-structured]
monolith, what makes you think
microservices are the answer?”
http://www.codingthearchitecture.com/2014/07/06/distributed_big_balls_of_mud.html
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/refactor-microservices-150401031616-conversion-gate01/85/Refactor-your-Java-EE-application-using-Microservices-and-Containers-Arun-Gupta-Codemotion-Rome-2015-26-320.jpg)





















