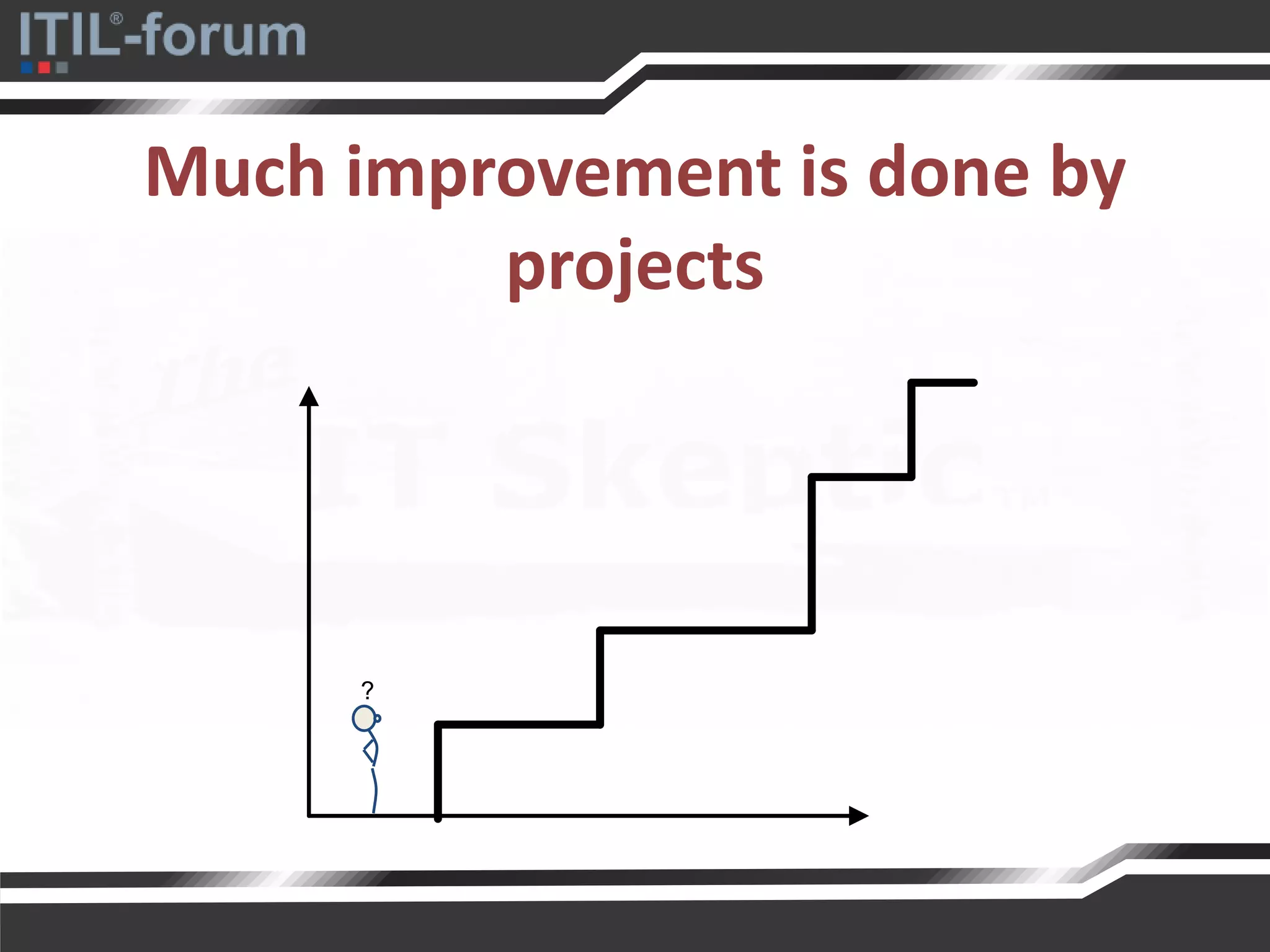
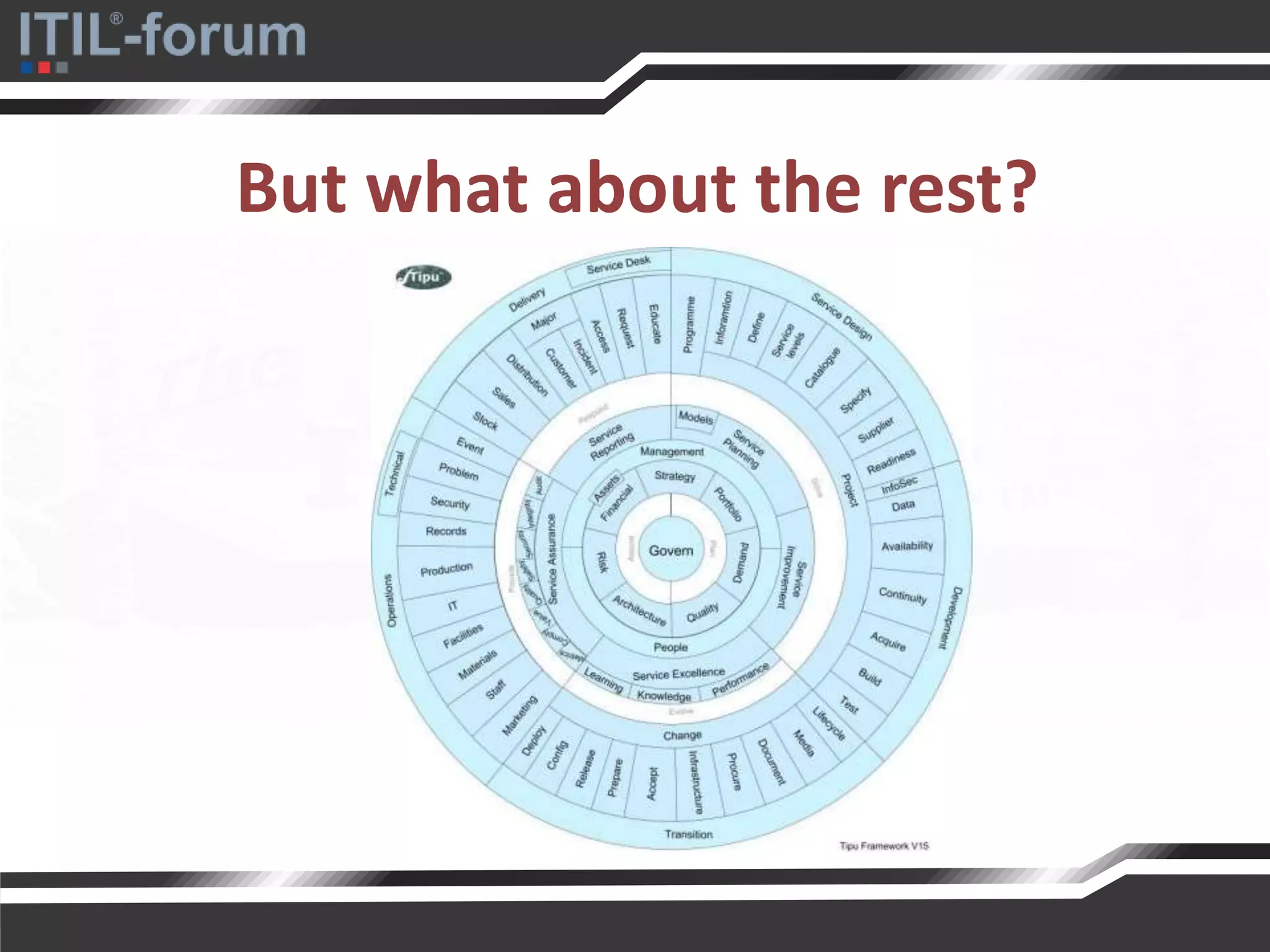
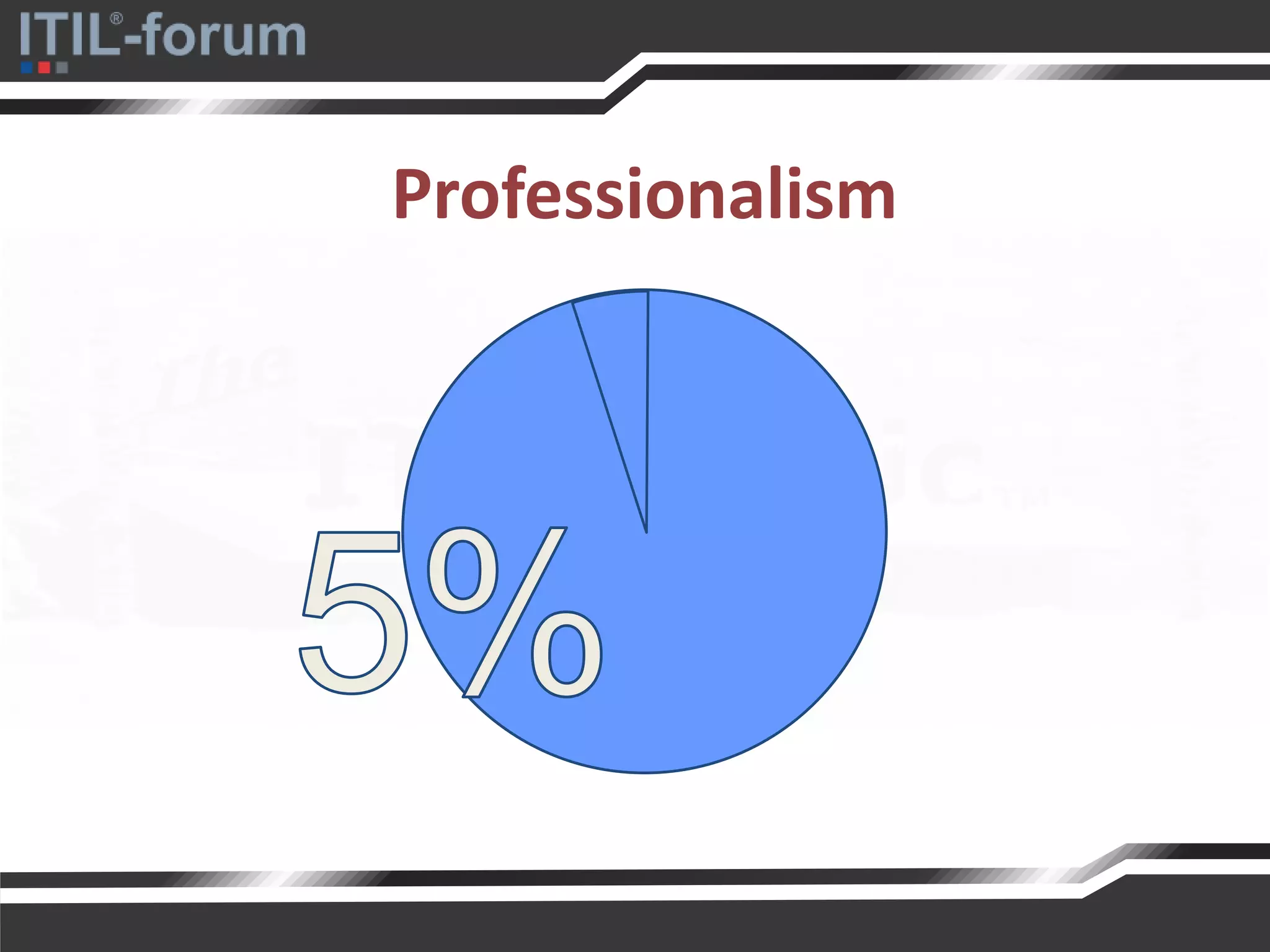
