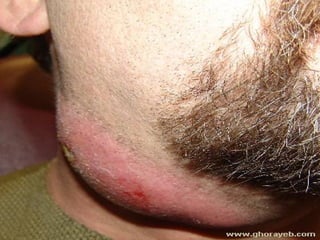
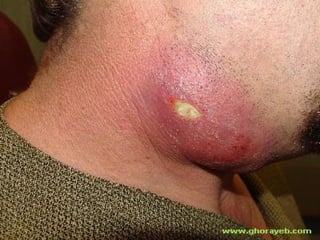
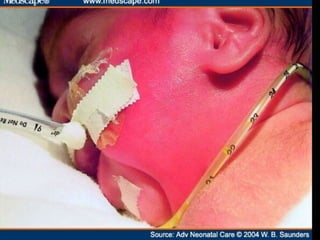
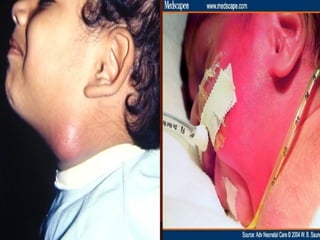
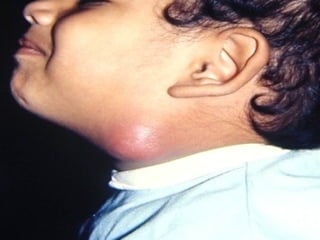
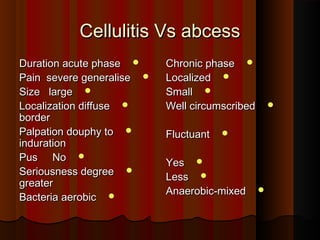
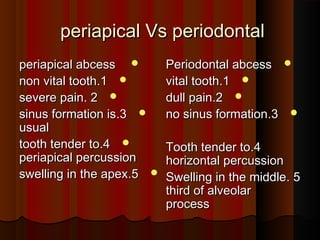
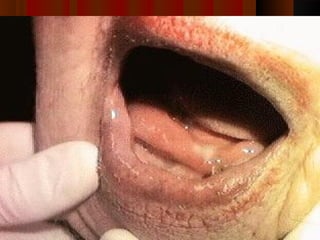
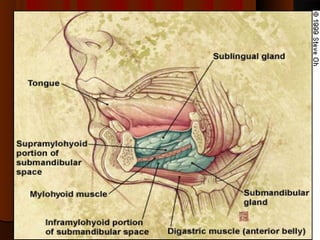
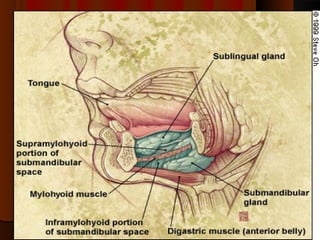
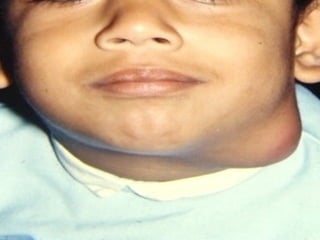
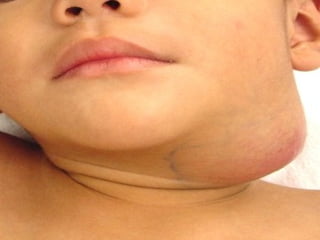
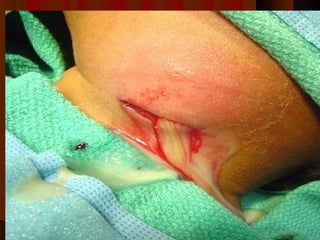
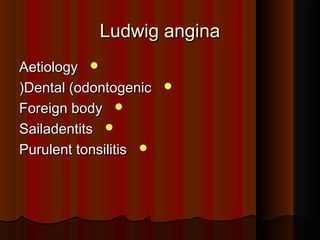
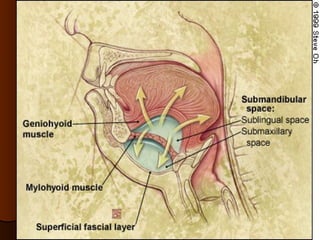
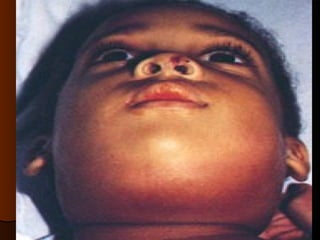
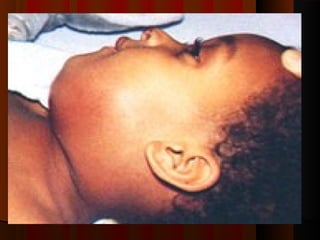
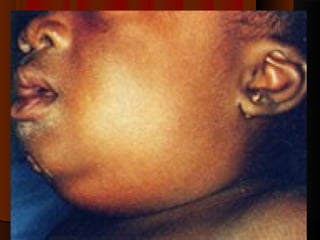
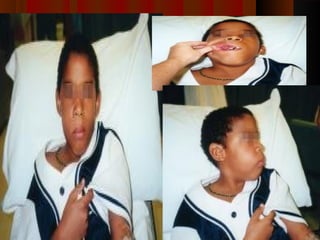
The document discusses tissue space infections, defining them as pathological spaces that can develop into abscesses requiring drainage to prevent severe complications. It covers various anatomical layers and muscle involvement, alongside the stages of infection, clinical features, and differences between cellulitis and abscesses. Treatment options and factors influencing infection spread are also highlighted, along with anatomical considerations relevant to specific spaces such as submental and sublingual regions.