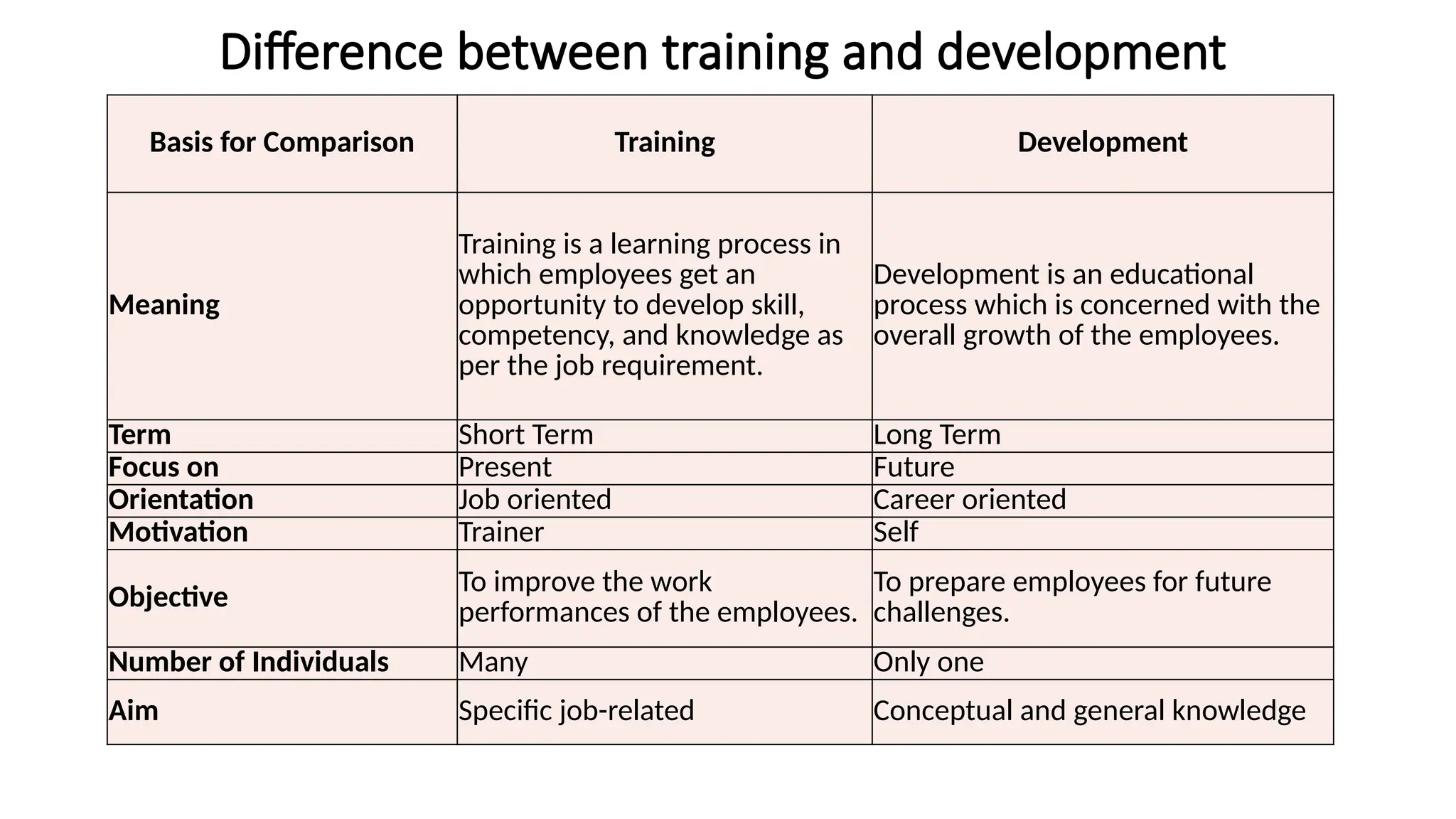
The document discusses the concepts of training and development, defining training as an educational process aimed at increasing specific job-related skills and development as a focus on overall employee growth. It outlines the objectives of training, differences between training and development, methods of on-the-job and off-the-job training, and the importance of training in human resource development (HRD) for organizational efficiency. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity of training for adapting to technical advances, organizational complexity, and changes in job assignments.