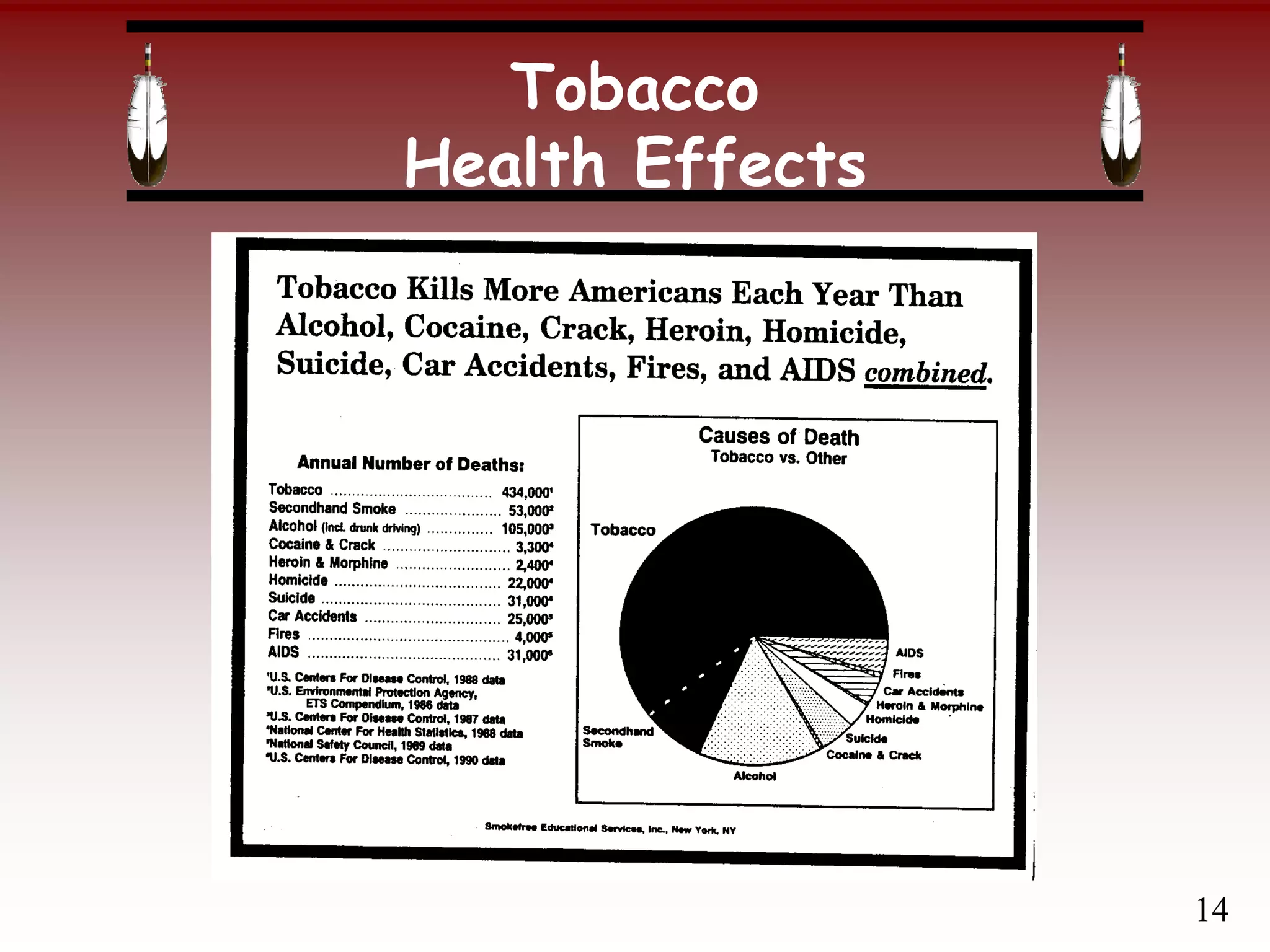
Tobacco was traditionally used by Indigenous peoples for ceremonial and medicinal purposes, but commercial tobacco contains over 4000 chemicals and 40 cancer-causing agents. Smoking and smokeless tobacco increase the risks of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Secondhand smoke also endangers children and pregnant women. Quitting smoking improves health over time, with risks decreasing significantly within just a few years of stopping.
