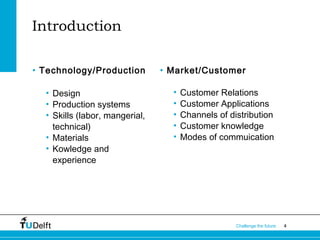
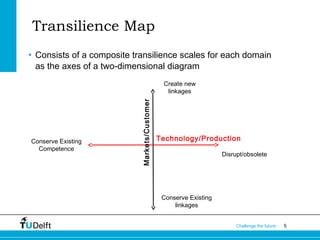
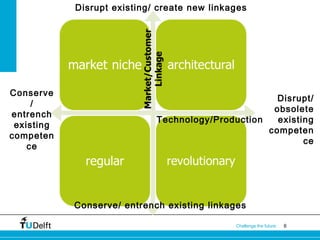
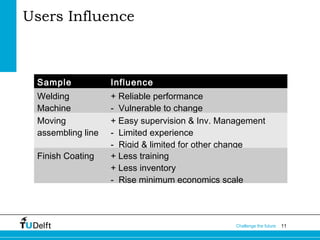
The document introduces the concept of a "transilience map" which maps types of innovation on two axes based on their impact on technology/production and markets/customers. The map shows four categories of innovation: architectural, market niche, regular, and revolutionary. It provides examples of each type and discusses how users can influence innovation and the managerial implications of the different innovation types.