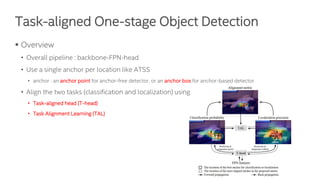
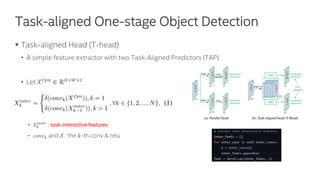
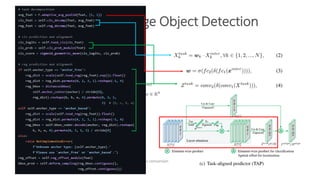
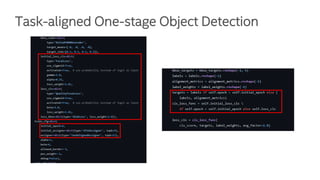
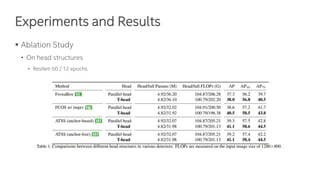
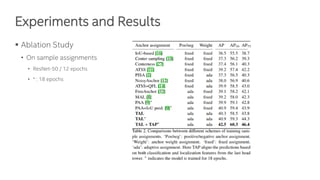
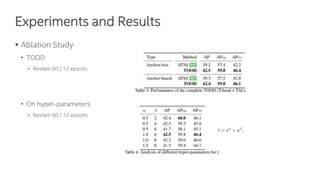
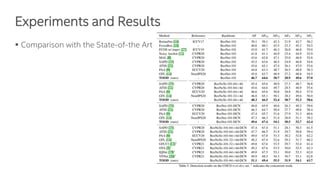
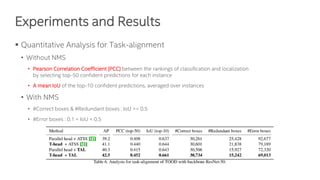
The document discusses a novel task-aligned one-stage object detection method called Tood, which aims to improve the performance of object detection by aligning classification and localization tasks through a specialized framework. It introduces task-aligned heads and learning mechanisms, resulting in superior detection accuracy compared to existing methods. Experiments demonstrate Tood's effectiveness using the COCO 2017 dataset, achieving significant advancements over the state-of-the-art models.