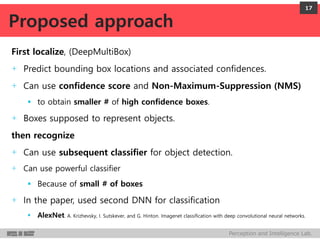
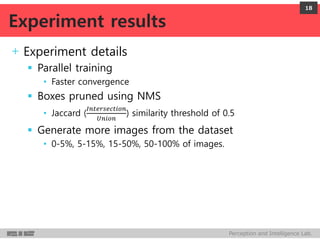
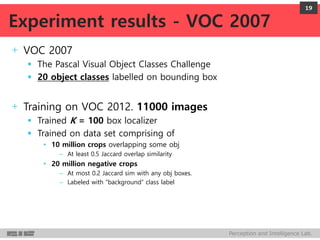
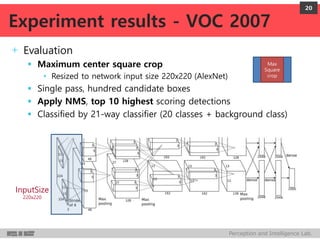
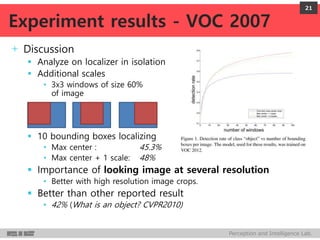
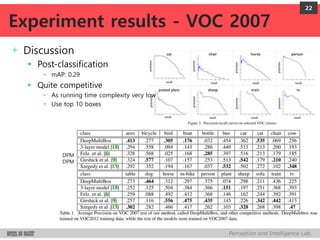
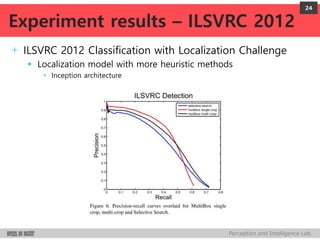
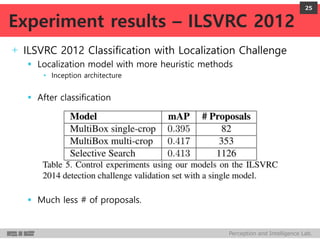
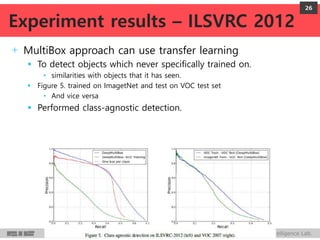
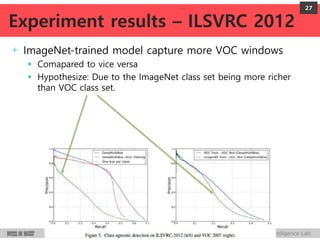
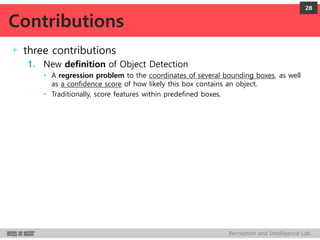
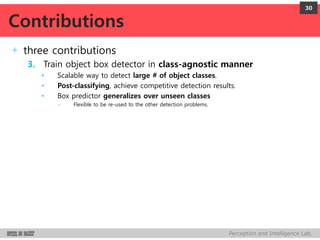
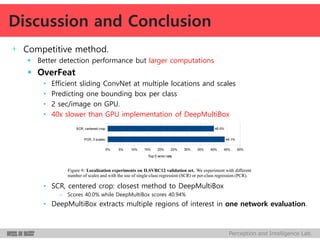
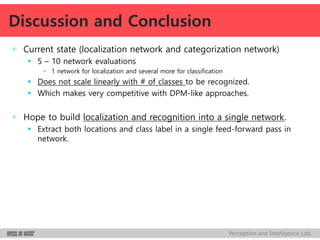
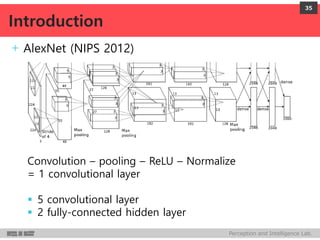
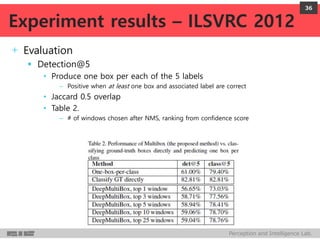
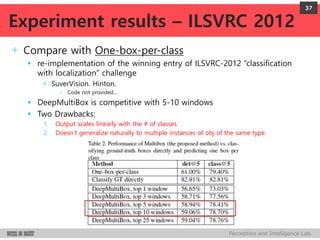
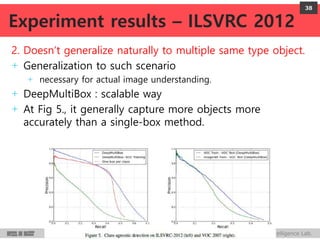
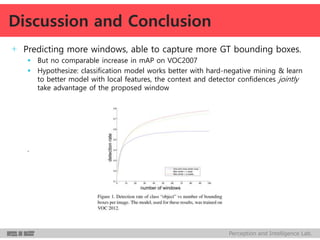
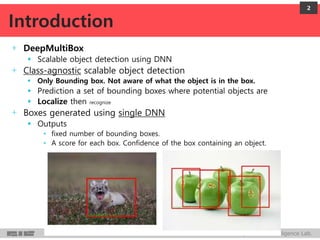
DeepMultiBox is a scalable object detection method using deep neural networks that detects objects in a class-agnostic manner. It predicts bounding boxes and confidence scores using a single DNN. It formulates object detection as a regression problem to optimize bounding box coordinates and confidences. It was shown to achieve competitive detection results on PASCAL VOC 2007 with faster runtime than other methods.

