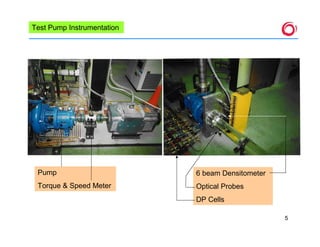
This document summarizes experimental work characterizing the performance of a two-phase flow pump. It describes the experimental loop used to test the pump under single-phase and two-phase flow conditions. The document also outlines instrumentation used to measure pump parameters like pressure, void fraction, and flow rates. Charts show experimental data on the pump's pressure distribution and performance at varying flow rates, pressures, and void fractions, along with comparisons to predictive models of single-phase and two-phase pump behavior. The conclusion calls for more experiments to develop more accurate predictive models of two-phase pump performance.






![10
Pump Single Phase Calculation
Input:
Impeller geometry: r1 [m],r2 [m], β’s
Suction pipe diameter: dpipe [m] ,
Volumetric flow rate: Q [liter/minute]
Water density (ρsp)
Pump Single-Phase Flow
Performance Prediction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9f9e5a3c-ebf3-4ae5-ab72-b59d4bc210b9-151127203834-lva1-app6892/85/TP_Pump_Presentation-10-320.jpg)
![11
Pump Two Phase Flow Pump Performances
Two-phase flow mass flux effect
N=1250 rpm, psuction=130 [kPa]
The effect of different suction
pressure on pump head.
Preliminary Test Result:
Void Fraction
Pump Suction Pressure
Test Matrix:
N, QW,Qair, Psuction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9f9e5a3c-ebf3-4ae5-ab72-b59d4bc210b9-151127203834-lva1-app6892/85/TP_Pump_Presentation-11-320.jpg)



![15
Two Phase Flow Pump Performances
Input:
Suction Pressure: psuction [kPa]
Two-Phase Flow Quality: x
S-P Water Flow Rate: m [kg/sec]
S-P pump pressure Distribution:
•Inlet Diffuser
•Pump Vane
•Pump Volute
Pump Two-Phase Flow
Performance Prediction
Psuction=101:150
X=2.5*10-5:1.2*10-3
Psuction=200:300
X=4.5*10-5:4.5*10-3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9f9e5a3c-ebf3-4ae5-ab72-b59d4bc210b9-151127203834-lva1-app6892/85/TP_Pump_Presentation-15-320.jpg)