![[Insert your name
and information here]
1
Tobacco 101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tobacco101-230529082732-3fa3b4c8/75/Tobacco-101-ppt-1-2048.jpg)


















![Tobacco
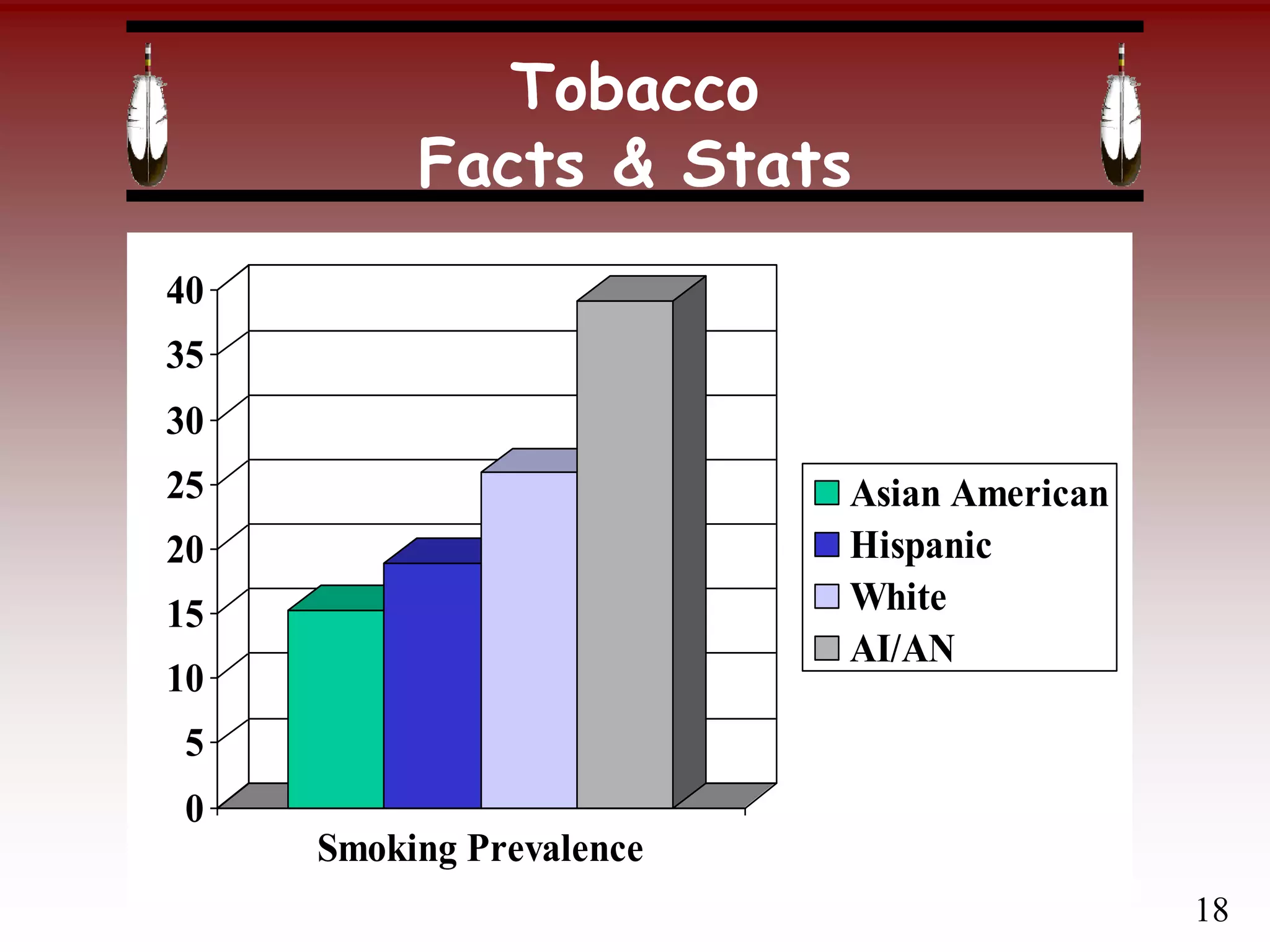
Facts & Stats
“If not one single young person
started smoking from this day
forward these losses [more than
400,000 deaths per year] would still
continue unabated for 30 years.”
C. Everett Koop (US Surgeon
General 1981-1989)
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tobacco101-230529082732-3fa3b4c8/75/Tobacco-101-ppt-22-2048.jpg)




















