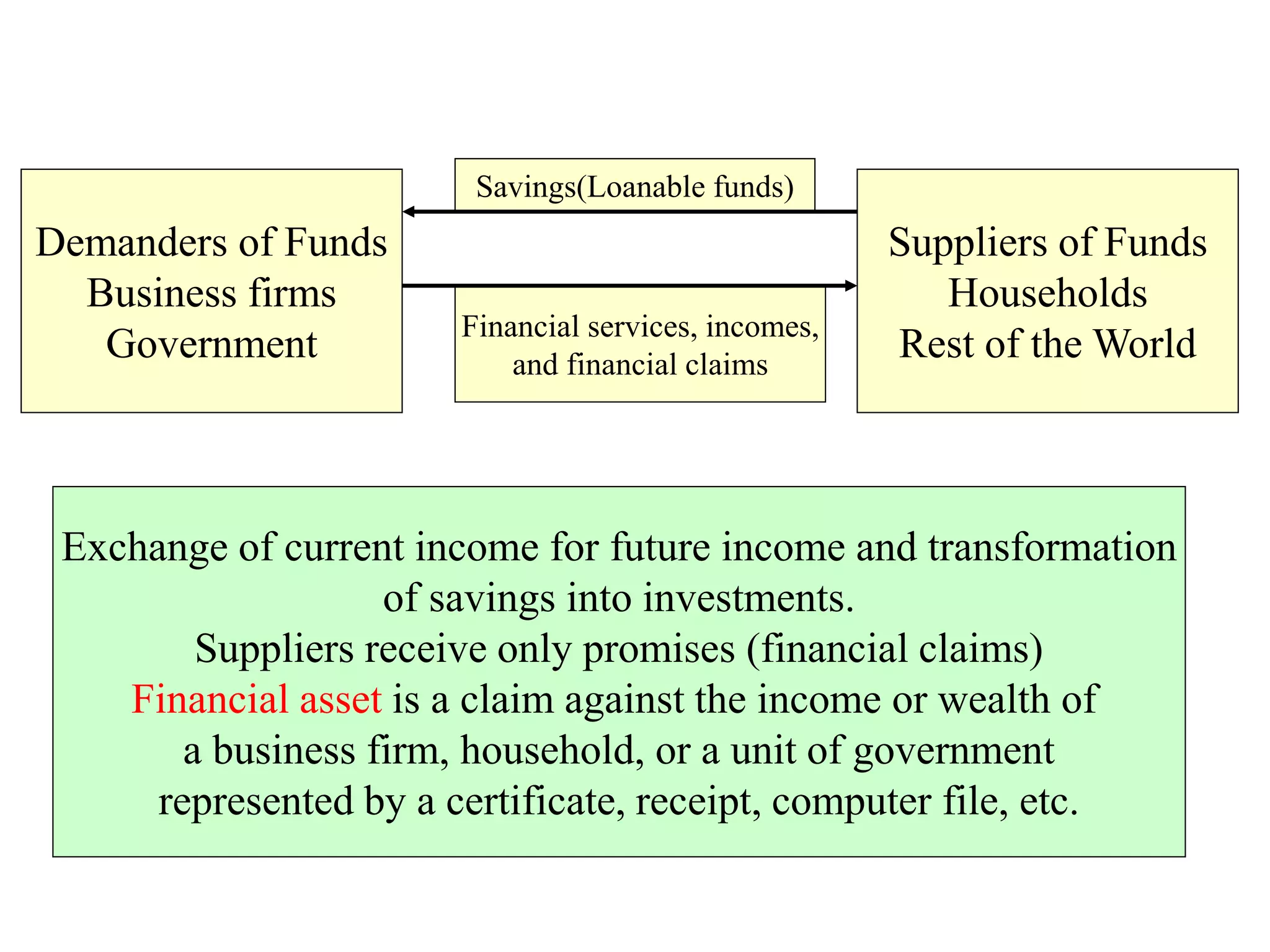
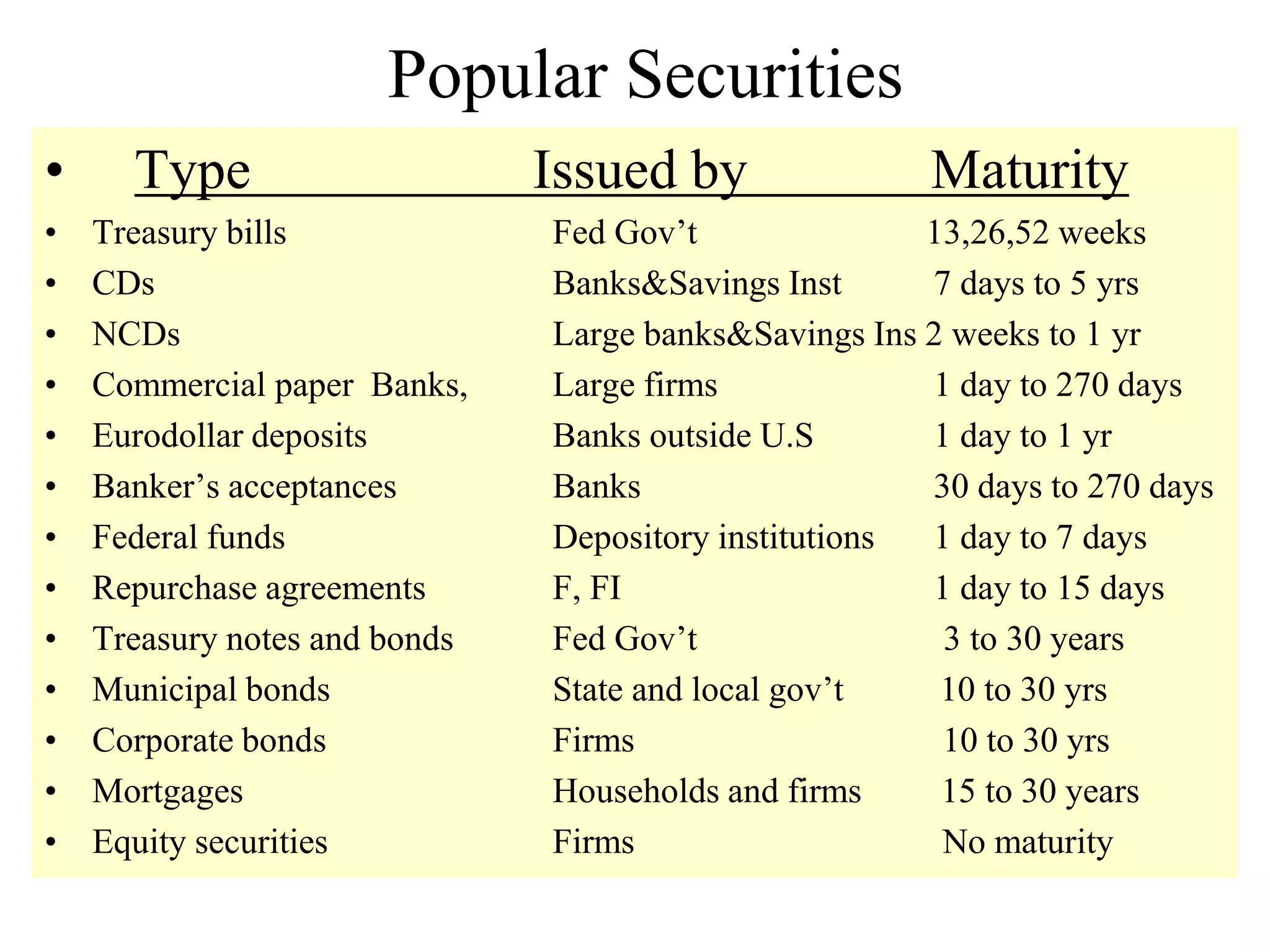
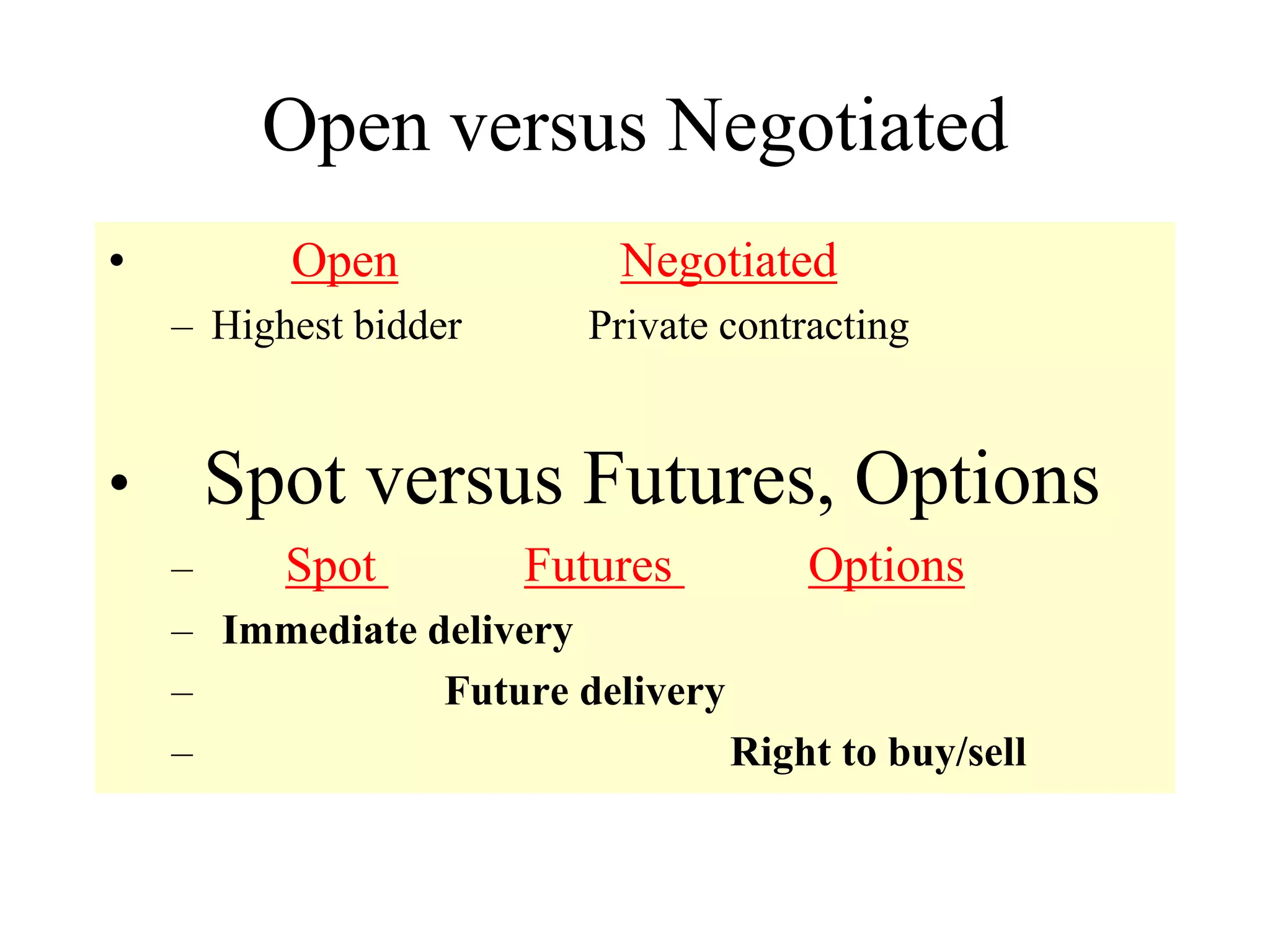
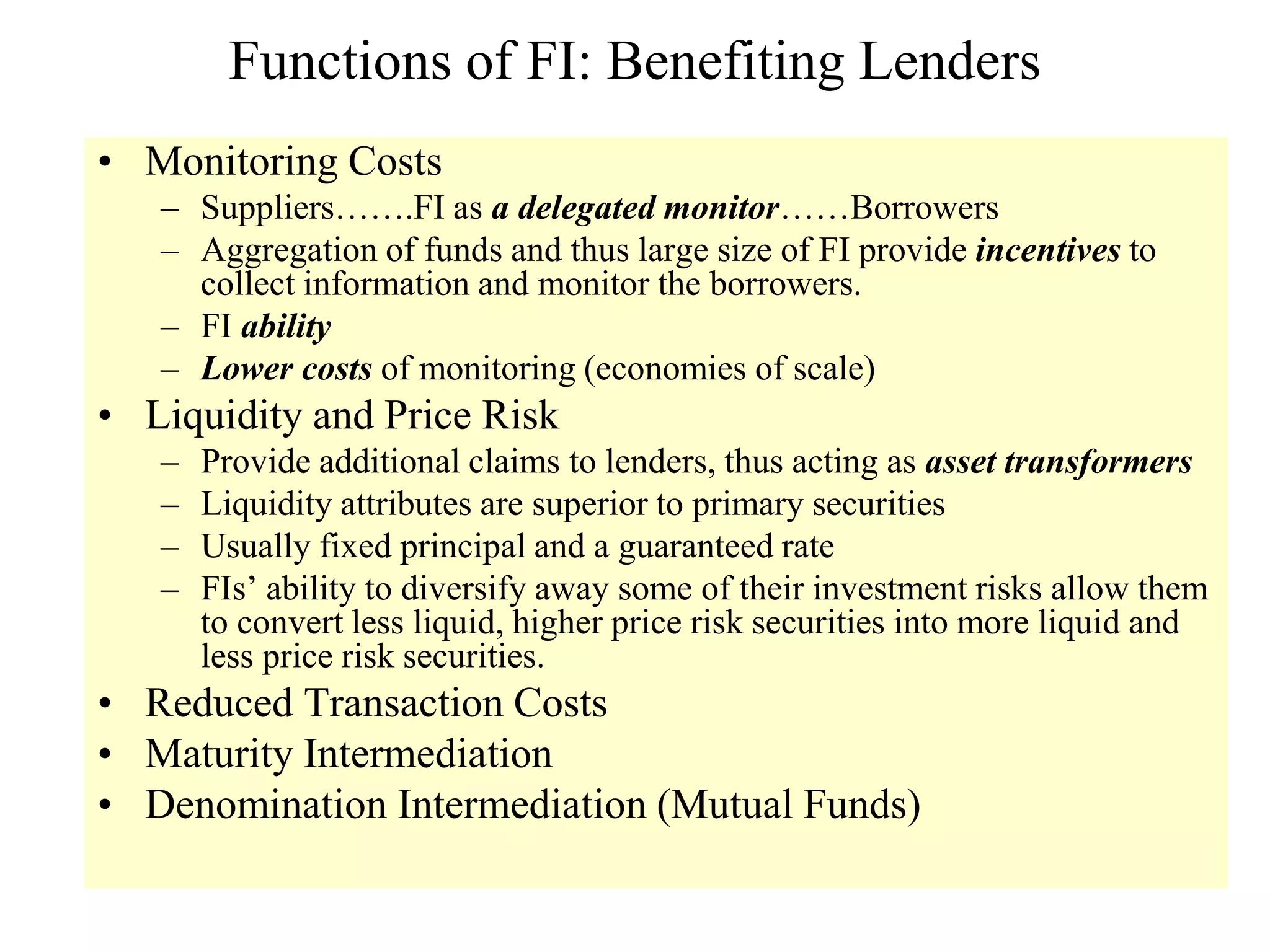
This document discusses different types of financial markets including product, factor, and financial markets. It defines markets and their role in allocating resources. It also discusses primary and secondary financial markets, money markets, capital markets, popular securities, foreign exchange markets, and types of financial institutions. Key points are that financial markets determine prices and distribute income, primary markets issue new securities while secondary markets provide liquidity, and depository institutions help transmit monetary policy.