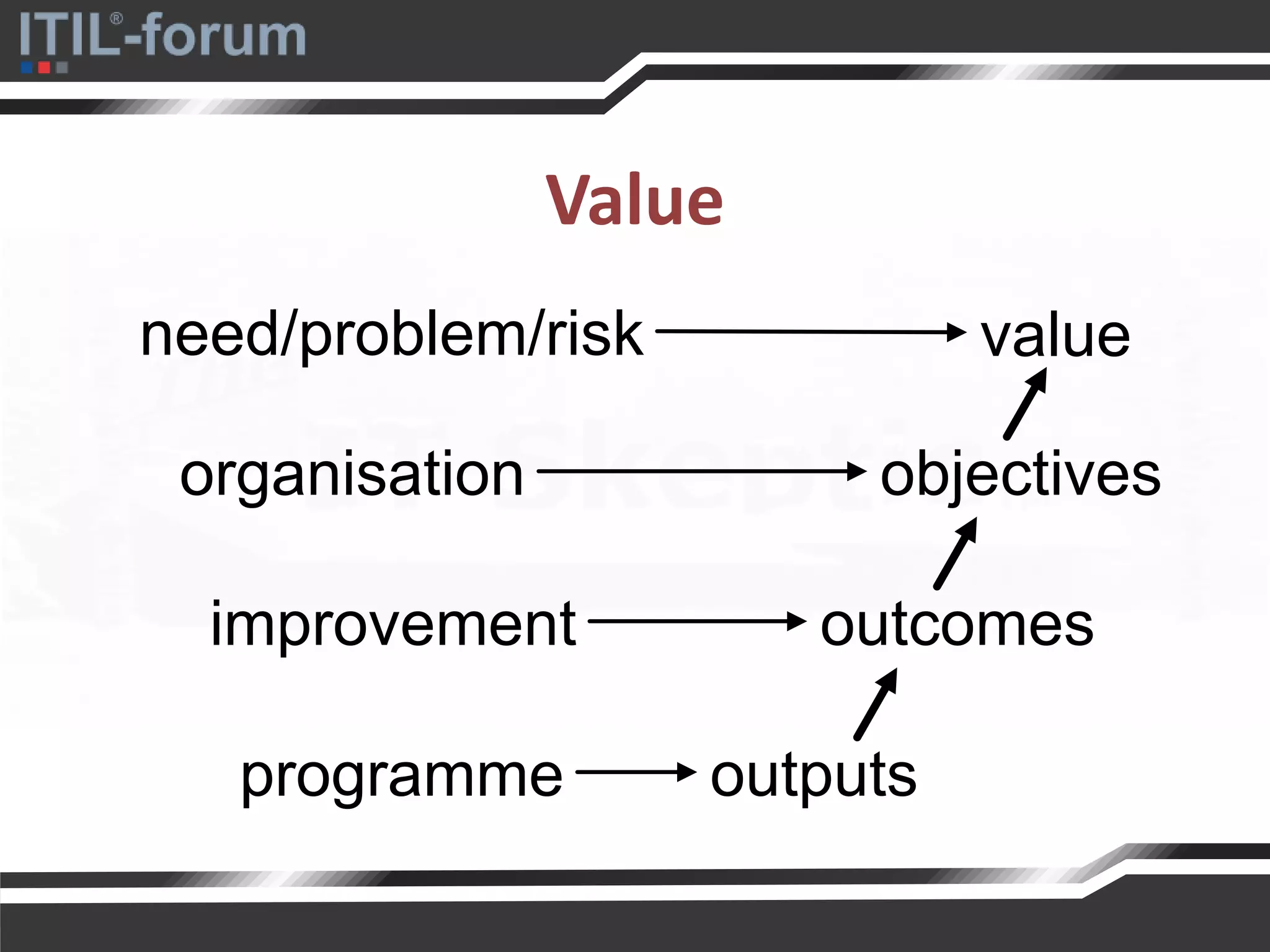
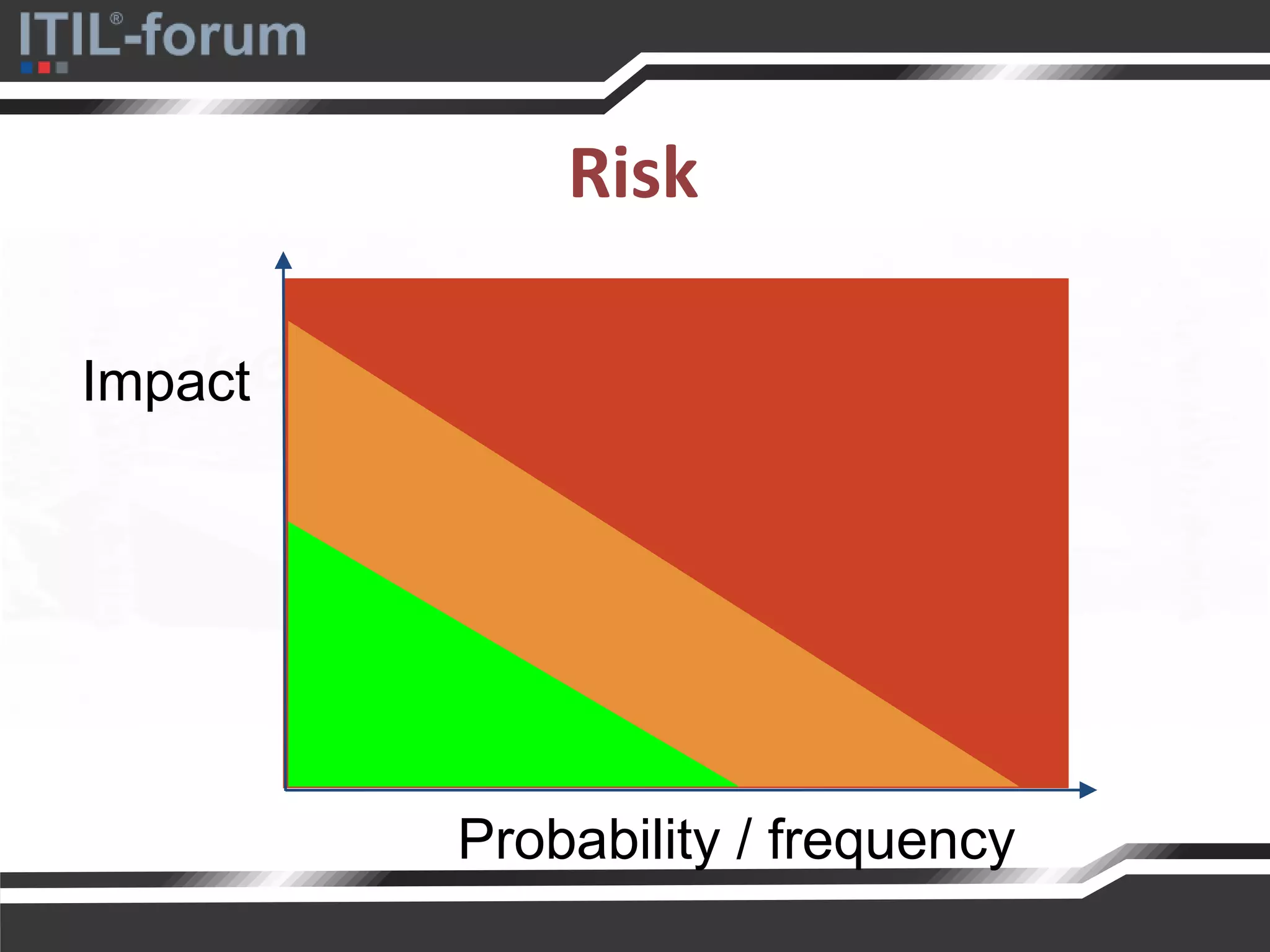