![Perception and Intelligence Lab.
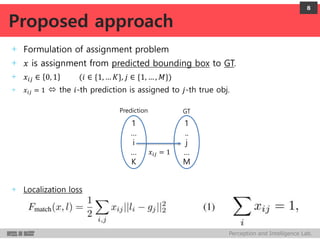
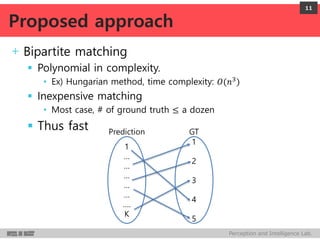
+ Model
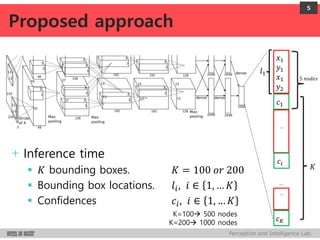
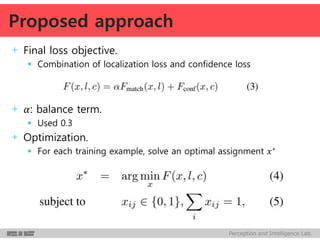
Encode i-th object box and its confidence as node values of last net layer
+ Bounding box
Upper-left and lower-right co-ordinates
Vector: 𝒍𝒊 ∈ ℝ 𝟒
4 node values
Normalized co-ordinates w.r.t. image dim.
Linear transform of the last hidden layer
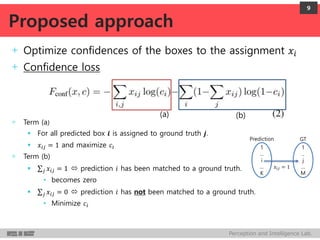
+ Confidence
Confidence score for the box containing an object
Score: 𝒄𝒊∈ [𝟎, 𝟏] 1 node value
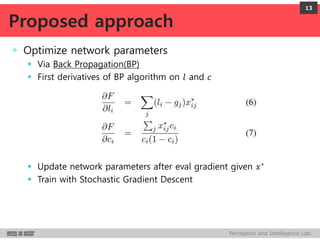
Linear transform of the last hidden layer followed by a sigmoid
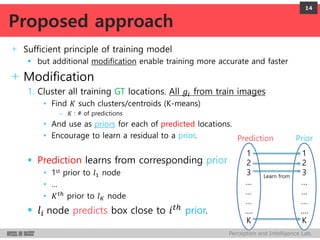
4
x1, y1
x2, y2
𝒍𝒊=[x1 y1 x2 y2]
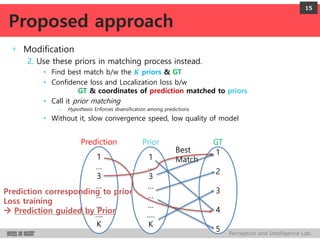
Proposed approach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/150424scalableobjectdetectionusingdnn-170610061034/85/150424-Scalable-Object-Detection-using-Deep-Neural-Networks-4-320.jpg)