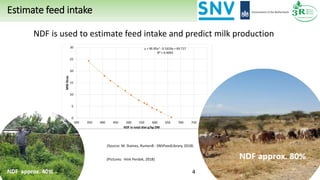
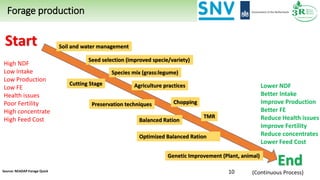
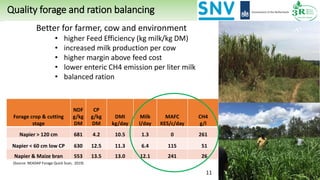
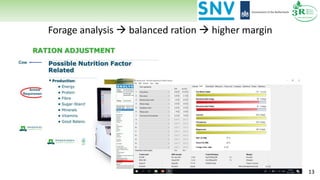
The document discusses Rumen8, a total diet ration balancing software for dairy cows designed to optimize milk production and improve feed cost margins. It emphasizes the need for a feed library that considers the variation in forage quality across Kenyan farms and integrates local agronomic practices. Additionally, it highlights the importance of continuous improvements in forage quality and management to enhance dairy efficiency and sustainability.