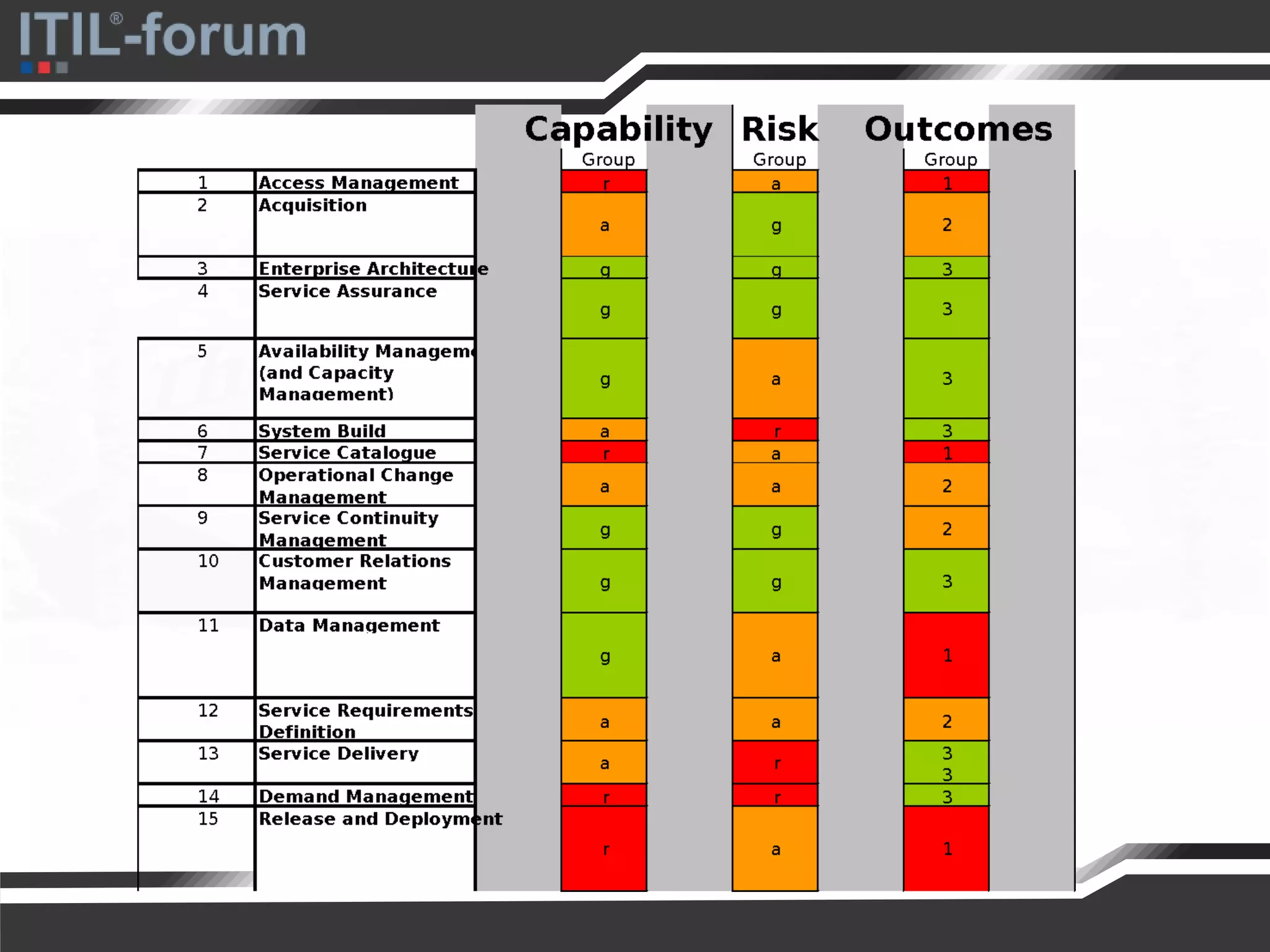
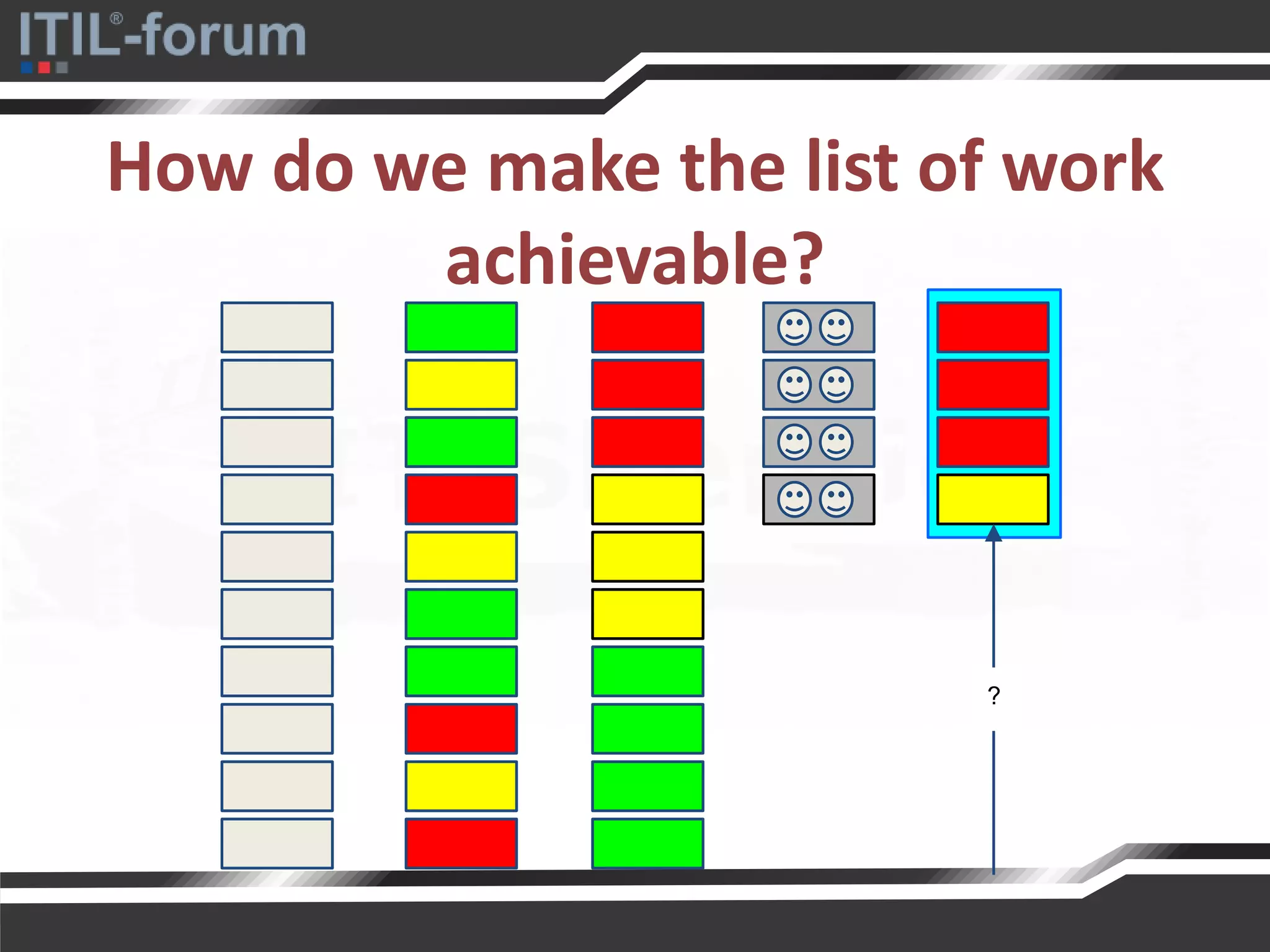
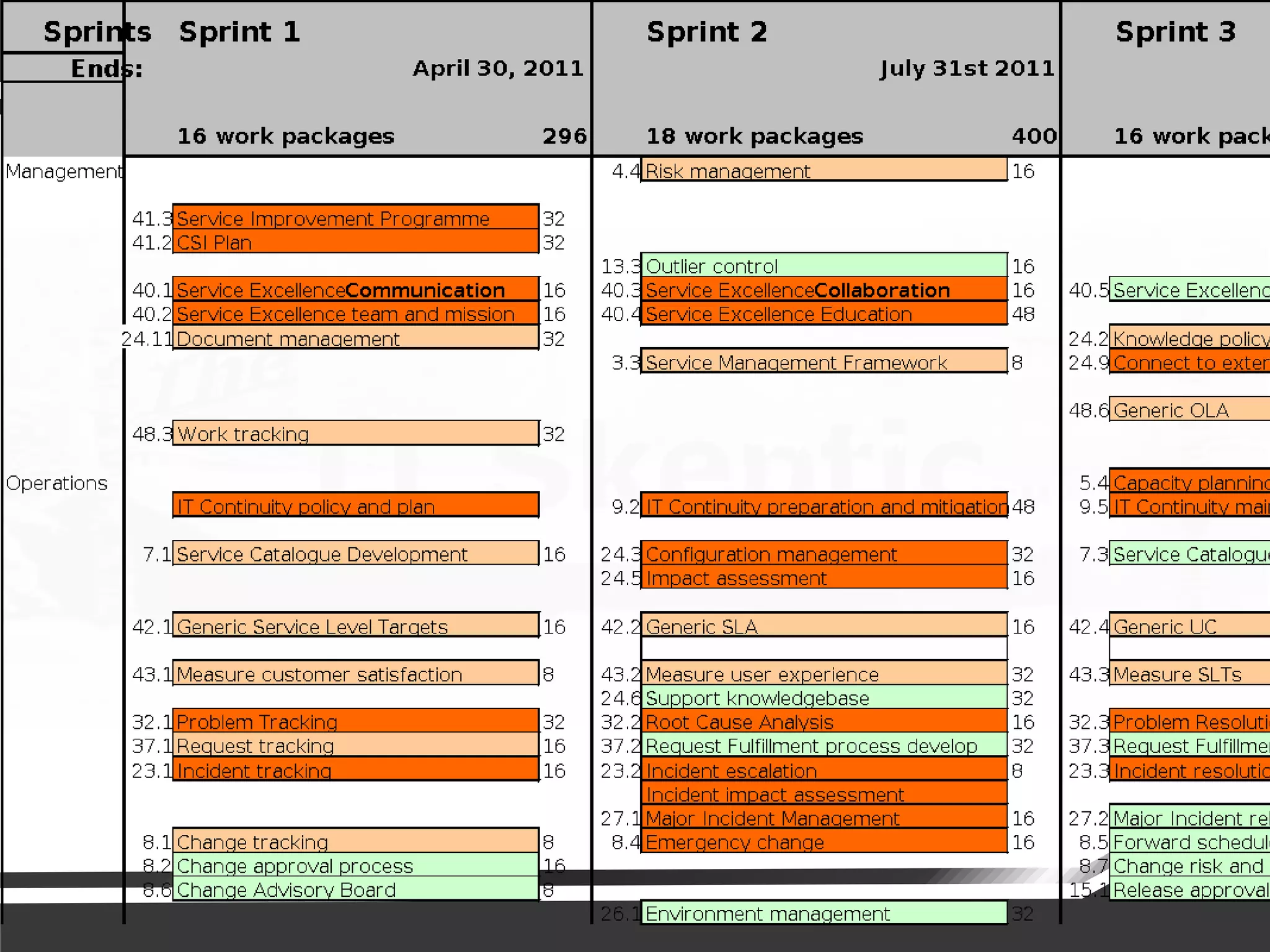
