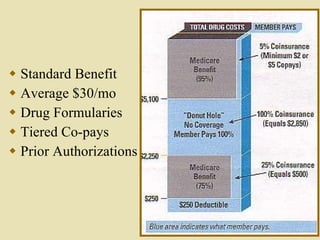
The document provides an overview of managed healthcare and third party financial issues, including an overview of prescription drug benefits and the various factors driving drug costs. It discusses the different players in the healthcare system including health plans, pharmacy benefit managers, government health insurance programs, employers and individuals. It also covers various cost containment tools and strategies used by payers and pharmacies to manage prescription drug costs and reimbursement.