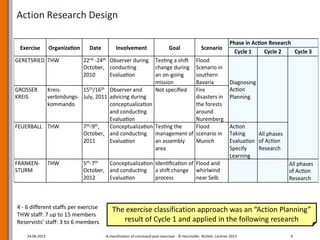
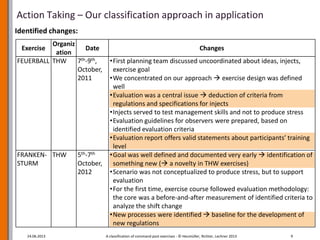
The document outlines a research project aimed at developing a framework for designing and evaluating command post exercises in disaster response organizations. It discusses challenges encountered during exercises, the need for defined performance criteria, and the importance of an organized evaluation methodology. The research culminates in a guide to support practitioners in achieving effective and goal-oriented exercise designs.