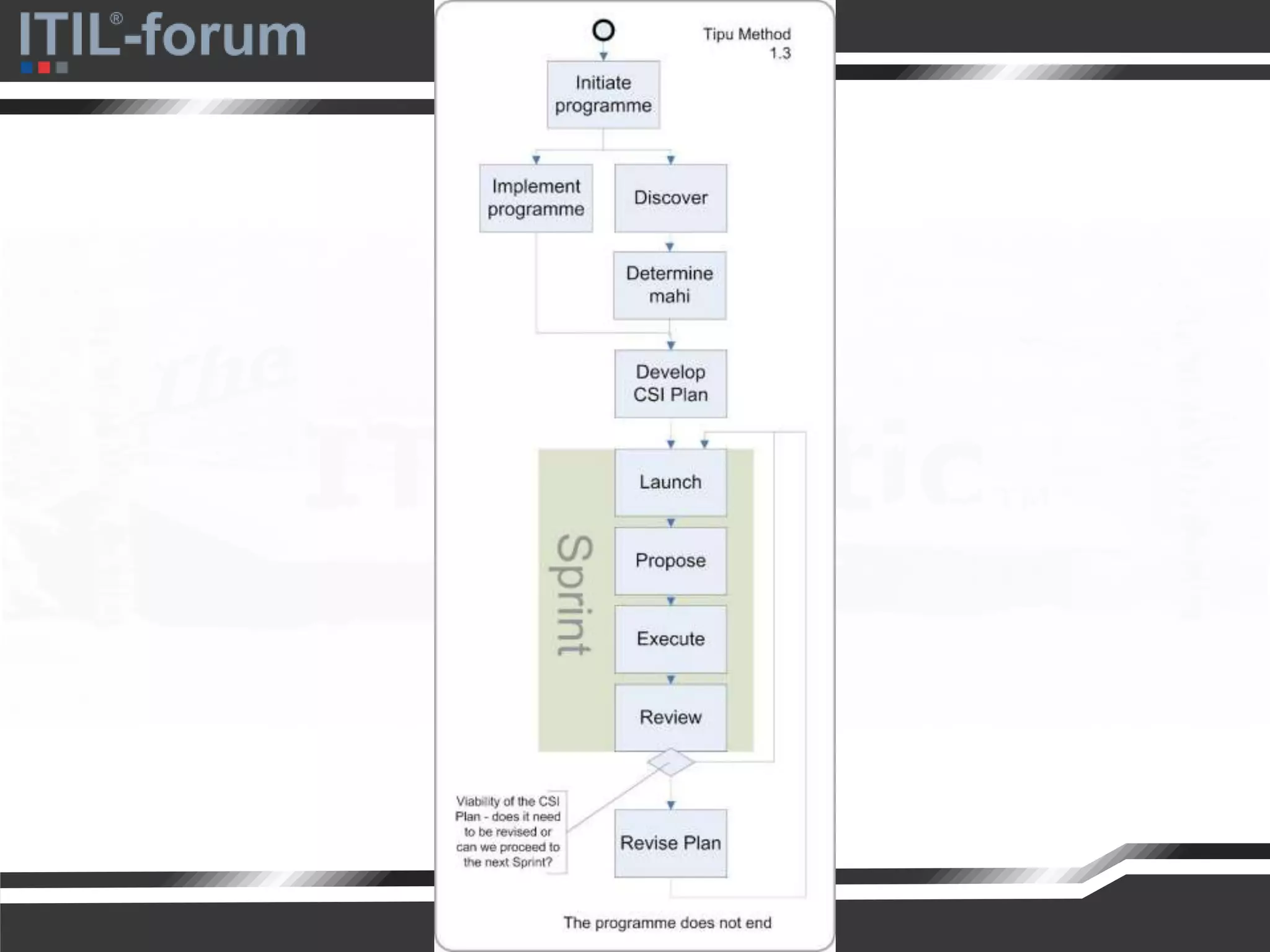
The document discusses a pragmatic approach to managed improvement within organizations, emphasizing the need for coordination, empowerment, and executable plans for staff. It addresses the importance of balancing urgent tasks with significant improvements and outlines a risk management framework aligned with organizational goals. Various strategies and tools for implementing service improvement programs and achieving operational readiness are also highlighted.